SPRUJF4 October 2024
- 1
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
- 2Hardware
- 3Motor Control Software
-
4Test Procedure and Results
- 4.1 Build Level 1: CPU and Board Setup
- 4.2 Build Level 2: Open-Loop Check With ADC Feedback
- 4.3 Build Level 3: Closed Current Loop Check
- 4.4 Build Level 4: Full Motor Drive Control
- 4.5 Test Procedure
- 4.6 Performance Data and Results
- 5Hardware Design Files
- 6Additional Information
- 7References
4.5.4.4 Build Level 4 Test Procedure
- Ensure initial steps listed in Section 4.5.4 have been completed.
- If the motor identification
routine is being utilized, as described in Section 4.5.2, the
motor identification routine begins execution immediately upon setting
motorVars_M1.flagEnableRunAndIdentify to "1" in the
Expressions window. This process takes about 150 seconds.
- Once
motorVars_M1.flagEnableRunAndIdentify is equal to "0",
the motor parameters have been identified. Record the watch window
values with the newly-defined motor parameters in user_mtr1.h as
follows:
- USER_MOTOR1_Rs = motorVars_M1.Rs_Ohm’s value
- USER_MOTOR1_Ls_d = motorVars_M1.Ls_d_H’s value
- USER_MOTOR1_Ls_q = motorVars_M1.Ls_q_H’s value
- USER_MOTOR_RATED_FLUX = motorVars_M1.flux_VpHz’s value
- Set userParams_M1.flag_bypassMotorId to "true" after successfully identify the motors parameters, rebuild the project and load the code into the controller.
- Once
motorVars_M1.flagEnableRunAndIdentify is equal to "0",
the motor parameters have been identified. Record the watch window
values with the newly-defined motor parameters in user_mtr1.h as
follows:
- Set the variables motorVars_M1.speedRef_Hz to a different value and watch how the motor shaft speed follows.
- To change the acceleration, enter a different acceleration value for the variables motorVars_M1.accelerationMax_Hzps and motorVars_M1.accelerationMax_Hzps.
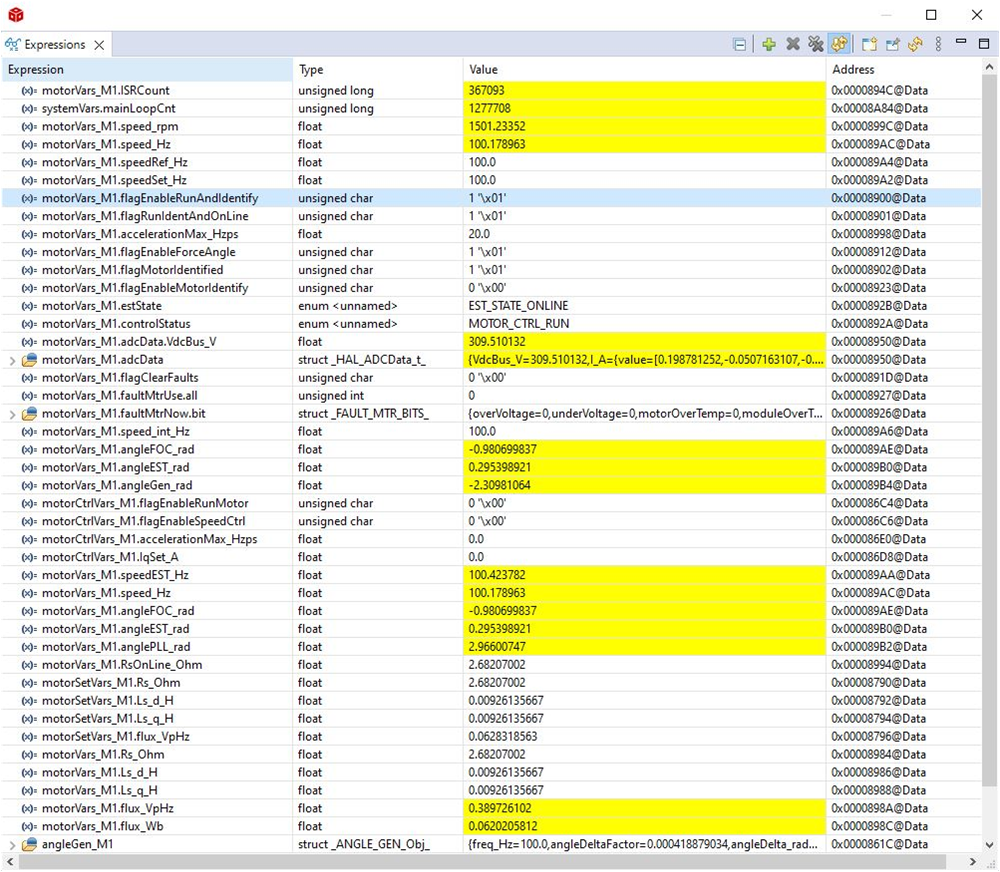 Figure 4-14 Build Level 4: Expressions
Window at Run Time
Figure 4-14 Build Level 4: Expressions
Window at Run Time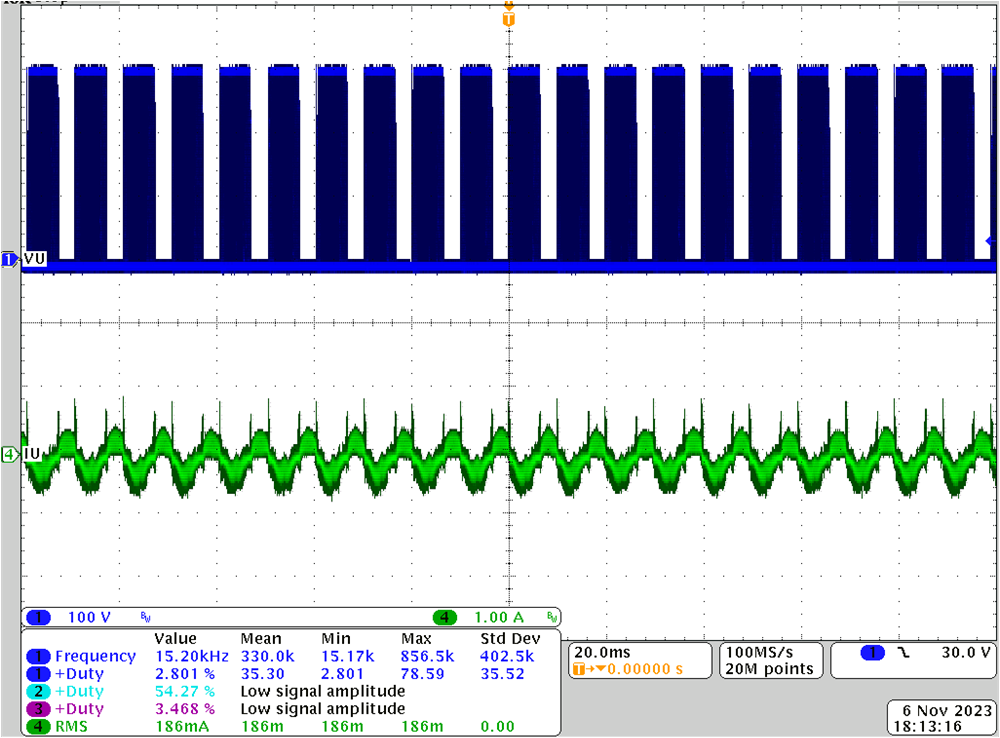 Figure 4-15 Build Level 4: Rotor Angle,
Phase Current of Motor
Figure 4-15 Build Level 4: Rotor Angle,
Phase Current of MotorAfter these initial tests, Build Level 4 is also where any other test conditions and tuning are optionally performed.