SSZT417 September 2019 IWR6843 , IWR6843AOP
This article was co-written by Keegan Garcia
According to Forbes, by 2050, the global population of people over the age of 60 is expected to hit 2 billion. To put this into perspective, this will represent over a fifth of the world’s population. With a growing elderly population comes the need for more advanced in-home monitoring, while still allowing people to maintain personal autonomy. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly one-fourth of seniors fall every year and falls are the leading cause of trauma-related hospital admissions among older adults, as shown in Figure 1. Fall detection systems can use sensor-driven solutions to provide non-contact, non-privacy invasive sensing through accurate point-cloud data.
 Figure 1 TI mmWave sensors can be used for stance detection in elderly, disabled and emergency monitoring systems
Figure 1 TI mmWave sensors can be used for stance detection in elderly, disabled and emergency monitoring systemsHow TI’s mmWave sensors help solve the challenges of today’s fall detection systems
| Learn more about “Detecting Human Falls and Stance” with mmWave sensors | |

|
View the demo |
Here we have TI’s “Detecting Human Falls and Stance” demo, which showcases TI’s 60 GHz IWR6843 single-chip sensor and its ability to detect the height and stance of a person when the sensor is mounted on a wall. The IWR6843 is used because the 60GHz band is open worldwide for industrial RF sensing applications
The demo uses the IWR6843ISK-ODS EVM, which has a 120-degree field of view in both azimuth and elevation. In the demo, the EVM is mounted at a height of 6.5ft, and the wide elevation field-of-view helps increase visibility down to the floor and minimizes dead zones. The demo can also be modified to use TI’s IWR6843AOPEVM antenna-on-package EVM.
Figure 2 shows the 3D point-cloud information, which enables the system to analyze the height and stance of an individual through point-cloud shape and color without revealing identifiable information. Notice the differences in the point-cloud outlines in the figure indicating the person’s stance.
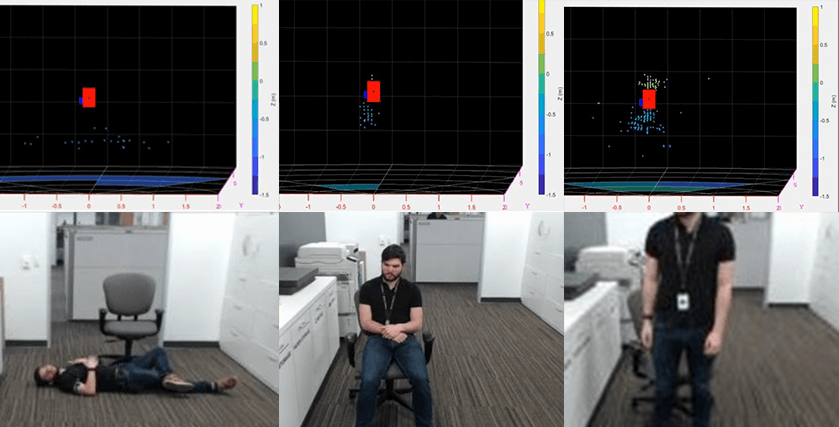 Figure 2 Various point-cloud screenshots and photos underneath for comparison: blue points with a horizontal outline of person laying down (a); blue and green points with a ball-shaped outline of a person sitting (b); blue, green, and yellow
points with a long vertical outline of a person standing (c)
Figure 2 Various point-cloud screenshots and photos underneath for comparison: blue points with a horizontal outline of person laying down (a); blue and green points with a ball-shaped outline of a person sitting (b); blue, green, and yellow
points with a long vertical outline of a person standing (c)(a) (b) (c)
Comparing Figure 2c to Figure 2a, you can see that the point-cloud formation changes. A person standing is typically shown with a long, thin cluster while a person lying down is indicated with a short, wide cluster. An algorithm can use this point cloud shape, size, and color information to detect the stance of a person and identify a fall. The sensor can observe the fall whenever there is a sudden negative change in height (the z dimension for this demo) and a sudden change in stance. Stance change could be detected when the z parameter changes from being much greater than x (length) and y (width) to being much less, indicating a quick transition from standing to laying.
Long-range, contact-less stance detection
Enabling non-invasive fall detection
Rich point-cloud data for accurate measurements
Conclusion
Additional resources
- View the applications for mmWave within building automation.
- Learn more about mmWave industrial sensors on the IWR overview.
- Check out these white papers: