SPRAC21A June 2016 – June 2019 OMAP-L132 , OMAP-L138 , TDA2E , TDA2EG-17 , TDA2HF , TDA2HG , TDA2HV , TDA2LF , TDA2P-ABZ , TDA2P-ACD , TDA2SA , TDA2SG , TDA2SX , TDA3LA , TDA3LX , TDA3MA , TDA3MD , TDA3MV
-
TDA2xx and TDA2ex Performance
- Trademarks
- 1 SoC Overview
- 2 Cortex-A15
- 3 System Enhanced Direct Memory Access (System EDMA)
- 4 DSP Subsystem EDMA
- 5 Embedded Vision Engine (EVE) Subsystem EDMA
- 6 DSP CPU
- 7 Cortex-M4 (IPU)
- 8 USB IP
- 9 PCIe IP
- 10 IVA-HD IP
- 11 MMC IP
- 12 SATA IP
- 13 GMAC IP
- 14 GPMC IP
- 15 QSPI IP
- 16 Standard Benchmarks
- 17
Error Checking and Correction (ECC)
- 17.1 OCMC ECC Programming
- 17.2 EMIF ECC Programming
- 17.3 EMIF ECC Programming to Starterware Code Mapping
- 17.4 Careabouts of Using EMIF ECC
- 17.5 Impact of ECC on Performance
- 18 DDR3 Interleaved vs Non-Interleaved
- 19 DDR3 vs DDR2 Performance
- 20 Boot Time Profile
- 21 L3 Statistics Collector Programming Model
- 22 Reference
- Revision History
1.7.1 GP Timers
The GP Timers are good tools to have a quick measurement of performance of different initiators in the system. Though this provides a quick way to measure throughput, it should be kept in mind that there are some inherent errors involved with this technique of measurement. To make sure the measurement error is relatively small the transfer size should be kept larger. The typical pseudo code for the GP Timer-based throughput measurement is as follows:
/*Get the Timer Start Stamp*/
timerStartStamp = timerRead(TIMER_NUM);
/*Start the transfer*/
transferStart();
/*Wait for Transfer Completion*/
waitForTransferCompletion();
/*Get the Time Stamp*/
timerEndStamp = timerRead(TIMER_NUM);
/* Calculate the bandwidth - Note that one needs to multiply x2 from the calculated value to get
* Bandwidth when the source and destination memory are the same */
if (timerEndStamp > timerStartStamp)
BW = (((float) (TRANSFER_SIZE)/ (float) (timerEndStamp - timerStartStamp)) * TIMER_FREQ);
else
BW = (((float) (TRANSFER_SIZE)/ (float) (timerEndStamp - timerStartStamp + 0xFFFFFFFF)) * TIMER_FREQ);
The formulas used for the throughput calculations are:
Actual Throughput = (Transfer Size/Time Taken)
Ideal Throughput = Frequency of Limiting Port × Data Bus Width in Bytes
Utilization or Efficiency = (Actual Throughput/Ideal Throughput) × 100
Consider the data is transferred from one memory M1 to another memory M2.
The interconnect signals that implement OCP protocol used to transfer the data between the two memories, are as shown in Figure 7.
