SWRA648 May 2019 CC1352P , CC1352R , CC1354P10 , CC1354R10 , CC2642R , CC2642R-Q1 , CC2652P , CC2652R , CC2652R7 , CC2652RB , CC2652RSIP
- Bluetooth Low Energy Tree Structure Network
3.2 Mesh
In mesh networks, each device is connected to one or more of the other devices. There is no clear role definition that parallels central/peripheral. A typical real mesh topology (such as Zigbee® or Thread) consists of one coordinator, several routers and several end devices. Routers can communicate with other nodes because the Mesh protocol defines the routing rules. Mesh is considered the most flexible network and it can provide a larger network coverage area. At the same time, Mesh has a strong fault-tolerant ability. If a router crashes in the network, information can still be automatically transmitted along other routing path. On the other hand, mesh networks use complex network protocols that require a lot from the hardware and software that is used. Also, the Mesh networks typically consume more power than other networks, and the data latency is both higher and more unpredictable since the number of jumps between peer devices is not fixed.
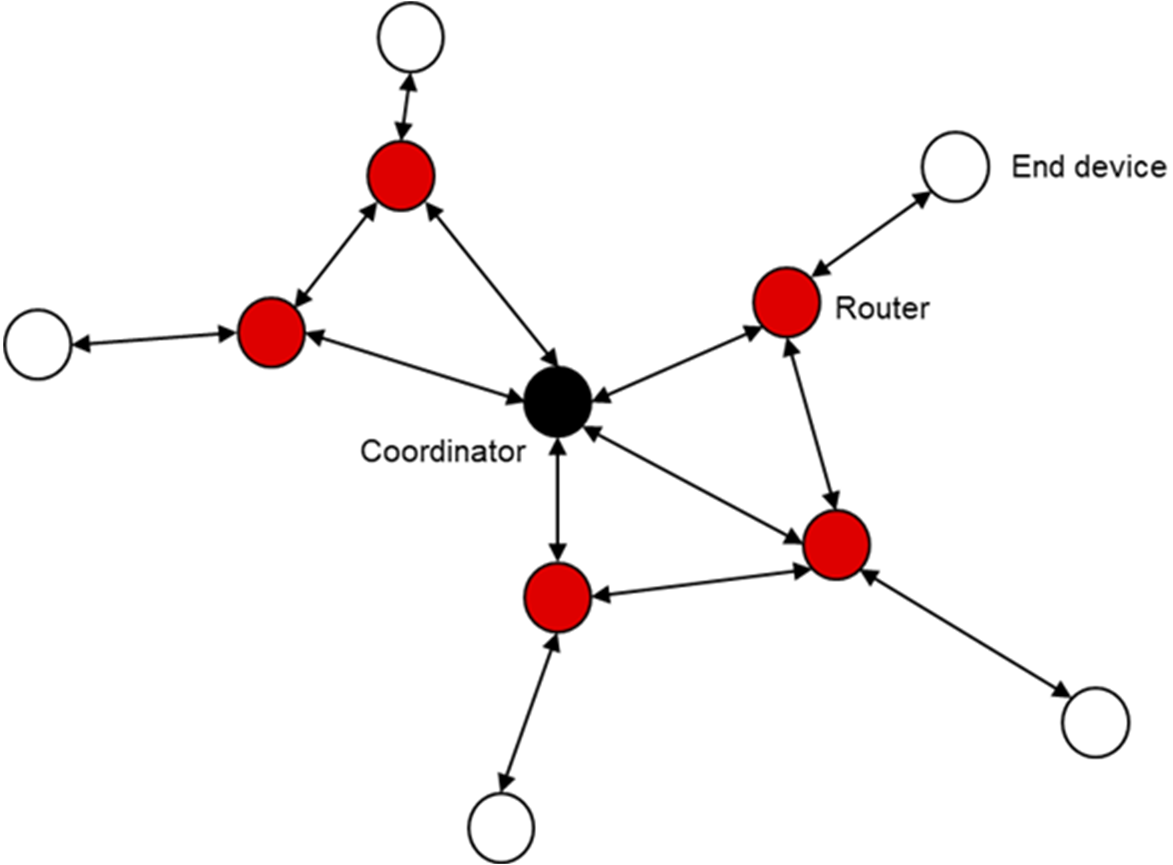 Figure 2. Mesh Network
Figure 2. Mesh Network Bluetooth Mesh is a mesh network protocol based on “message flooding” using the Bluetooth Low Energy Broadcaster and Observer GAP roles. This protocol is quite complicated and is not considered power and latency efficient compared to star networks. Bluetooth Low Energy manufacturers are still researching and developing their Bluetooth Low Energy mesh solutions at this time.