TIDT319 December 2022
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
- 3Waveforms for 2 × LM5143A-Q1 in Four Phase Configuration and Interleaved Operation
- A Individual Adjusting of the Rising Edge and Falling Edge With LM5143A
- B Measurements Across the Low-Side FETs to Check at All Four Phases
- C ON Demand – Assembly of Thermal Interface
3.1.1.1 24-V Input Voltage
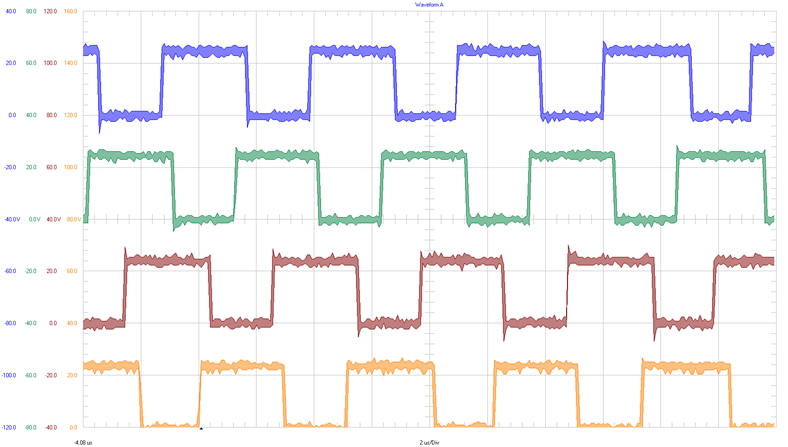
|
(SW1 to SW4) 20 V / div 2 µs / div Full bandwidth |
Figure 3-1 Four Switching Phases at 0,
90, 180, 270 Degrees Phase Shift at 24 VIN
| Primary Controller U1 | phase 1(1) | 0 degrees |
| phase 2(1) | 180 degrees | |
| Secondary Controller U2 | phase 3(1) | 90 degrees |
| phase 4(1) | 270 degrees |
(1) The
background color in the table cells correspond to the waveform colors in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 highlights the four phase interleaved operation of the two stacked controllers in primary and secondary configuration. Four phase interleaved operation results in ripple rejection at 25%, 50% and 75% duty cycle.
This evidence shows that at 24-V input voltage (duty cycle around 50%) and at 480-V input voltage (duty-cycle around 25%) and around 12-V output voltage, the ripple rejection is best.
This ripple rejection is illustrated in Figure 3-8, output ripple < 10 mVPP and noise < 50 mVPP.