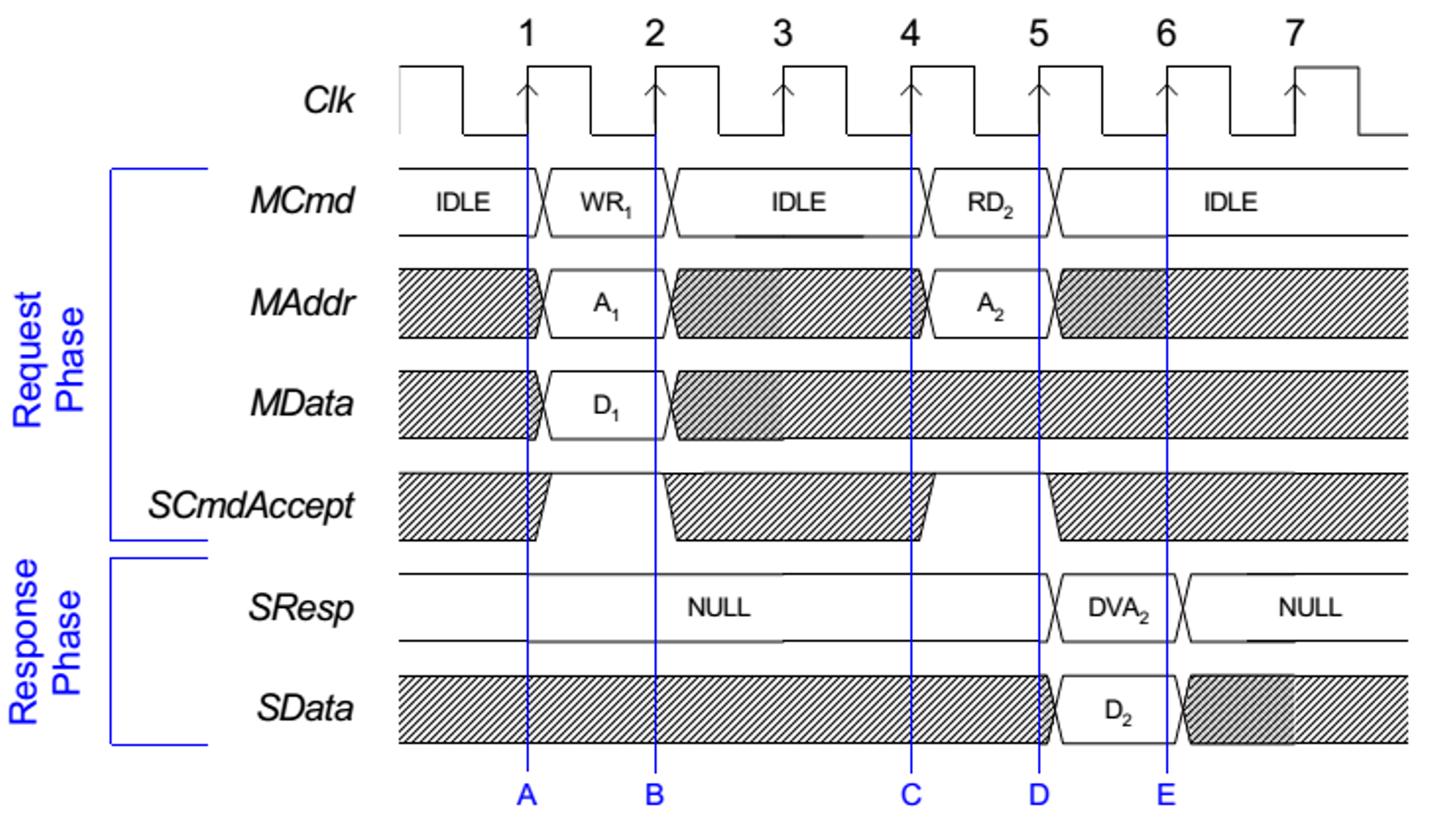 Figure 7. OCP Interconnect Signals
Figure 7. OCP Interconnect Signals There are two data lanes:
- MData that contains the data to be written
- SData that contains the data to be read
For further details on the exact operation of the OCP signals, see the OCP specifications.
Due to the presence of two data lanes, the case when the theoretical maximum throughput is obtained is when the MData contains valid data to be written and SData contains valid data to be read on every clock cycle of the transaction.
Mathematically stating this:
if Source Mem = Destination Mem, Ideal Throughputmem2mem = 2 × Frequency × Bus Width
if Source Mem ≠ Destination Mem, Ideal Throughputmem2mem = Frequency × Bus Width
Hence, when the source and destination memories are the same, the measured bandwidth should be multiplied into 2.