ZHCS179F August 2011 – July 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | –20 | 20 | V | |
| Signal input pins | Voltage | (–VS) – 40 | (+VS) + 40 | V |
| REF pin | –20 | +20 | ||
| Output short-circuit(2) | Continuous | |||
| Temperature | Operating, TA | –50 | 150 | °C |
| Junction, TJ | 175 | |||
| Storage, Tstg | –65 | 150 | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Short-circuit to VS / 2.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2500 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
| Machine model (MM) | ±150 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | Single supply | 3 | 36 | V | |
| Dual supply | ±1.5 | ±18 | |||
| Specified temperature | –40 | +125 | °C | ||
| Operating temperature | –50 | +150 | °C | ||
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | INA826 | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DGK (VSSOP) | DRG (WSON) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 141.4 | 215.4 | 50.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 75.4 | 66.3 | 60.0 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 59.6 | 97.8 | 25.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 27.4 | 10.5 | 1.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 59.1 | 96.1 | 25.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | n/a | n/a | 7.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, RL = 10 kΩ, VREF = 0 V, and G = 1 (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | |||||||
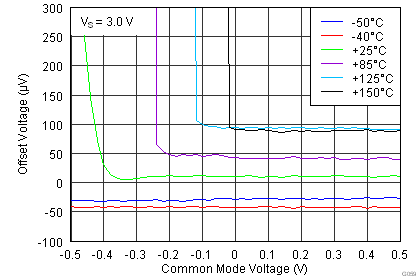
| VOSI | Input stage offset voltage(1) | RTI | 40 | 150 | µV | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 0.4 | 2 | µV/°C | ||||
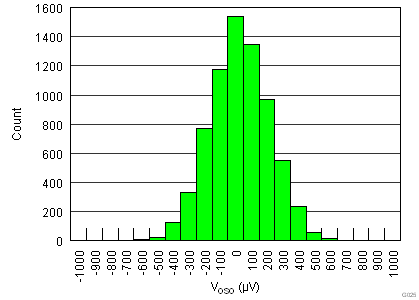
| VOSO | Output stage offset voltage(1) | RTI | 200 | 700 | µV | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 2 | 10 | µV/°C | ||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | G = 1, RTI | 100 | 124 | dB | ||
| G = 10, RTI | 115 | 130 | |||||
| G = 100, RTI | 120 | 140 | |||||
| G = 1000, RTI | 120 | 140 | |||||
| zid | Differential impedance | 20 || 1 | GΩ || pF | ||||
| zic | Common-mode impedance | 10 || 5 | GΩ || pF | ||||
| RFI filter, –3-dB frequency | 20 | MHz | |||||
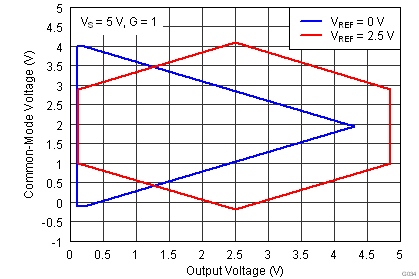
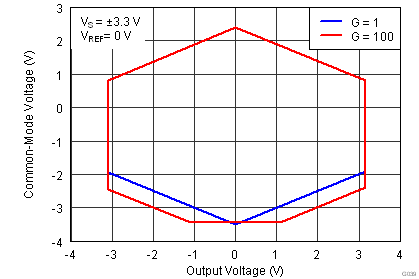
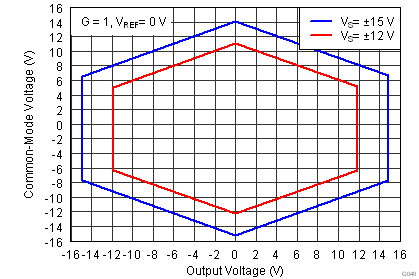
| VCM | Operating input range(2) | V– | (V+) – 1 | V | |||
