SPRUI33H November 2015 – June 2024 TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
- 1 C2000™ Microcontrollers Software Support
- 2 C28x Processor
-
3 System Control and
Interrupts
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Power Management
- 3.3 Device Identification and Configuration Registers
- 3.4 Resets
- 3.5 Peripheral Interrupts
- 3.6 Exceptions and Non-Maskable Interrupts
- 3.7
Clocking
- 3.7.1 Clock Sources
- 3.7.2 Derived Clocks
- 3.7.3 Device Clock Domains
- 3.7.4 XCLKOUT
- 3.7.5 Clock Connectivity
- 3.7.6 Clock Source and PLL Setup
- 3.7.7 Using an External Crystal or Resonator
- 3.7.8 Using an External Oscillator
- 3.7.9 Choosing PLL Settings
- 3.7.10 System Clock Setup
- 3.7.11 Clock Configuration Examples
- 3.7.12 Missing Clock Detection
- 3.8 32-Bit CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 3.9 Watchdog Timer
- 3.10 Low-Power Modes
- 3.11
Memory Controller Module
- 3.11.1
Functional Description
- 3.11.1.1 Dedicated RAM (Mx RAM)
- 3.11.1.2 Local Shared RAM (LSx RAM)
- 3.11.1.3 Global Shared RAM (GSx RAM)
- 3.11.1.4 Message RAM (CLA MSGRAM)
- 3.11.1.5 Access Arbitration
- 3.11.1.6 Access Protection
- 3.11.1.7 Memory Error Detection, Correction and Error Handling
- 3.11.1.8 Application Test Hooks for Error Detection and Correction
- 3.11.1.9 RAM Initialization
- 3.11.1
Functional Description
- 3.12
Flash and OTP Memory
- 3.12.1 Features
- 3.12.2 Flash Tools
- 3.12.3 Default Flash Configuration
- 3.12.4 Flash Bank, OTP and Pump
- 3.12.5 Flash Module Controller (FMC)
- 3.12.6 Flash and OTP and Wakeup Power-Down Modes
- 3.12.7 Flash and OTP Performance
- 3.12.8 Flash Access Interface
- 3.12.9 Erase/Program Flash
- 3.12.10 Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
- 3.12.11 Reserved Locations Within Flash and OTP
- 3.12.12 Procedure to Change the Flash Control Registers
- 3.12.13 Simple Procedure to Modify an Application from RAM Configuration to Flash Configuration
- 3.13
Dual Code Security Module (DCSM)
- 3.13.1 Functional Description
- 3.13.2 C Code Example to Get Zone Select Block Addr for Zone1 in BANK0
- 3.13.3 Flash and OTP Erase/Program
- 3.13.4 Safe Copy Code
- 3.13.5 SafeCRC
- 3.13.6 CSM Impact on Other On-Chip Resources
- 3.13.7
Incorporating Code Security in User Applications
- 3.13.7.1 Environments That Require Security Unlocking
- 3.13.7.2 CSM Password Match Flow
- 3.13.7.3 C Code Example to Unsecure C28x Zone1
- 3.13.7.4 C Code Example to Resecure C28x Zone1
- 3.13.7.5 Environments That Require ECSL Unlocking
- 3.13.7.6 ECSL Password Match Flow
- 3.13.7.7 ECSL Disable Considerations for any Zone
- 3.13.7.8 Device Unique ID
- 3.14 System Control Register Configuration Restrictions
- 3.15
System Control Registers
- 3.15.1 System Control Base Address Table
- 3.15.2 CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 3.15.3 PIE_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.4 WD_REGS Registers
- 3.15.5 NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.6 XINT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.7 DMA_CLA_SRC_SEL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.8 DEV_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.9 CLK_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.10 CPU_SYS_REGS Registers
- 3.15.11 PERIPH_AC_REGS Registers
- 3.15.12 DCSM_BANK0_Z1_REGS Registers
- 3.15.13 DCSM_BANK0_Z2_REGS Registers
- 3.15.14 DCSM_COMMON_REGS Registers
- 3.15.15 DCSM_BANK1_Z1_REGS Registers
- 3.15.16 DCSM_BANK1_Z2_REGS Registers
- 3.15.17 MEM_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.18 ACCESS_PROTECTION_REGS Registers
- 3.15.19 MEMORY_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.15.20 FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.21 FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 3.15.22 UID_REGS Registers
- 3.15.23 DCSM_BANK0_Z1_OTP Registers
- 3.15.24 DCSM_BANK0_Z2_OTP Registers
- 3.15.25 DCSM_BANK1_Z1_OTP Registers
- 3.15.26 DCSM_BANK1_Z2_OTP Registers
- 3.15.27
Register to Driverlib Function Mapping
