TIDT382 February 2024
- 1
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
- 3Waveforms
- 4Summary
- 5References
2.5 Common-Mode Current (CMI)
Common-Mode Current (CMI) tests were done while running both isolated bias power supply converter circuits at 15V output and switching the GaN half-bridge at 400V. Common-mode current flows from the high-voltage side to the low-voltage side through the parasitic capacitance across the isolation barrier. Common mode current is generated due to switching of the high- and low-side GaN half bridge switches at a high slew rate. During the measurements, high- and low-voltage grounds were shorted using a wire (shown in Figure 2-15) to minimize the length of the common-mode current loop from high-voltage side to low-voltage side. This can be considered as a worst-case scenario for common-mode current and results in the highest possible common-mode current through the isolation barrier. CMI current measurements are taken on two different high slew rate values: 40V/ns and 100V/ns. CMI measurements are taken while bypassing the input filter. Using a potentiometer at the RDRV pin of the LMG3525R030Q, the slew rate can be varied with reference to the selected resistor value. Figure 2-15 shows the CMI test setup.
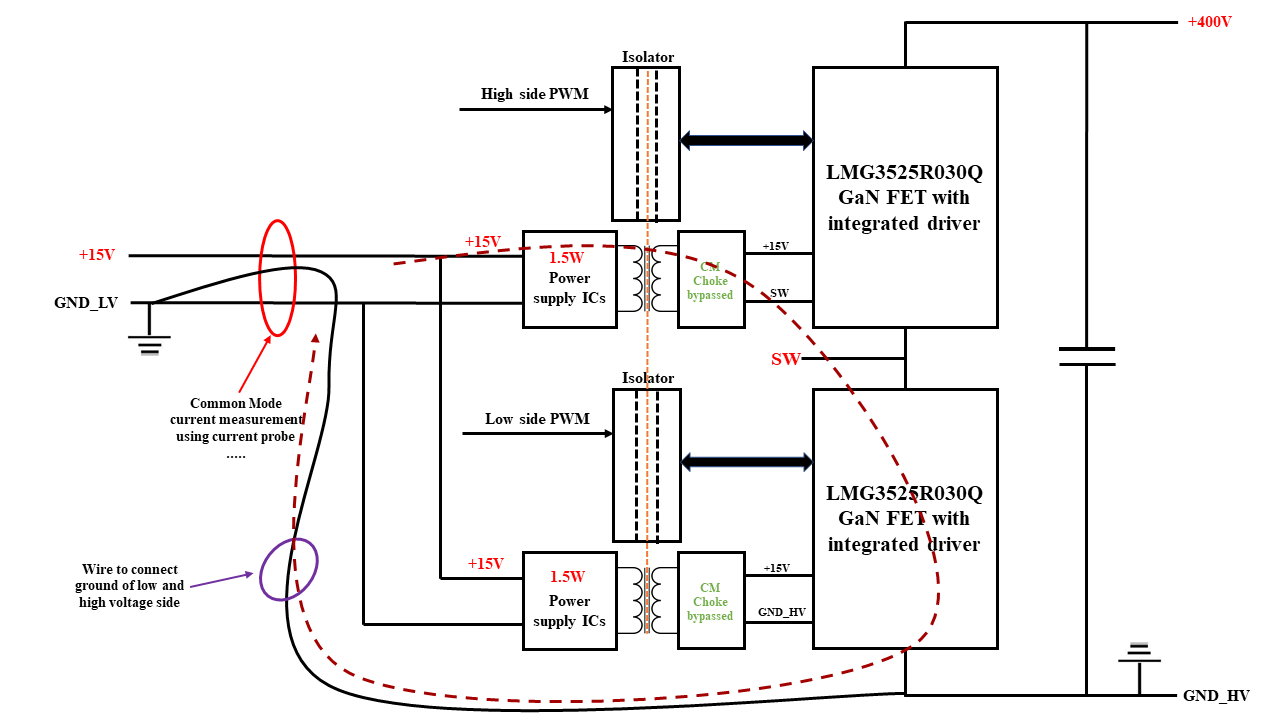 Figure 2-15 Common-Mode Current (CMI) Test Setup
Figure 2-15 Common-Mode Current (CMI) Test Setup