| VS = ±1.5 V to ±18 V, TA = –40°C to +125°C | See Figure 41 to Figure 44 | ||||||
| Input overvoltage range | TA = –40°C to 125°C | ±40 | V | ||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | At dc to 60 Hz, RTI | G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 84 | 95 | dB | |
| G = 10, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 104 | 115 | |||||
| G = 100, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 120 | 130 | |||||
| G = 1000, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 120 | 130 | |||||
| G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V, TA = –40°C to +125°C |
80 | ||||||
| At 5 kHz, RTI | G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 84 | |||||
| G = 10, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 100 | ||||||
| G = 100, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 105 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 105 | ||||||
| BIAS CURRENT | |||||||
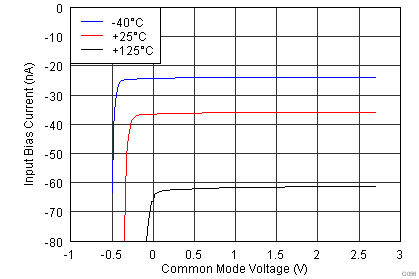
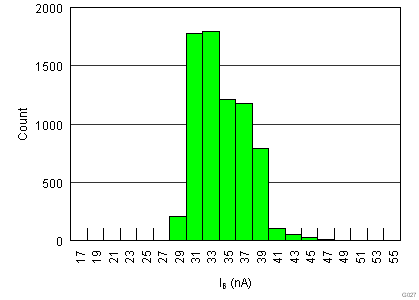
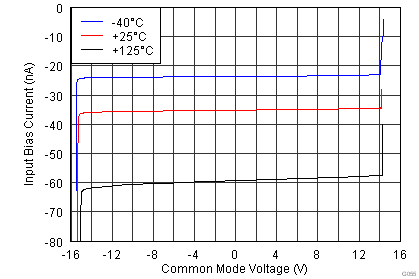
| IB | Input bias current | VCM = VS / 2 | 35 | 65 | nA | ||
| TA = –40°C to +125°C | 95 | ||||||
| IOS | Input offset current | VCM = VS / 2 | 0.7 | 5 | nA | ||
| TA = –40°C to +125°C | 10 | ||||||
| NOISE VOLTAGE | |||||||
| eNI | Input stage voltage noise(4) | f = 1 kHz, G = 100, RS = 0 Ω | 18 | 20 | nV/√Hz | ||
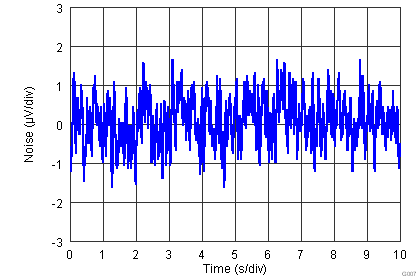
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz, G = 100, RS = 0 Ω | 0.52 | µVPP | |||||
| eNO | Output stage voltage noise(4) | f = 1 kHz, G = 1, RS = 0 Ω | 110 | 115 | nV/√Hz | ||
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz, G = 1, RS = 0 Ω | 3.3 | µVPP | |||||
| In | Noise current | f = 1 kHz | 100 | fA/√Hz | |||
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 5 | pAPP | |||||
| GAIN | |||||||
| G | Gain equation | 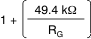 |
V/V | ||||
| Range of gain | 1 | 1000 | V/V | ||||
| GE | Gain error | G = 1, VO = ±10 V | ±0.003% | ±0.015% | |||
| G = 10, VO = ±10 V | ±0.03% | ±0.15% | |||||
| G = 100, VO = ±10 V | ±0.04% | ±0.15% | |||||
| G = 1000, VO = ±10 V | ±0.04% | ±0.15% | |||||
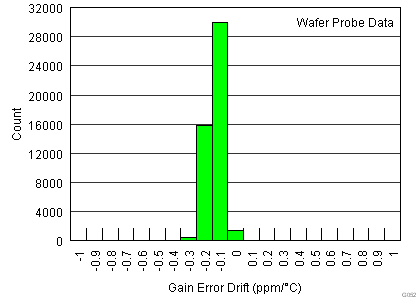
| Gain vs temperature(3) | G = 1, TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±0.1 | ±1 | ppm/°C | |||
| G > 1, TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±10 | ±35 | |||||