- 3.15.27.1 ASYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.2 CPUTIMER Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.3 DCSM Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.4 FLASH Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.5 MEMCFG Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.6 NMI Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.7 PIE Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.8 SYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.9 XINT Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
4 ROM Code and Peripheral Booting
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Device Boot Sequence
- 4.3 Device Boot Modes
- 4.4 Device Boot Flow Diagrams
- 4.5 Device Reset and Exception Handling
- 4.6
Boot ROM Description
- 4.6.1 Boot ROM Registers
- 4.6.2 Boot ROM User OTP
- 4.6.3 Entry Points
- 4.6.4 Wait Points
- 4.6.5 Memory Maps
- 4.6.6 ROM Tables
- 4.6.7 Boot Modes
- 4.6.8 Boot Data Stream Structure
- 4.6.9 GPIO Assignments
- 4.6.10 Secure ROM Function APIs
- 4.6.11 DCSM Usage
- 4.6.12 Clock Initialization
- 4.6.13 Boot Status Information
- 4.6.14 ROM Version
- 4.7 The C2000 Hex Utility
-
5 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 CLA Interface
- 5.3 CLA, DMA, and CPU Arbitration
- 5.4 CLA Configuration and Debug
- 5.5 Pipeline
- 5.6
Software
- 5.6.1
CLA Examples
- 5.6.1.1 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01)
- 5.6.1.2 CLA arctangent(x) using a lookup table (cla_atan_cpu01)
- 5.6.1.3 CLA background nesting task
- 5.6.1.4 Controlling PWM output using CLA
- 5.6.1.5 Just-in-time ADC sampling with CLA
- 5.6.1.6 Optimal offloading of control algorithms to CLA
- 5.6.1.7 Handling shared resources across C28x and CLA
- 5.6.1
CLA Examples
- 5.7
Instruction Set
- 5.7.1 Instruction Descriptions
- 5.7.2 Addressing Modes and Encoding
- 5.7.3
Instructions
- MABSF32 MRa, MRb
- MADD32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MAND32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MASR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MBCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCLRC BGINTM
- MCMP32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MDEBUGSTOP
- MDEBUGSTOP1
- MEALLOW
- MEDIS
- MEINVF32 MRa, MRb
- MEISQRTF32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI32 MRa, MRb
- MFRACF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MLSL32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MLSR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MMACF32 MR3, MR2, MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMAXF32 MRa, MRb
- MMAXF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMINF32 MRa, MRb
- MMINF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMOV16 MARx, MRa, #16I
- MMOV16 MARx, mem16
- MMOV16 mem16, MARx
- MMOV16 mem16, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MSTF
- MMOV32 MRa, mem32 [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MSTF, mem32
- MMOVD32 MRa, mem32
- MMOVF32 MRa, #32F
- MMOVI16 MARx, #16I
- MMOVI32 MRa, #32FHex
- MMOVIZ MRa, #16FHi
- MMOVZ16 MRa, mem16
- MMOVXI MRa, #16FLoHex
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MMPYF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc||MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc ||MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MNEGF32 MRa, MRb[, CNDF]
- MNOP
- MOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MRCNDD [CNDF]
- MSETC BGINTM
- MSETFLG FLAG, VALUE
- MSTOP
- MSUB32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MSWAPF MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MTESTTF CNDF
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MXOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- 5.8 CLA Registers
- 6 Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 7 CLA Program ROM CRC (CLAPROMCRC)
- 8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 9 Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 10Direct Memory Access (DMA)
-
11Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD)
- 11.1 Introduction
- 11.2 Enhanced Bus Comparator Unit
- 11.3 System Event Counter Unit
- 11.4 ERAD Ownership, Initialization and Reset
- 11.5 ERAD Programming Sequence
- 11.6
Software
- 11.6.1
ERAD Examples
