TIDUCL3 February 2017
- 1 Overview
- 2 Resources
- 3 Features
- 4 Applications
- 5 Design Images
- 6 System Overview
-
7 System Design Theory
- 7.1 PCB and Form Factor
- 7.2 Optimizing Board Performance Based on LED String Voltage and Current
- 7.3 Switching Frequency
- 7.4 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.5 Current Monitoring (IMON)
- 7.6 Thermal Foldback
- 7.7 Clock Generation (PWM)
- 7.8 Onboard Supply and Setting Duty Cycle
- 7.9 Buffering, Averaging, and Filtering
- 7.10 Boost Converter
- 8 Getting Started Hardware
- 9 Testing and Results
- 10Design Files
- 11Related Documentation
- 12About the Author
9.1 Duty Cycle Accuracy
- The board ran continuously with a fixed duty cycle set and the duty cycle recorded continuously with the oscilloscope and standard deviation calculated (see Figure 24).
- Different clock devices (TLC555) from a different production batch were tested on the same board.
- Temperature test: –40°C to 110°C. The board ran continuously with a fixed duty cycle set and the duty cycle continuously recorded with an oscilloscope and standard deviation calculated.
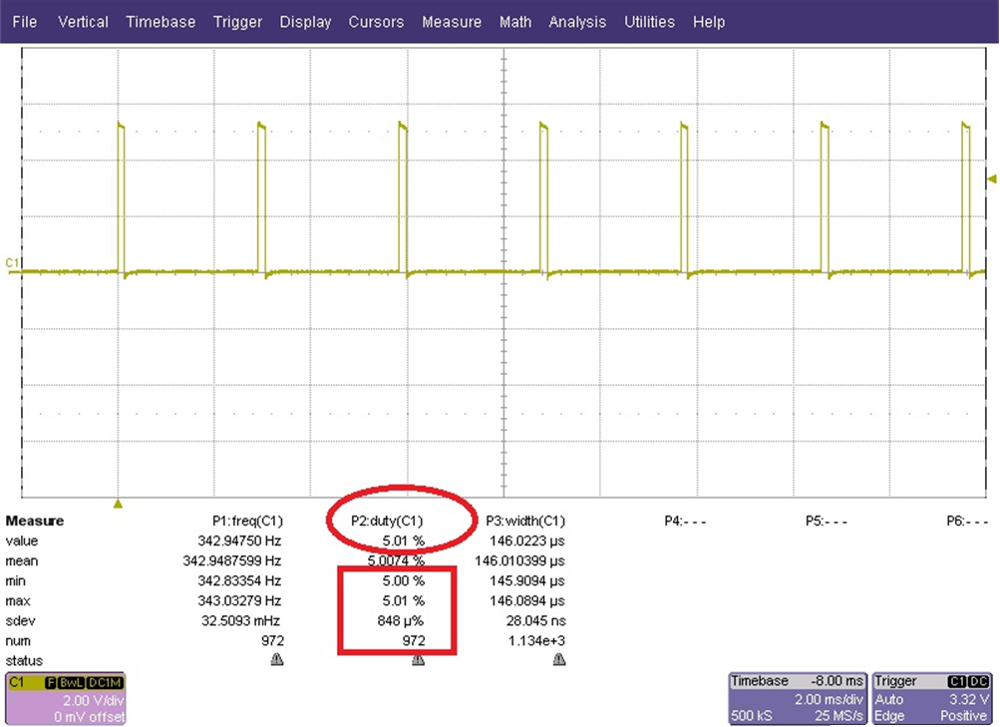 Figure 24. Duty Cycle Accuracy
Figure 24. Duty Cycle Accuracy The result was a very accurate duty cycle with a standard deviation of 848µ% (0.000848%).
The result was a very accurate duty cycle with a standard deviation of less than 0.5%.
The result was a very accurate duty cycle with a standard deviation of less than 0.5%.