| Gain nonlinearity | G = 1 to 100, VO = –10 V to +10 V | 1 | 5 | ppm | |||
| G = 1000, VO = –10 V to +10 V | 5 | 20 | |||||
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| Voltage swing | RL = 10 kΩ | (V–) + 0.1 | (V+) – 0.15 | V | |||
| Load capacitance stability | 1000 | pF | |||||
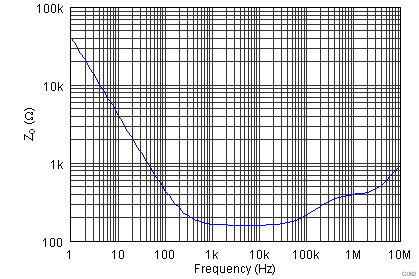
| ZO | Open-loop output impedance | See Figure 56 | |||||
| ISC | Short-circuit current | Continuous to VS / 2 | ±16 | mA | |||
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | |||||||
| BW | Bandwidth, –3 dB | G = 1 | 1 | MHz | |||
| G = 10 | 500 | kHz | |||||
| G = 100 | 60 | ||||||
| G = 1000 | 6 | ||||||
| SR | Slew rate | G = 1, VO = ±14.5 V | 1 | V/µs | |||
| G = 100, VO = ±14.5 V | 1 | ||||||
| tS | Settling time | 0.01% | G = 1, VSTEP = 10 V | 12 | µs | ||
| G = 10, VSTEP = 10 V | 12 | ||||||
| G = 100, VSTEP = 10 V | 24 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VSTEP = 10 V | 224 | ||||||
| 0.001% | G = 1, VSTEP = 10 V | 14 | |||||
| G = 10, VSTEP = 10 V | 14 | ||||||
| G = 100, VSTEP = 10 V | 31 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VSTEP = 10 V | 278 | ||||||
| REFERENCE INPUT | |||||||
| RIN | Input impedance | 100 | kΩ | ||||
| Voltage range | (V–) | (V+) | V | ||||
| Gain to output | 1 | V/V | |||||
| Reference gain error | 0.01% | ||||||
| POWER SUPPLY | |||||||
| VS | Power-supply voltage | Single supply | 3 | 36 | V | ||
| Dual supply | ±1.5 | ±18 | |||||
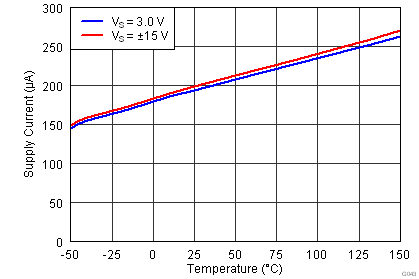
| IQ | Quiescent current | VIN = 0 V | 200 | 250 | µA | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 250 | 300 | |||||
| TEMPERATURE RANGE | |||||||
| Specified | –40 | 125 | °C | ||||
| Operating | –50 | 150 | °C | ||||
(1) Total offset, referred-to-input (RTI): VOS = (VOSI) + (VOSO / G).
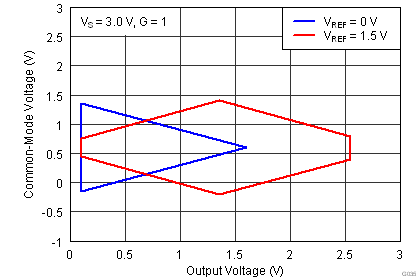
(2) Input voltage range of the INA826 input stage. The input range depends on the common-mode voltage, differential voltage, gain, and reference voltage. See Typical Characteristic curves Figure 9 through Figure 16 and Figure 41 through Figure 44 for more information.
(3) The values specified for G > 1 do not include the effects of the external gain-setting resistor, RG.
(4)
Total RTI voltage noise =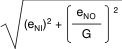 .
.
Total RTI voltage noise =
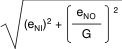 .