- 11.6.1.1 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.2 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.3 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.4 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 11.6.1.5 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 11.6.1.6 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.7 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 11.6.1.8 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 11.6.1.9 ERAD Stack Overflow
- 11.6.1.10 ERAD Profile Interrupts CLA
- 11.6.1.11 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.12 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.13 ERAD MEMORY ACCESS RESTRICT
- 11.6.1.14 ERAD INTERRUPT ORDER
- 11.6.1.15 ERAD AND CLB
- 11.6.1.16 ERAD PWM PROTECTION
- 11.6.1
ERAD Examples
- 11.7 ERAD Registers
- 12Analog Subsystem
-
13Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 13.1 Introduction
- 13.2 ADC Configurability
- 13.3 SOC Principle of Operation
- 13.4 SOC Configuration Examples
- 13.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 13.6 Burst Mode
- 13.7 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 13.8 Post-Processing Blocks
- 13.9 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 13.10 Power-Up Sequence
- 13.11 ADC Calibration
- 13.12 ADC Timings
- 13.13
Additional Information
- 13.13.1 Ensuring Synchronous Operation
- 13.13.2 Choosing an Acquisition Window Duration
- 13.13.3 Achieving Simultaneous Sampling
- 13.13.4 Result Register Mapping
- 13.13.5 Internal Temperature Sensor
- 13.13.6 Designing an External Reference Circuit
- 13.13.7 ADC-DAC Loopback Testing
- 13.13.8 Internal Test Mode
- 13.13.9 ADC Gain and Offset Calibration
- 13.14
Software
- 13.14.1
ADC Examples
- 13.14.1.1 ADC Software Triggering
- 13.14.1.2 ADC ePWM Triggering
- 13.14.1.3 ADC Temperature Sensor Conversion
- 13.14.1.4 ADC Synchronous SOC Software Force (adc_soc_software_sync)
- 13.14.1.5 ADC Continuous Triggering (adc_soc_continuous)
- 13.14.1.6 ADC Continuous Conversions Read by DMA (adc_soc_continuous_dma)
- 13.14.1.7 ADC PPB Offset (adc_ppb_offset)
- 13.14.1.8 ADC PPB Limits (adc_ppb_limits)
- 13.14.1.9 ADC PPB Delay Capture (adc_ppb_delay)
- 13.14.1.10 ADC ePWM Triggering Multiple SOC
- 13.14.1.11 ADC Burst Mode
- 13.14.1.12 ADC Burst Mode Oversampling
- 13.14.1.13 ADC SOC Oversampling
- 13.14.1.14 ADC PPB PWM trip (adc_ppb_pwm_trip)
- 13.14.1.15 ADC Open Shorts Detection (adc_open_shorts_detection)
- 13.14.1
ADC Examples
- 13.15 ADC Registers
-
14Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
- 14.1 Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) Overview
- 14.2 Linear Output Range
- 14.3 Gain Modes
- 14.4 External Filtering
- 14.5 Error Calibration
- 14.6 Ground Routing
- 14.7 Enabling and Disabling the PGA Clock
- 14.8 Lock Register
- 14.9 Examples
- 14.10 Analog Front End Integration
- 14.11 Software
- 14.12 PGA Registers
- 15Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 16Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 17Sigma Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
-
18Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 18.1 Introduction
- 18.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 18.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 18.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 18.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 18.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 18.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 18.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 18.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 18.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 18.4.7 Global Load
- 18.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 18.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 18.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 18.8 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 18.9 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 18.10 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 18.11 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 18.12 ePWM Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 18.13
Applications to Power Topologies
