TIDT261 March 2022
3.4 Load Transients
Electronic load was used for the waveforms taken in the following images. The load is switching from 2.5 A to 5 A with a frequency of 100 Hz.
4-V Input Voltage
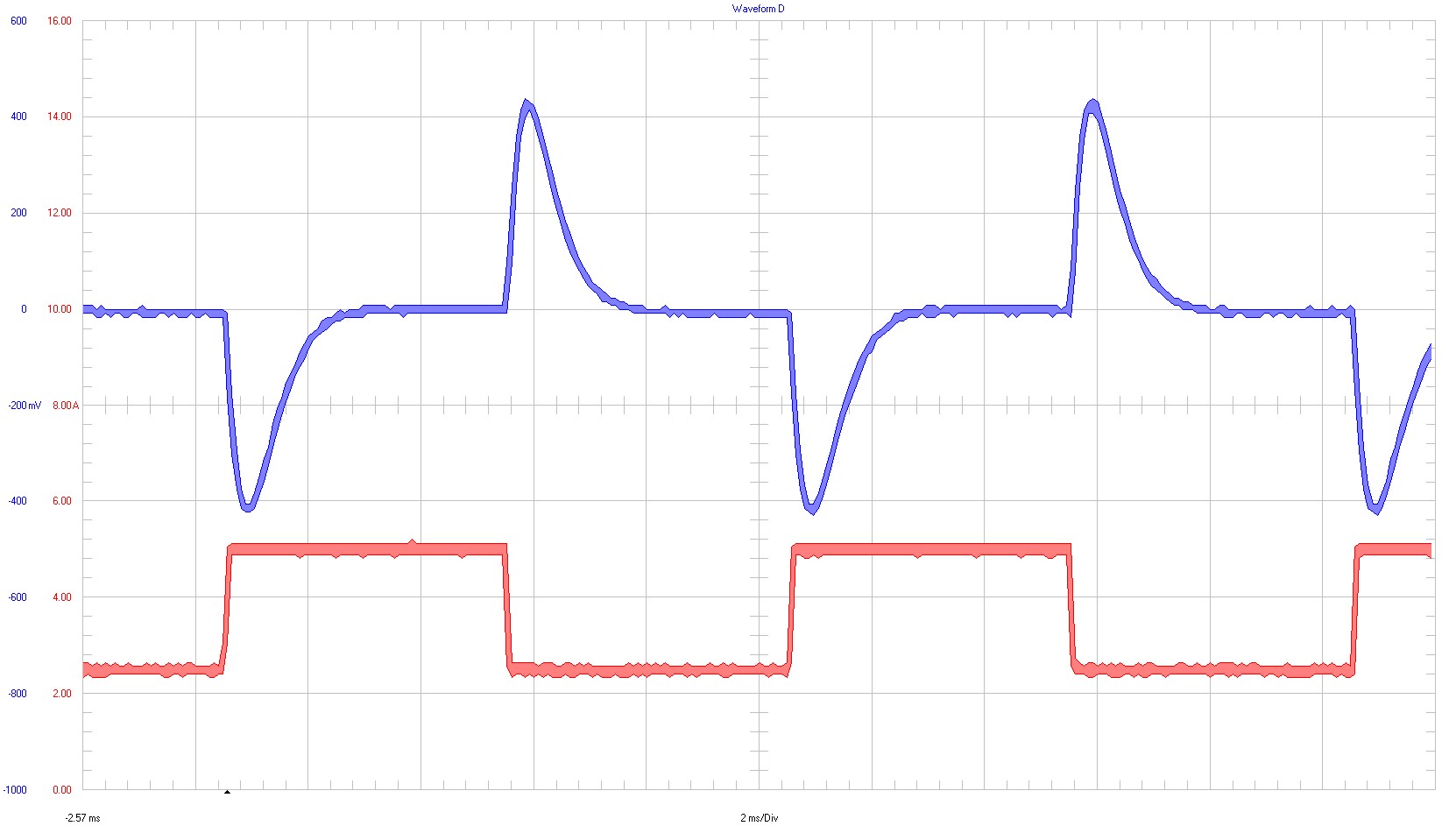
Ch1 ⇒ output voltage; 200 mV / div; AC-coupling; 10-kHz bandwidth
