TIDT412A October 2024 – November 2024
3.4 High Current Load Transients
Figure 3-9 shows how the system responds to a load transient that starts at a nominal 7.5A, and in-line with audio applications, jumps up to 25A for a brief period. Operation is completed with 48V at the input, and 35V at the output, such that the system jumps from a nominal 262W of power to 875W of power.
On the load step from 7.5A to 25A, an undershoot of 1.47V, or 4.20%, is present; while on the load dump from 25A to 7.5A, an overshoot of 1.3V, or 3.71%, is present.
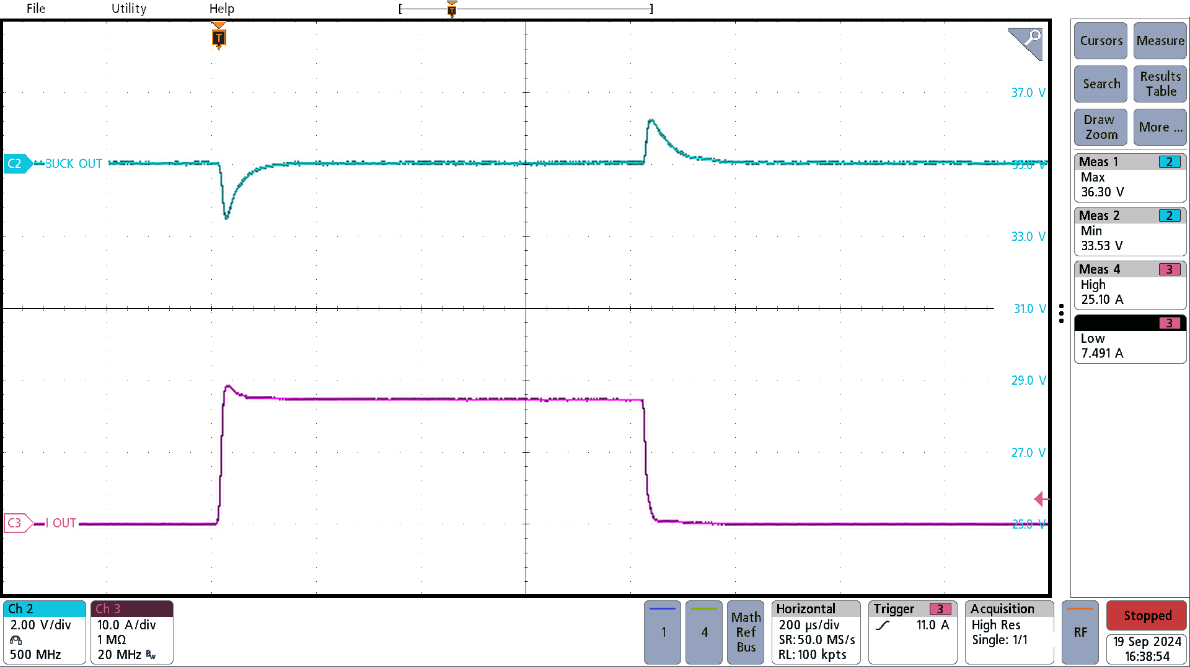 Figure 3-9 7.5A to 25A Load Transient at
35VOUT
Figure 3-9 7.5A to 25A Load Transient at
35VOUT