- 18.13.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 18.13.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 18.13.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 18.13.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 18.13.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 18.13.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 18.13.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 18.13.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 18.13.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 18.13.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 18.13.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 18.14 Register Lock Protection
- 18.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 18.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 18.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 18.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 18.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 18.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 18.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 18.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 18.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 18.15.1.8 HRPWM Examples Using Optimized Assembly Code
- 18.15.2 SFO Library Software - SFO_TI_Build_V8.lib
- 18.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 18.16
Software
- 18.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 18.16.1.1 ePWM Trip Zone
- 18.16.1.2 ePWM Up Down Count Action Qualifier
- 18.16.1.3 ePWM Synchronization
- 18.16.1.4 ePWM Digital Compare
- 18.16.1.5 ePWM Digital Compare Event Filter Blanking Window
- 18.16.1.6 ePWM Valley Switching
- 18.16.1.7 ePWM Digital Compare Edge Filter
- 18.16.1.8 ePWM Deadband
- 18.16.1.9 ePWM DMA
- 18.16.1.10 ePWM Chopper
- 18.16.1.11 EPWM Configure Signal
- 18.16.1.12 Realization of Monoshot mode
- 18.16.1.13 EPWM Action Qualifier (epwm_up_aq)
- 18.16.2 HRPWM Examples
- 18.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 18.17 ePWM Registers
-
19Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 19.1 Introduction
- 19.2 Description
- 19.3 Configuring Device Pins for the eCAP
- 19.4 Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 19.5
Capture Mode Description
- 19.5.1 Event Prescaler
- 19.5.2 Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 19.5.3 Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 19.5.4 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 19.5.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 19.5.6 eCAP Synchronization
- 19.5.7 Interrupt Control
- 19.5.8 DMA Interrupt
- 19.5.9 Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 19.5.10 APWM Mode Operation
- 19.6
Application of the eCAP Module
- 19.6.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 19.7 Application of the APWM Mode
- 19.8 Software
- 19.9 eCAP Registers
- 20High Resolution Capture (HRCAP)
-
21Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 21.1 Introduction
- 21.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 21.3 Description
- 21.4 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 21.5 Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 21.6 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 21.7 eQEP Watchdog
- 21.8 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 21.9 QMA Module
- 21.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 21.11 eQEP Registers
-
22Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 22.1 Introduction
- 22.2 System-Level Integration
- 22.3 SPI Operation
- 22.4 Programming Procedure
- 22.5 Software
- 22.6 SPI Registers
-
23Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 23.1 Introduction
- 23.2 Architecture
- 23.3 SCI Module Signal Summary
- 23.4 Configuring Device Pins
- 23.5 Multiprocessor and Asynchronous Communication Modes
- 23.6 SCI Programmable Data Format
- 23.7 SCI Multiprocessor Communication
- 23.8 Idle-Line Multiprocessor Mode
- 23.9 Address-Bit Multiprocessor Mode
- 23.10 SCI Communication Format
- 23.11 SCI Port Interrupts
- 23.12 SCI Baud Rate Calculations
- 23.13 SCI Enhanced Features
- 23.14 Software
- 23.15 SCI Registers
-
24Inter-Integrated Circuit Module (I2C)
- 24.1 Introduction
- 24.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 24.3
I2C Module Operational Details
- 24.3.1 Input and Output Voltage Levels
- 24.3.2 Selecting Pullup Resistors
- 24.3.3 Data Validity
- 24.3.4 Operating Modes
- 24.3.5 I2C Module START and STOP Conditions
- 24.3.6 Non-repeat Mode versus Repeat Mode
- 24.3.7 Serial Data Formats
