SPRUHJ0C April 2013 – October 2021 TMS320F28068M , TMS320F28069-Q1 , TMS320F28069M , TMS320F28069M-Q1
5.3.3 Step Response
The step tests for a position controller provide giving a step input to the controller to determine how quickly the controller can respond to a sudden input change. The two metrics evaluated during these tests are settling time and maximum overshoot. This test is also a measure of stability of your controller. If the controller oscillates upon reaching the goal speed then it is not very stable.
A step profile was applied to SpinTAC Position Control and the PI control system. This step input bypassed the profile generator. The following parameters were measured:
- Settling Time (from the step input until within 2% of the target position) - the settling time reflects how long it takes the controller to reach the goal position.
- Maximum Overshoot - maximum mechanical degrees measured after the step input.
Figure 6-13 compares the step responses of SpinTAC Position Control and the PI control system. It also provides a visual representation showing how these metrics were calculated. SpinTAC Position Control was able to reach the goal position with zero overshoot and a shorter settling time than the PI control system.
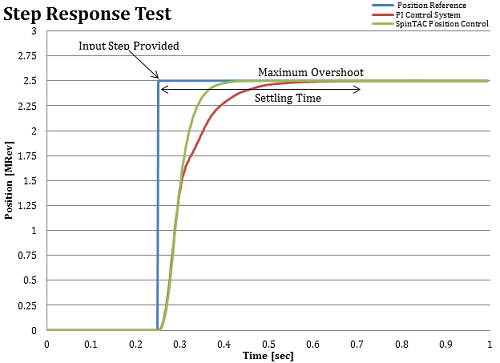 Figure 5-13 Step Response Test of Maximum Overshoot and Settling Time
Figure 5-13 Step Response Test of Maximum Overshoot and Settling Time
| Settling Time(s) | Overshoot (mechanical degrees) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpinTAC | PI | SpinTAC Advantage (percentage improvement over PI) | SpinTAC | PI | SpinTAC Advantage (percentage improvement over PI) | |
| 0-4.9 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.23 | 0.54 | 57.4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.22 | 0.45 | 51.1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.25 | 0.46 | 45.7 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.28 | 0.45 | 37.8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.27 | 0.43 | 37.2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0-2.5 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.24 | 0.36 | 34.4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.23 | 0.38 | 39.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.24 | 0.41 | 41.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.23 | 0.40 | 42.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.21 | 0.41 | 48.8 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0-1.25 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.21 | 0.41 | 48.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.20 | 0.41 | 51.2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.18 | 0.46 | 60.9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.18 | 0.40 | 55.0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| 0.23 | 0.38 | 39.5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.0 | |
| Settling Time(s) | Overshoot (mechanical degrees) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpinTAC | PI | SpinTAC Advantage (percentage improvement over PI) | SpinTAC | PI | SpinTAC Advantage (percentage improvement over PI) | |
| 0-4.9 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.67 | 0.59 | -13.6 | 4.54e+2 | 1.26e+3 | 63.9 | |
| 0.94 | 0.57 | -66.1 | 4.57e+2 | 1.26e+3 | 63.7 | |
| 0.86 | 0.57 | -49.6 | 4.58e+2 | 1.27e+3 | 63.8 | |
| 0.70 | 0.60 | -15.5 | 4.58e+2 | 1.27e+3 | 63.8 | |
| 0.81 | 0.62 | -30.1 | 4.58e+2 | 1.28e+3 | 64.3 | |
| 0-2.5 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.53 | 0.50 | -5.8 | 8.14e+1 | 4.03e+2 | 79.8 | |
| 0.52 | 0.48 | -8.3 | 8.14e+1 | 4.18e+2 | 80.5 | |
| 0.62 | 0.49 | -27.2 | 8.17e+1 | 4.10e+2 | 80.1 | |
| 0.56 | 0.47 | -18.2 | 8.17e+1 | 4.18e+2 | 80.5 | |
| 0.17 | 0.49 | 65.2 | 8.14e+1 | 3.70e+2 | 78.0 | |
| 0-1.25 mechanical degrees | ||||||
| 0.53 | 0.42 | -26.2 | 0.00 | 1.69e+1 | 100 | |
| 0.53 | 0.32 | -65.6 | 0.00 | 1.44e+1 | 100 | |
| 0.53 | 0.33 | -63.1 | 0.00 | 1.69e+1 | 100 | |
| 0.53 | 0.41 | -30.6 | 0.00 | 1.63e+1 | 100 | |
| 0.60 | 0.36 | -68.4 | 0.00 | 1.63e+1 | 100 | |