TIDT292 June 2022
3.5 Inrush Current
During this test, the AC source was turned on and input current and voltage, as well as the PFC voltage, were measured (with 20-MHz BWL). Figure 3-14 and Figure 3-15 show the inrush current limitation during start-up at VIN = 115 VAC, F = 400 Hz, no load.
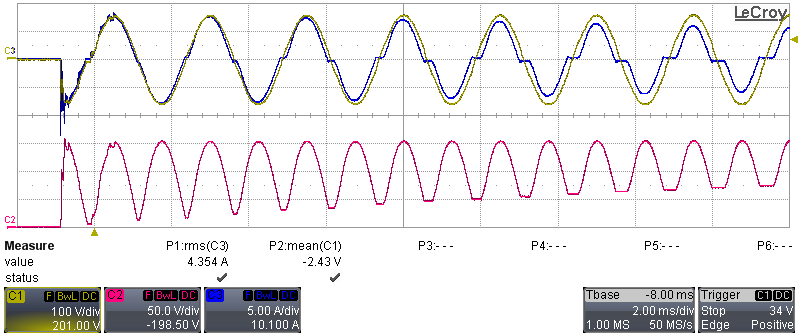 Figure 3-14 Time Division: 2 ms/div, (C2: VPFC,
C1: VIN, C3: IIN)
Figure 3-14 Time Division: 2 ms/div, (C2: VPFC,
C1: VIN, C3: IIN)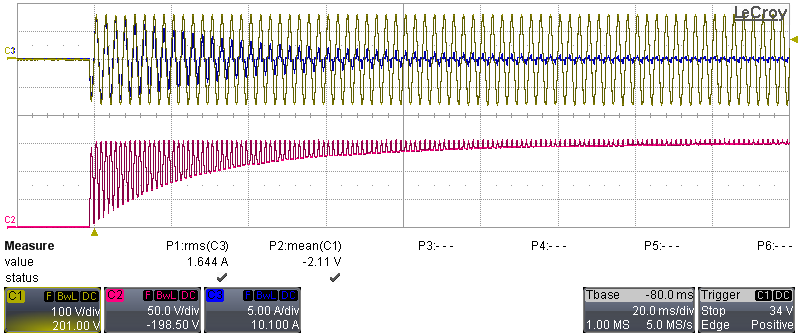 Figure 3-15 Time Division: 20 ms/div, (C2:
VPFC, C1: VIN, C3: IIN)
Figure 3-15 Time Division: 20 ms/div, (C2:
VPFC, C1: VIN, C3: IIN)