Ch2 ⇒ output current; 2 A / div; 20-MHz bandwidth
2-ms / div
Figure 3-18 2.5-A to 5-A Load Transient at 4-V Input Voltage12-V Input Voltage
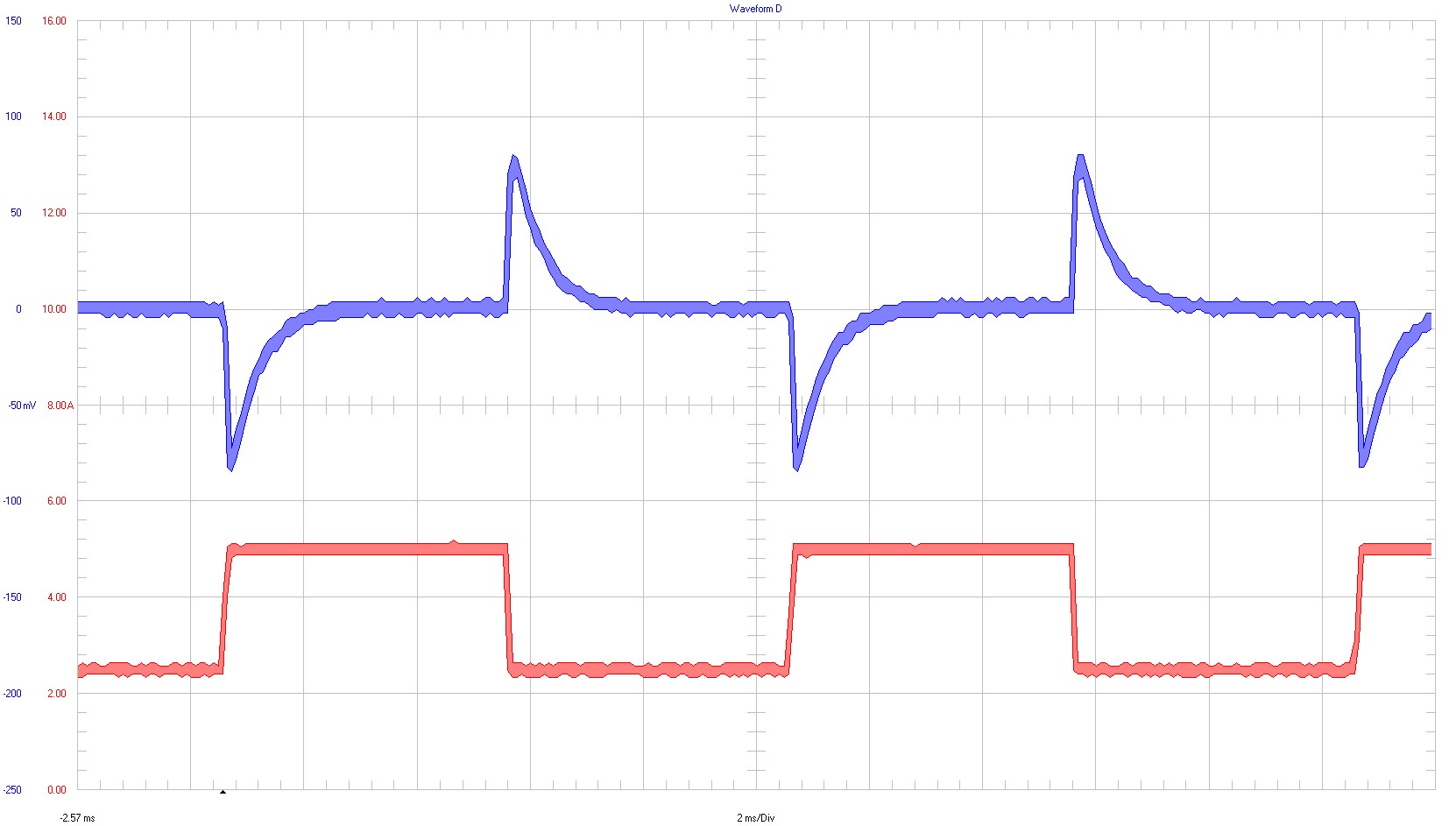
Ch1 ⇒ output voltage; 50 mV / div; AC-coupling; 10-kHz bandwidth
Ch2 ⇒ output current; 2 A / div; 20-MHz bandwidth
2-ms / div