.7.6 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, RL = 10 kΩ, VREF = 0 V, and G = 1 (unless otherwise noted)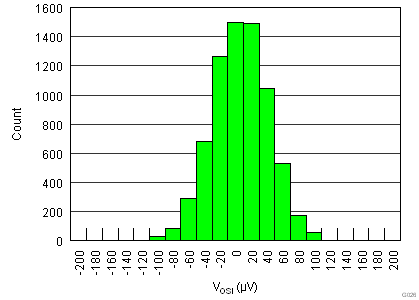
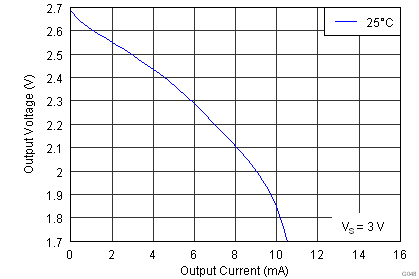
| Single supply |
| Dual supply |
| Dual supply |
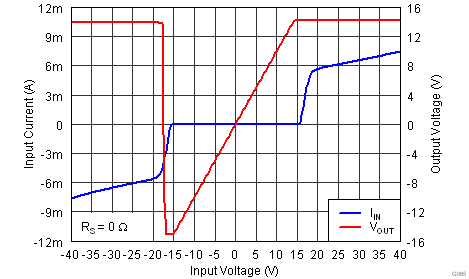
| G = 1, VS = ±15 V |
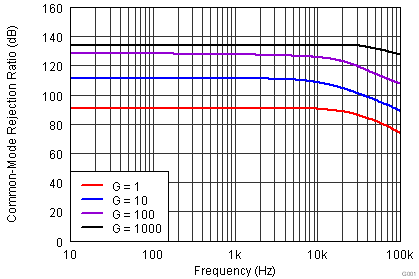
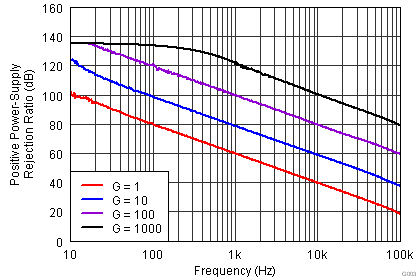
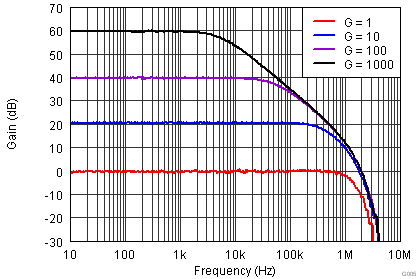
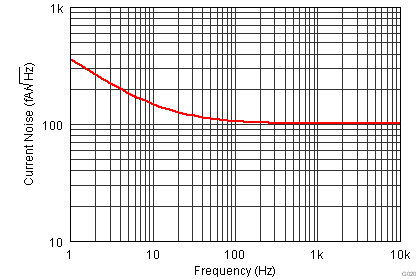
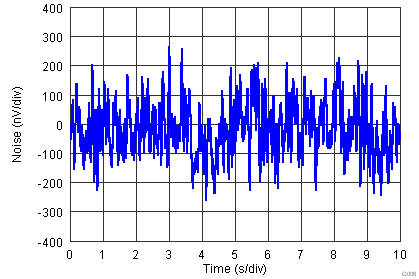
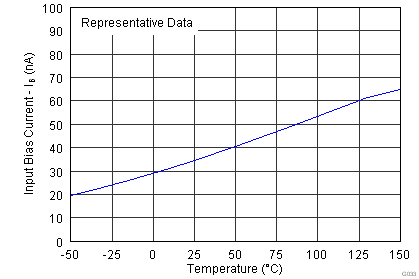
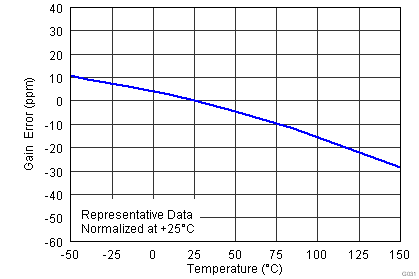