- 24.3.8 Clock Synchronization
- 24.3.9 Arbitration
- 24.3.10 Digital Loopback Mode
- 24.3.11 NACK Bit Generation
- 24.4 Interrupt Requests Generated by the I2C Module
- 24.5 Resetting or Disabling the I2C Module
- 24.6 Software
- 24.7 I2C Registers
-
25Power Management Bus Module (PMBus)
- 25.1 Introduction
- 25.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 25.3
Slave Mode
Operation
- 25.3.1 Configuration
- 25.3.2
Message Handling
- 25.3.2.1 Quick Command
- 25.3.2.2 Send Byte
- 25.3.2.3 Receive Byte
- 25.3.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 25.3.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 25.3.2.6 Process Call
- 25.3.2.7 Block Write
- 25.3.2.8 Block Read
- 25.3.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 25.3.2.10 Alert Response
- 25.3.2.11 Extended Command
- 25.3.2.12 Group Command
- 25.4
Master Mode
Operation
- 25.4.1 Configuration
- 25.4.2
Message Handling
- 25.4.2.1 Quick Command
- 25.4.2.2 Send Byte
- 25.4.2.3 Receive Byte
- 25.4.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 25.4.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 25.4.2.6 Process Call
- 25.4.2.7 Block Write
- 25.4.2.8 Block Read
- 25.4.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 25.4.2.10 Alert Response
- 25.4.2.11 Extended Command
- 25.4.2.12 Group Command
- 25.5 PMBus Registers
-
26Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 26.1 Introduction
- 26.2 Functional Description
- 26.3 Operating Modes
- 26.4 Multiple Clock Source
- 26.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 26.6 DMA Functionality
- 26.7 Parity Check Mechanism
- 26.8 Debug Mode
- 26.9 Module Initialization
- 26.10 Configuration of Message Objects
- 26.11
Message Handling
- 26.11.1 Message Handler Overview
- 26.11.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 26.11.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 26.11.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 26.11.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 26.11.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 26.11.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 26.11.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 26.11.9 Reading Received Messages
- 26.11.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 26.11.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 26.11.12 Reading from a FIFO Buffer
- 26.12 CAN Bit Timing
- 26.13 Message Interface Register Sets
- 26.14 Message RAM
- 26.15
Software
- 26.15.1
CAN Examples
- 26.15.1.1 CAN External Loopback
- 26.15.1.2 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts
- 26.15.1.3 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit
- 26.15.1.4 CAN External Loopback with DMA
- 26.15.1.5 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations
- 26.15.1.6 CAN Error Generation Example
- 26.15.1.7 CAN Remote Request Loopback
- 26.15.1.8 CAN example that illustrates the usage of Mask registers
- 26.15.1
CAN Examples
- 26.16 CAN Registers
-
27Local Interconnect Network
(LIN)
- 27.1 Introduction
- 27.2 Serial Communications Interface Module
- 27.3
Local Interconnect Network Module
- 27.3.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 27.3.1.1 LIN Standards
- 27.3.1.2 Message Frame
- 27.3.1.3 Synchronizer
- 27.3.1.4 Baud Rate
- 27.3.1.5 Header Generation
- 27.3.1.6 Extended Frames Handling
- 27.3.1.7 Timeout Control
- 27.3.1.8 TXRX Error Detector (TED)
- 27.3.1.9 Message Filtering and Validation
- 27.3.1.10 Receive Buffers
- 27.3.1.11 Transmit Buffers
- 27.3.2 LIN Interrupts
- 27.3.3 Servicing LIN Interrupts
- 27.3.4 LIN DMA Interface
- 27.3.5 LIN Configurations
- 27.3.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 27.4 Low-Power Mode
- 27.5 Emulation Mode
- 27.6 Software
- 27.7 SCI/LIN Registers
-
28Fast Serial Interface
(FSI)
- 28.1 Introduction
- 28.2 System-level Integration
- 28.3
FSI Functional Description
- 28.3.1 Introduction to Operation
- 28.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 28.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 28.3.3.1 Initialization
