TIDUDT4A May 2018 – November 2021 AM3351 , AM3352 , AM3354 , AM3356 , AM3357 , AM3358 , AM3358-EP , AM3359
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
3.2.2.1 Power-Up and Power-Down Sequence Test
The following waveforms show the power-up and power-down sequence provided by this power solution that meet the requirements of the AM335x. The test environment includes the following:
- The input capacitor is 220 µF.
- The status of the board is: Linux running with Wi-Fi enabled.
- The style of the power down directly removes the DC power through the switch.
Figure 3-4 shows the power sequences of the input voltage rail and 1.8-V, 3.3-V, and 1.35-V rails.
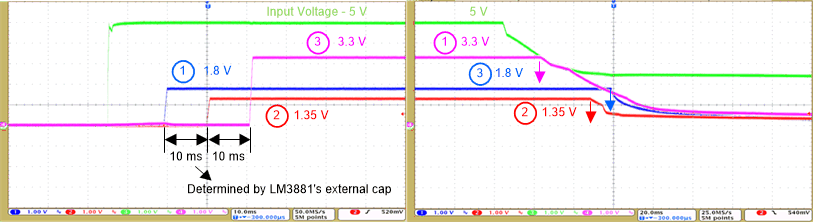 Figure 3-4 Power Sequence for 5-Vin,1.8-V, 3.3-V, and 1.35-V Rails
Figure 3-4 Power Sequence for 5-Vin,1.8-V, 3.3-V, and 1.35-V RailsFor the power-up sequencing, the 1.8-V, 1.35-V, and 3.3-V rails power turn on sequentially after the input voltage rail turns on. For the power-down sequencing, the 3.3-V, 1.35-V, and 1.8-V rails turn off sequentially in the precise reverse order after the input voltage rail turns off. The delay time between the different power rails is approximately 10 ms, which can be adjusted by changing the external capacitor of the LM3881MM.
Figure 3-5 shows the power sequences of the 3.3-V, 1.8-V, 1.35-V, and 1.1-V rails.
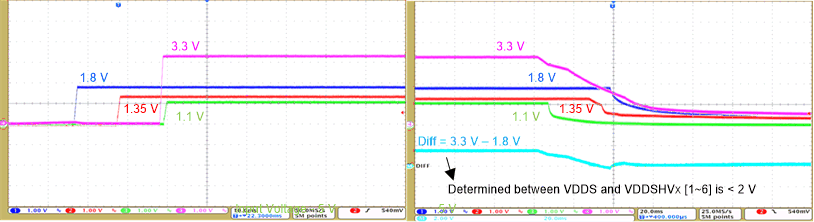 Figure 3-5 Power Sequence for 3.3-V, 1.8-V, 1.35-V, and 1.1-V Rails
Figure 3-5 Power Sequence for 3.3-V, 1.8-V, 1.35-V, and 1.1-V RailsFor the power-up sequencing, the 1.8-V, 1.35-V, and 3.3-V rails power turn on sequentially after the input voltage rail turns on. For the power-down sequencing, the 3.3-V, 1.35-V, and 1.8-V rails turn off sequentially in the precise reverse order after the input voltage rail turns off. The difference between VDDS and VDDSHVx[1-6] during the entire power down sequence is < 2 V.
Figure 3-6 shows the power sequences of the 5-Vin, 1.8-V, 3.3-V, and PWRONRSTn rails.
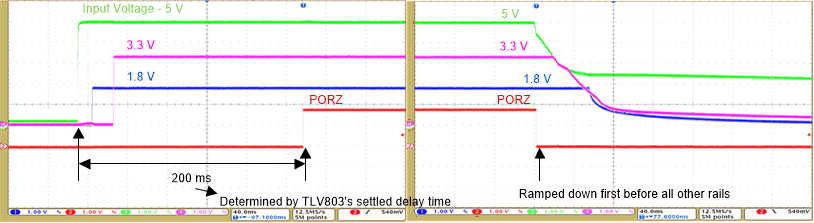 Figure 3-6 Power Sequence for 5-Vin, 1.8-V, 3.3-V, and PWRONRSTn Rails
Figure 3-6 Power Sequence for 5-Vin, 1.8-V, 3.3-V, and PWRONRSTn RailsFor the power-up sequencing, the 1.8-V, 3.3-V, and PWRONRSTn rails turn on sequentially after the input voltage rail turns on, and the PWRONRSTn rail turns on after all the other rails are ON. For the power-down sequencing, the PWRONRSTn rail ramps down first before all other rails turn off, and the other rails ramp down sequentially. The delay time between PWRONRSTn and input voltage rail is 200 ms, which depends on the fixed delay time of the supervisor for the TLV803.
Figure 3-7 shows the power sequences of the 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.1-V, and 1.325-V rails.
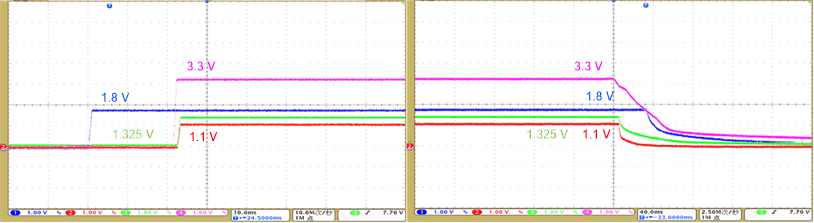 Figure 3-7 Power Sequence for 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.1-V, and 1.325-V Rails
Figure 3-7 Power Sequence for 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.1-V, and 1.325-V RailsFor the power-up sequencing, the 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.1-V, and 1.325-V rails turn on sequentially, and the 1.325-V and 1.1-V rails ramp up at the same time. For the power-down sequencing, the 1.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.1-V, and 1.325-V rails ramp down sequentially, and the 1.325-V and 1.1-V rails ramp down at the same time.