TIDT354 November 2023
2.1 Efficiency Graphs
The efficiency of the system is demonstrated across an input voltage range of 20 V to 60 V.
According to Figure 3-11, when operating at full 60-A load, the efficiency is within the range of 84% to 90%.
The efficiency graph is derived from the conversion loss vs load current graph (Figure 2-2), which also spans over a 24-V to 60-V input range. The no-load loss varies from just over 2 W when the input voltage is 24 V, increasing to just under 8 W when the input voltage reaches 60 V. The range of full-load loss extends from 24 W at 24 V input to 37.3 W at 60-V input.
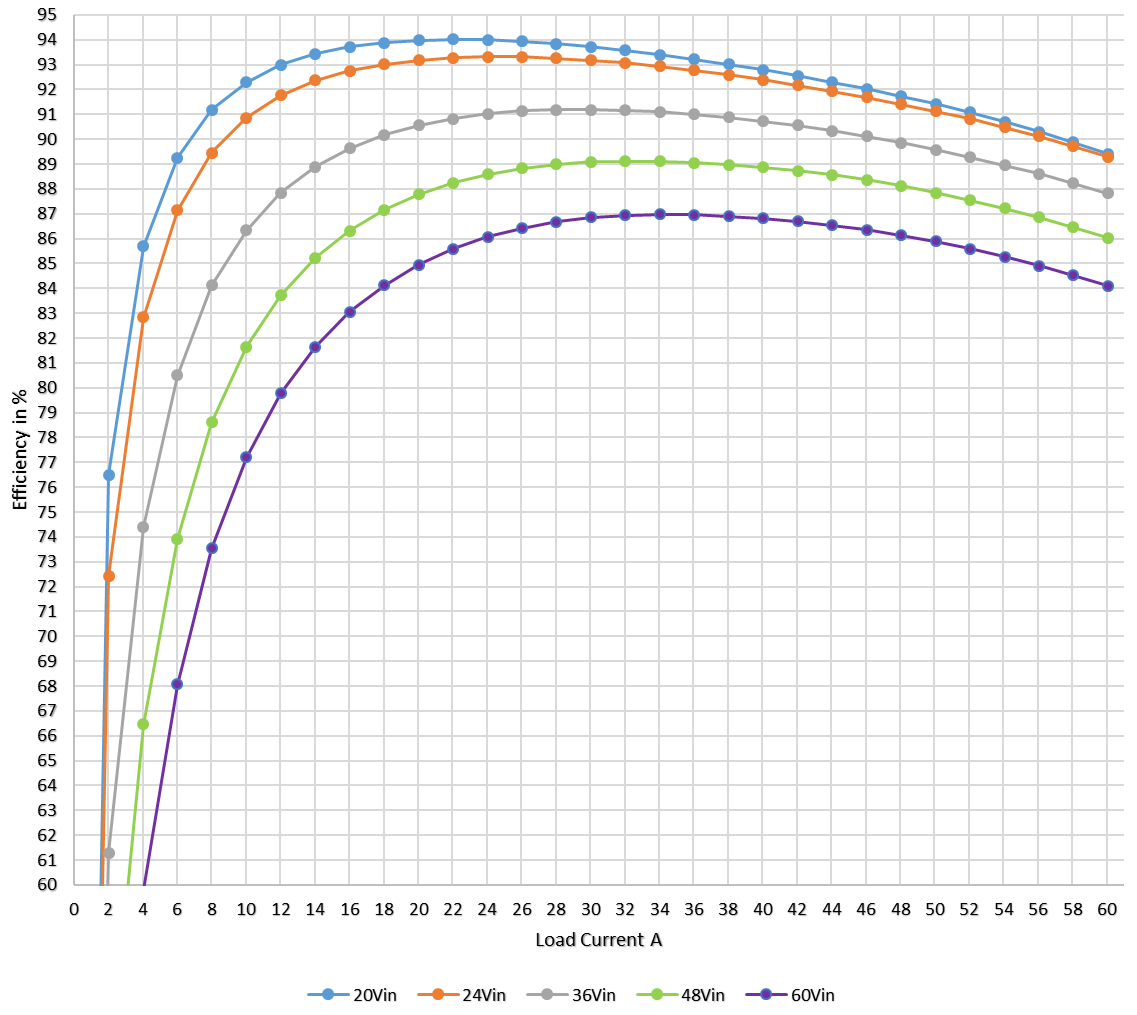 Figure 2-1 3.3 V, 2-Phase Conversion Efficiency
Figure 2-1 3.3 V, 2-Phase Conversion Efficiency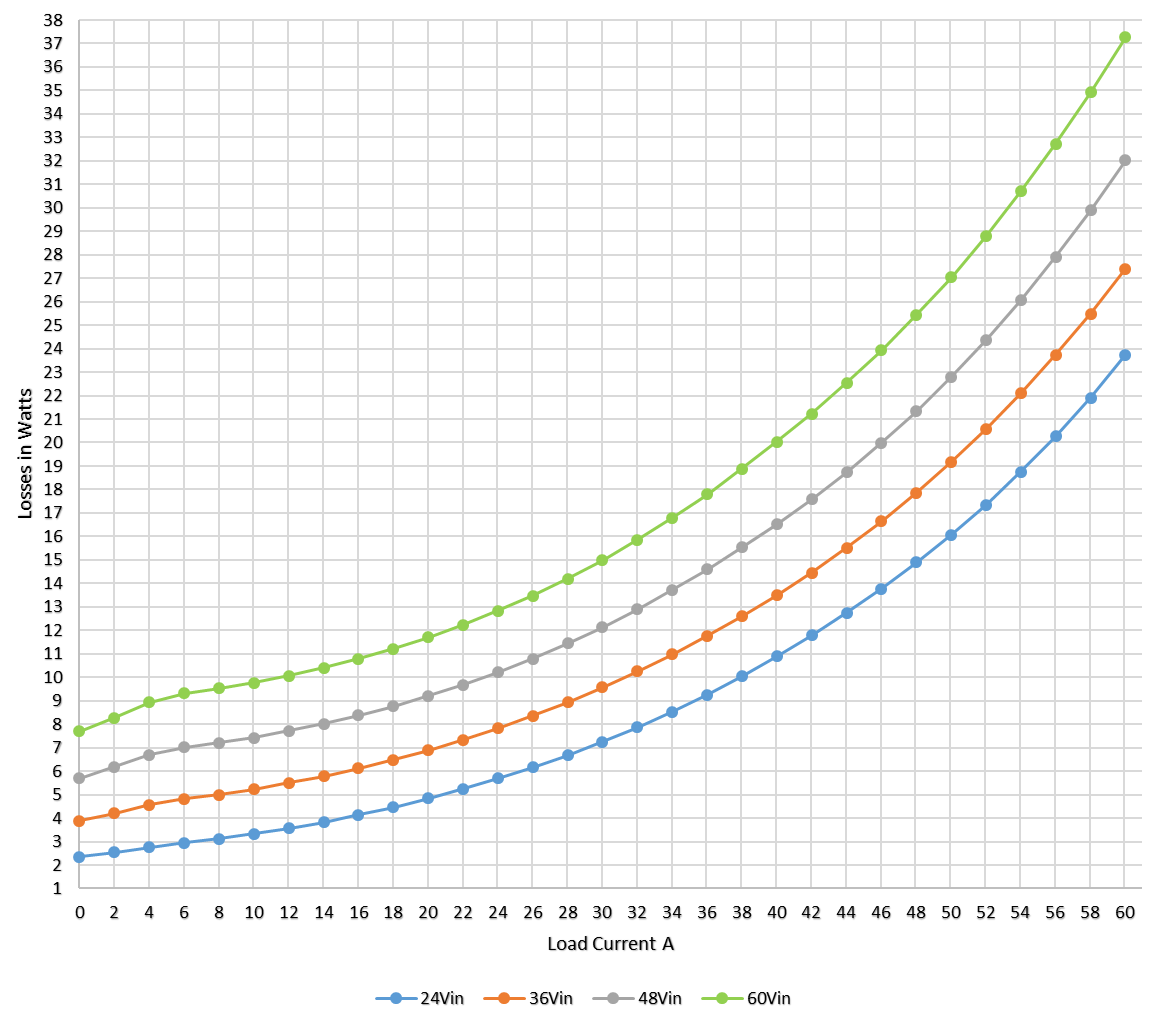 Figure 2-2 3.3 V, 2-Phase Conversion Losses
Figure 2-2 3.3 V, 2-Phase Conversion Losses