- 28.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 28.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 28.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 28.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 28.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 28.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 28.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 28.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 28.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 28.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 28.3.4 Frame Format
- 28.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 28.3.6 Internal Loopback
- 28.3.7 CRC Generation
- 28.3.8 ECC Module
- 28.3.9 FSI Trigger Generation
- 28.3.10 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 28.4 FSI Programing Guide
- 28.5
Software
- 28.5.1
FSI Examples
- 28.5.1.1 FSI Loopback:CPU Control
- 28.5.1.2 FSI Loopback CLA control
- 28.5.1.3 FSI DMA frame transfers:DMA Control
- 28.5.1.4 FSI data transfer by external trigger
- 28.5.1.5 FSI data transfers upon CPU Timer event
- 28.5.1.6 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex6_spi_main_tx)
- 28.5.1.7 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex7_spi_remote_rx)
- 28.5.1.8 FSI P2Point Connection:Rx Side
- 28.5.1.9 FSI P2Point Connection:Tx Side
- 28.5.1.10 FSI and SPI communication (fsi_ex9_spi_master_tx_drivers)
- 28.5.1.11 FSI and SPI communication (fsi_ex10_spi_slave_rx_driver)
- 28.5.1.12 FSI and SPI communication full-duplex
- 28.5.1.13 FSI Receive Skew Compensation Block Element Delays
- 28.5.1.14 FSI Skew Calibration in Single Data Line Mode (RX Device)
- 28.5.1.15 FSI Skew Calibration in Single Data Line Mode (TX Device)
- 28.5.1.16 FSI Skew Calibration in Dual Data Line Mode (RX Device)
- 28.5.1.17 FSI Skew Calibration in Dual Data Line Mode (TX Device)
- 28.5.1.18 FSI Find Optimal Number of Delay Elements Activated For FSIRX
- 28.5.1.19 FSI Find Optimal Number of Delay Elements Activated For FSIRX
- 28.5.1.20 FSI daisy chain topology, lead device example
- 28.5.1.21 FSI daisy chain topology, node device example
- 28.5.1
FSI Examples
- 28.6 FSI Registers
-
29Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 29.1 Introduction
- 29.2 Description
- 29.3 CLB Input/Output Connection
- 29.4 CLB Tile
- 29.5 CPU Interface
- 29.6 DMA Access
- 29.7
Software
- 29.7.1
CLB Examples
- 29.7.1.1 CLB Empty Project
- 29.7.1.2 CLB Combinational Logic
- 29.7.1.3 CLB GPIO Input Filter
- 29.7.1.4 CLB Auxilary PWM
- 29.7.1.5 CLB PWM Protection
- 29.7.1.6 CLB Event Window
- 29.7.1.7 CLB Signal Generator
- 29.7.1.8 CLB State Machine
- 29.7.1.9 CLB External Signal AND Gate
- 29.7.1.10 CLB Timer
- 29.7.1.11 CLB Timer Two States
- 29.7.1.12 CLB Interrupt Tag
- 29.7.1.13 CLB Output Intersect
- 29.7.1.14 CLB PUSH PULL
- 29.7.1.15 CLB Multi Tile
- 29.7.1.16 CLB Glue Logic
- 29.7.1.17 CLB based One-shot PWM
- 29.7.1.18 CLB AOC Control
- 29.7.1.19 CLB AOC Release Control
- 29.7.1.20 CLB AOC Control
- 29.7.1.21 CLB Serializer
- 29.7.1.22 CLB LFSR
- 29.7.1.23 CLB Trip Zone Timestamp
- 29.7.1.24 CLB CRC
- 29.7.1
CLB Examples
- 29.8 CLB Registers
- 30Revision History
25.4.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
The Write Byte and Write Word messages (Figure 25-5) consist of a device address, a command byte, transmitted data bytes, and an optional PEC byte. Write Byte messages include a single byte, while the Write Word messages support transmission of 2 bytes to the corresponding slave module. Similar to the Send Byte protocol, the PMBMC register is configured to send 1 or 2 bytes, the CMD_EN bit is set to enable command byte transmission and the optional PEC_EN bit is set.
With the command byte transmission enabled, the format of the PMBTXBUF register differs from the Send Byte protocol. In bits 7-0, the firmware must program the command byte to be sent to the slave. The data bytes are programmed into bits 15-8 and bits 23-16.
After programming the PMBMC register, the PMBus module transmits the Write Byte/Word message. The firmware can wait for an End of Message interrupt from the module to verify the accuracy of the message transmission. The PMBSTS register indicates if the slave acknowledged the message properly.
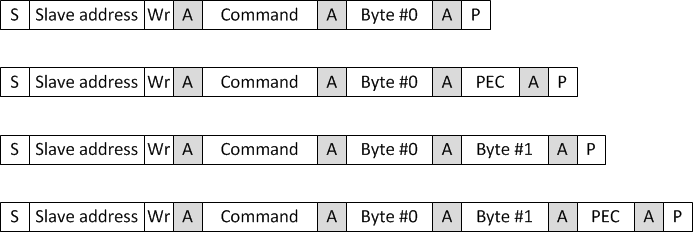 Figure 25-18 Write Byte and Write Word
Messages With and Without PEC
Figure 25-18 Write Byte and Write Word
Messages With and Without PEC