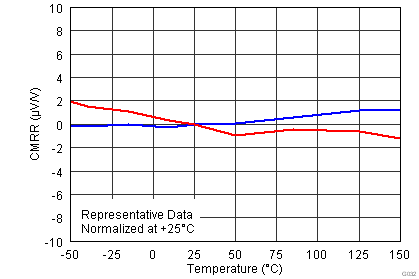
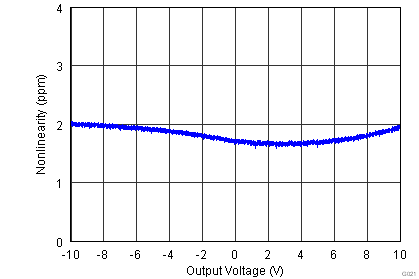
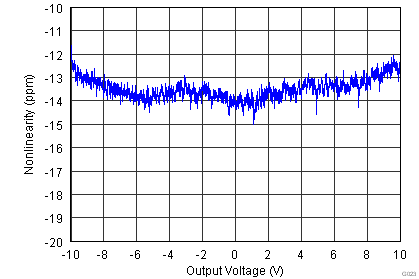
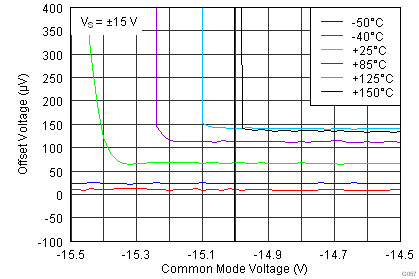
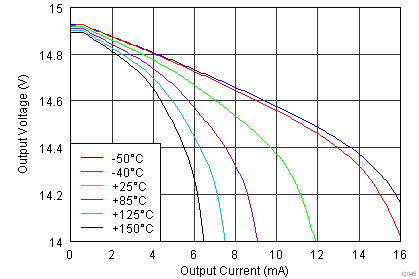
| VS = ±15 V |
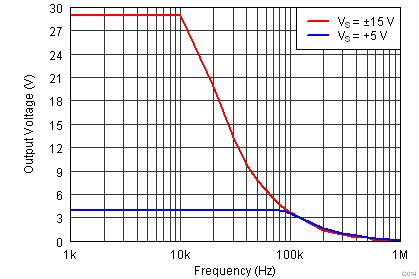
(G = 1)
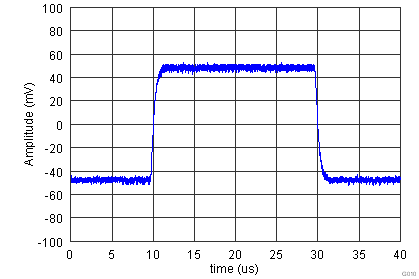
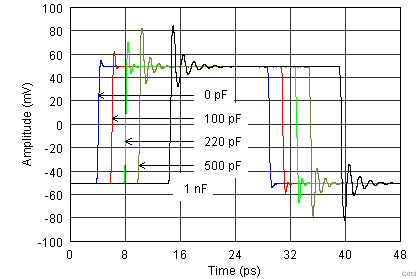
| G = 10, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 100 pF |
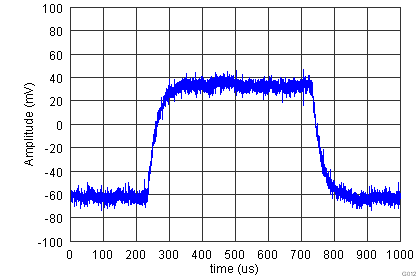
| G = 1000, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 100 pF |
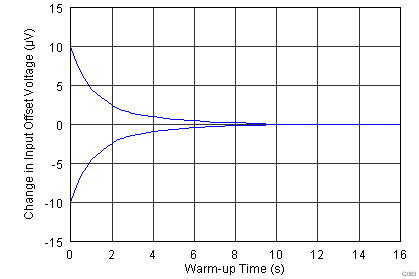
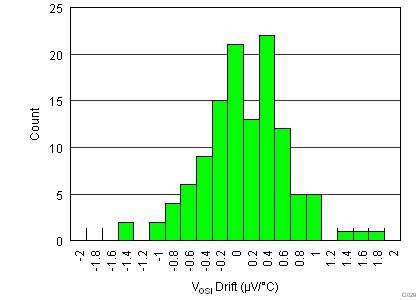
