SPRABA5D January 2014 – January 2019 AM1802 , AM1802 , AM1806 , AM1806 , AM1808 , AM1808 , AM1810 , AM1810
-
Using the AM18xx Bootloader
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Boot Modes
- 3 Non-AIS Boot Modes
- 4
Application Image Script (AIS) Boot
- 4.1 Section Load Command (0x58535901)
- 4.2 Section Fill Command (0x5853590A)
- 4.3 Enable CRC Command (0x58535903)
- 4.4 Disable CRC Command (0x58535904)
- 4.5 Validate CRC Command (0x58535902)
- 4.6 Jump & Close Command (0x58535906)
- 4.7 Jump Command (0x58535905)
- 4.8 Sequential Read Enable Command (0x58535963)
- 4.9 Function Execute Command (0x5853590D)
- 4.10 Boot Table Command (0x58535907)
- 5
AISgen: Tool to Generate Boot Script (AIS Image)
- 5.1 Installation
- 5.2 Getting Started
- 5.3
Generating AIS
- 5.3.1 Boot Mode and Boot Peripheral Setup
- 5.3.2 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Setup
- 5.3.3 Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) Setup
- 5.3.4 DDR Setup
- 5.3.5 PSC Setup
- 5.3.6 Pin Multiplexing Setup
- 5.3.7 Application File Selection
- 5.3.8 AIS File Selection
- 5.3.9 Status and Messages
- 5.3.10 Additional AIS Options
- 5.3.11 Command Line Usage
- 6 Master Boot – Booting From a Slave Memory Device
- 7 Slave Boot – Booting From an External Master Host
- 8 UART Boot Host - Using Your PC as a UART Boot Master
- 9 Boot Requirements, Constraints and Default Settings
- 10 References
- A Boot Mode Selection Table
- B Details of Supported NAND Devices
- C CRC Computation Algorithm
-
D Details of Pre-Defined ROM Functions
- D.1 PLL0 Configuration (Index = 0, Argument Count = 2)
- D.2 PLL1 Configuration (Index = 1, Argument Count = 2)
- D.3 Clock Configuration (Index = 2, Argument Count = 1)
- D.4 mDDR/DDR2 Controller Configuration (Index = 3, Argument Count = 8)
- D.5 EMIFA SDRAM Configuration (Index = 4, Argument Count = 5)
- D.6 EMIFA Async Configuration (Index = 5, Argument Count = 5)
- D.7 PLL and Clock Configuration (Index = 6, Argument Count = 3)
- D.8 Power and Sleep Configuration (PSC) (Index = 7, Argument Count = 1)
- D.9 Pinmux Configuration (Index = 8, Argument Count = 3)
- E ROM Revision History
- Revision History
5.3.1 Boot Mode and Boot Peripheral Setup
The General tab allows you to specify the boot mode that you plan to use. Depending on your selection, a Flash or Peripheral tab may appear. These tabs contain additional controls that allow you to optimize boot time (in master mode).
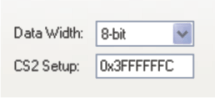
The Flash tab appears when either NOR Flash or NAND Flash-boot mode is selected. This tab contains controls that specify 8- or 16-bit data width (NAND is fixed at 8-bit data width) and interface timing settings for the EMIF flash interface. For more information on the register fields, see AM17x/AM18x ARM Microprocessor External Memory Interface A (EMIFA) User's Guide (SPRUFV0).
The Peripheral tab appears when one of the SPI or I2C master-boot modes is selected or when universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) boot mode is selected. This tab configures the peripheral speed and defaults to conservative speeds for broader compatibility. These are documented in Table 6. If the boot peripheral supports faster speeds, you can specify a speed so that the bootloader can re-configure clocks and boot faster. The Module Clock field displays the clock input to the boot peripheral from the PLL. This value may change based on PLL configuration.
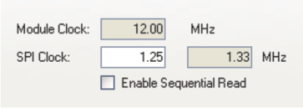
For SPI and I2C master modes, you can enter a desired speed. Depending on the PLL settings and granularity in peripheral clock division, AISgen calculates the actual speed nearest to the desired speed and shows it in an adjacent box. Recent I2C devices support speeds up to 400 kHz, and SPI devices support speeds up to 33 MHz.
SPI and I2C master modes also support sequential read mode. This option speeds up the boot process by allowing the bootloader to repeatedly read sequential data words from a slave memory device after sending only one read request and address to the device. Make sure that your slave memory device supports sequential read mode before selecting the Enable Sequential Read checkbox.
For UART-boot modes, baud rate is fixed at 115.2 kbps for boot purposes and cannot be changed. However, AISgen will still calculate an actual baud rate based on your PLL configuration and show it in the Peripheral tab.