TIDT339 june 2023
3.2 Output Voltage Ripple
The output voltage ripple was measured by supplying the converter at 230 VAC, while loaded at 1.7 A; the bandwidth limit of oscilloscope (BWL) was set to 20 MHz.
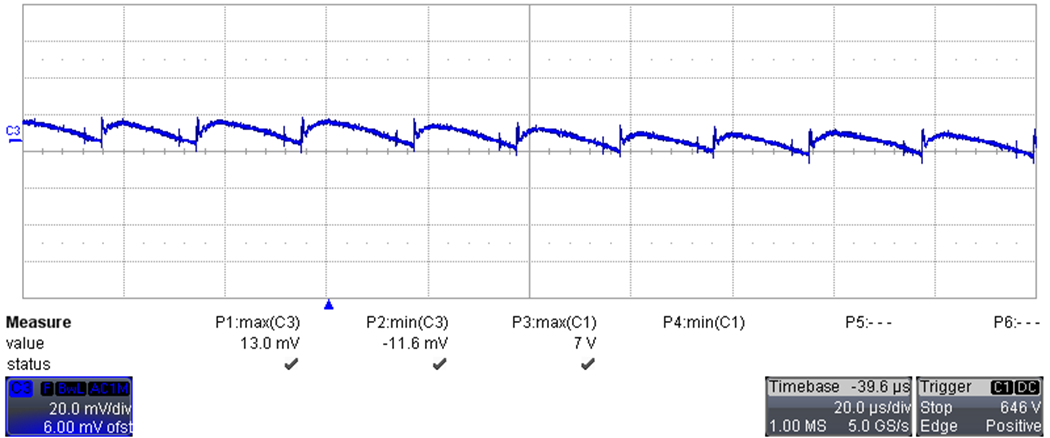 Figure 3-3 Output Voltage (20 mV/div, 20 µs/div,
AC coupling)
Figure 3-3 Output Voltage (20 mV/div, 20 µs/div,
AC coupling)Figure 3-4 is the same measurement as in Figure 3-3 but with longer time division, showing details about low frequency ripple.
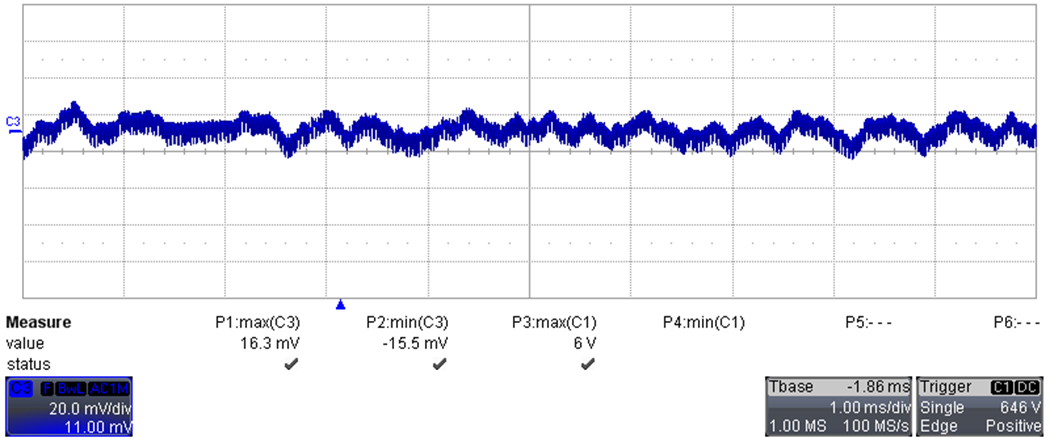 Figure 3-4 Output Voltage (20 mV/div, 1 ms/div,
AC coupling)
Figure 3-4 Output Voltage (20 mV/div, 1 ms/div,
AC coupling)