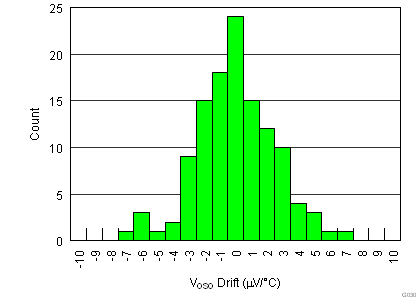
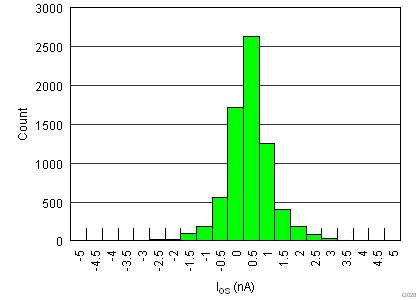
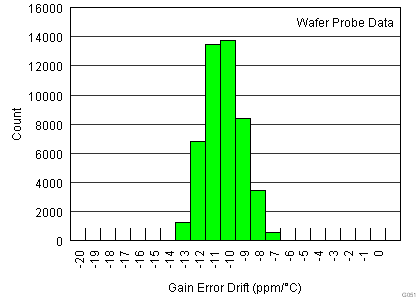
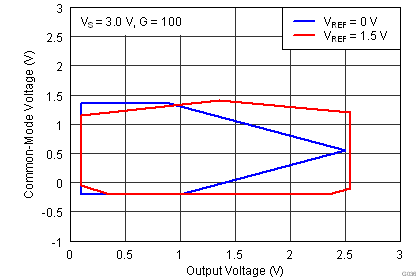
| Single supply |
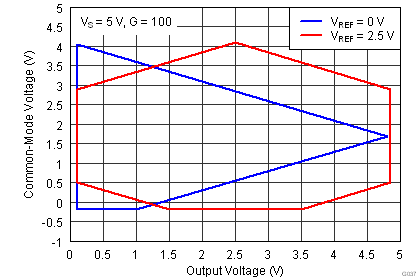
| Single supply |
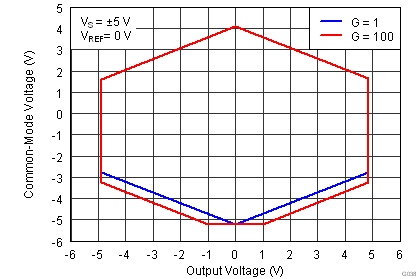
| Dual supply |
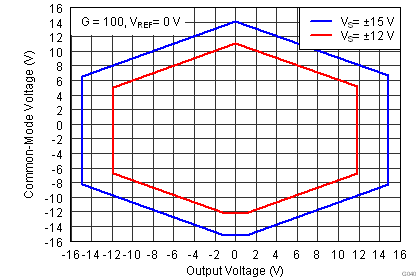
| Dual supply |
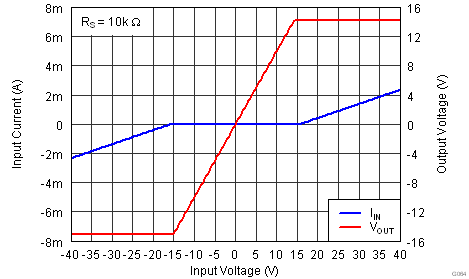
| G = 1, VS = ±15 V |
with 10-kΩ Resistance
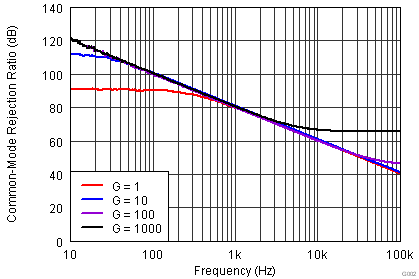
(RTI, 1-kΩ Source Imbalance)
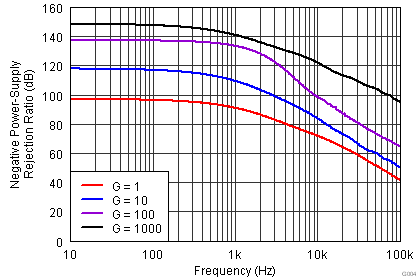
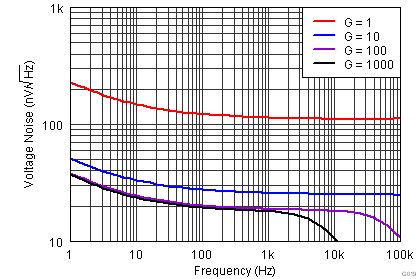
vs Frequency (RTI)