Figure 3-19 2.5-A to 5-A Load Transient at 12-V Input Voltage18-V Input Voltage
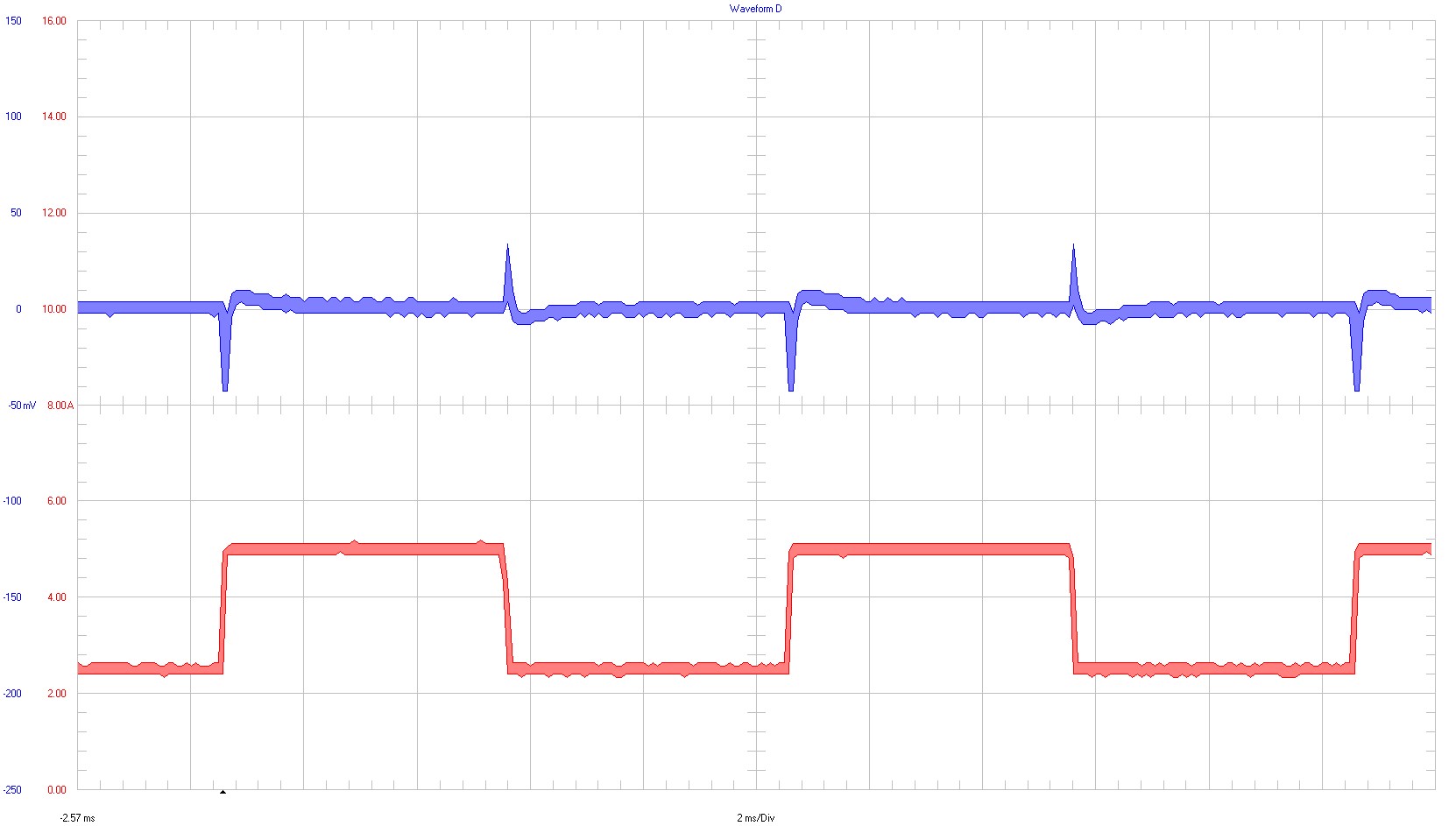
Ch1 ⇒ output voltage; 50 mV / div; AC-coupling; 10-kHz bandwidth
Ch2 ⇒ output current; 2 A / div; 20-MHz bandwidth
2-ms / div
Figure 3-20 2.5-A to 5-A Load Transient at 18-V Input Voltage