| VS = ±15 V |
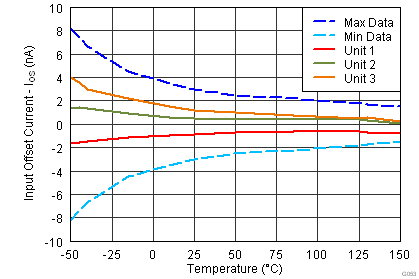
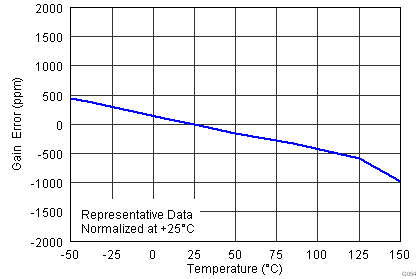
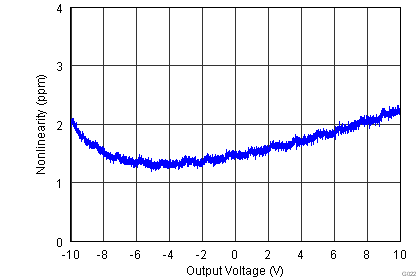
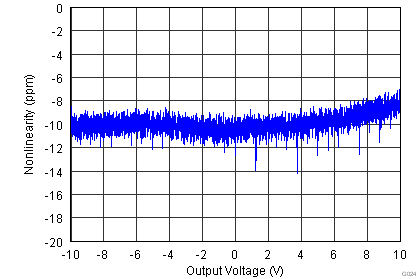
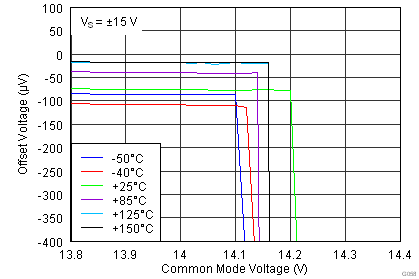
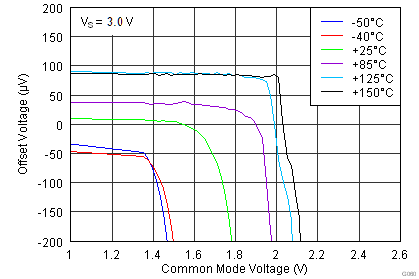
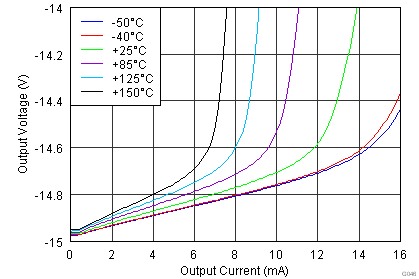
| VS = ±15 V |
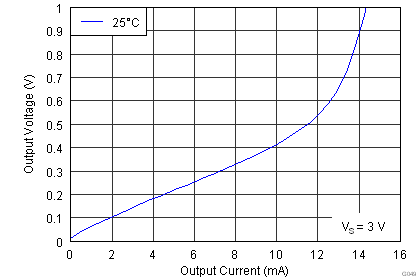
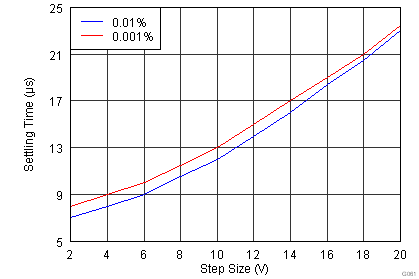
| VS = ±15 V |
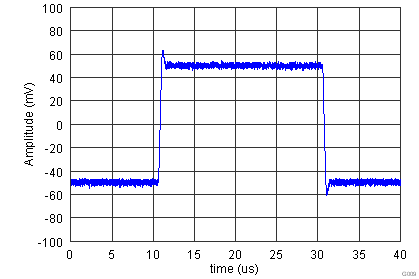
| G = 1, RL = 1 kΩ, CL = 100 pF |
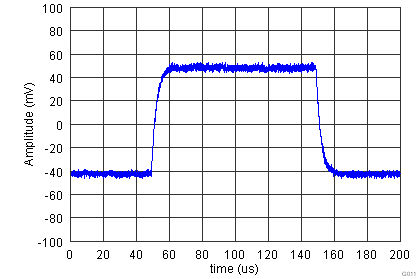
| G = 100, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 100 pF |