ZHCS688I November 2011 – March 2018 TPS65217
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Wake-Up and Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.3.2 Power Good
- 8.3.3 Push-Button Monitor (PB_IN)
- 8.3.4 nWAKEUP Pin (nWAKEUP)
- 8.3.5 Power Enable Pin (PWR_EN)
- 8.3.6 Reset Pin (nRESET)
- 8.3.7 Interrupt Pin (nINT)
- 8.3.8 Analog Multiplexer
- 8.3.9 Battery Charger and Power Path
- 8.3.10 Battery Charging
- 8.3.11 Precharge
- 8.3.12 Charge Termination
- 8.3.13 Battery Detection and Recharge
- 8.3.14 Safety Timer
- 8.3.15 Battery-Pack Temperature Monitoring
- 8.3.16 DC/DC Converters
- 8.3.17 Standby LDO Regulators (LDO1, LDO2)
- 8.3.18 Load Switches or LDO Regulators (LS1 or LDO3, LS2 or LDO4)
- 8.3.19 White LED Driver
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Register Address Map
- 8.6.2 Chip ID Register (CHIPID) (Address = 0x00) [reset = X]
- 8.6.3 Power Path Control Register (PPATH) (Address = 0x01) [reset = 0x3D]
- 8.6.4 Interrupt Register (INT) (Address = 0x02) [reset = 0x80]
- 8.6.5 Charger Configuration Register 0 (CHGCONFIG0) (Address = 0x03) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.6 Charger Configuration Register 1 (CHGCONFIG1) (Address = 0x04) [reset = 0xB1]
- 8.6.7 Charger Configuration Register 2 (CHGCONFIG2) (Address = 0x05) [reset = 0x80]
- 8.6.8 Charger Configuration Register 3 (CHGCONFIG3) (Address = 0x06) [reset = 0xB2]
- 8.6.9 WLED Control Register 1 (WLEDCTRL1) (Address = 0x07) [reset = 0xB1]
- 8.6.10 WLED Control Register 2 (WLEDCTRL2) (Address = 0x08) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.11 MUX Control Register (MUXCTRL) (Address = 0x09) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.12 Status Register (STATUS) (Address = 0x0A) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.13 Password Register (PASSWORD) (Address = 0x0B) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.14 Power Good Register (PGOOD) (Address = 0x0C) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.15 Power-Good Control Register (DEFPG) (Address = 0x0D) [reset = 0x0C]
- 8.6.16 DCDC1 Control Register (DEFDCDC1) (Address = 0x0E) [reset = X]
- 8.6.17 DCDC2 Control Register (DEFDCDC2) (Address = 0x0F) [reset = X]
- 8.6.18 DCDC3 Control Register (DEFDCDC3) (Address = 0x10) [reset = 0x08]
- 8.6.19 Slew-Rate Control Register (DEFSLEW) (Address = 0x11) [reset = 0x06]
- 8.6.20 LDO1 Control Register (DEFLDO1) (Address = 0x12) [reset = 0x09]
- 8.6.21 LDO2 Control Register (DEFLDO2) (Address = 0x13) [reset = 0x38]
- 8.6.22 Load Switch1 or LDO3 Control Register (DEFLS1) (Address = 0x14) [reset = X]
- 8.6.23 Load Switch2 or LDO4 Control Register (DEFLS2) (Address = 0x15) [reset = X]
- 8.6.24 Enable Register (ENABLE) (Address = 0x16) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.6.25 UVLO Control Register (DEFUVLO) (Address = 0x18) [reset = 0x03]
- 8.6.26 Sequencer Register 1 (SEQ1) (Address = 0x19) [reset = X]
- 8.6.27 Sequencer Register 2 (SEQ2) (Address = 0x1A) [reset = X]
- 8.6.28 Sequencer Register 3 (SEQ3) (Address = 0x1B) [reset = X]
- 8.6.29 Sequencer Register 4 (SEQ4) (Address = 0x1C) [reset = 0x40]
- 8.6.30 Sequencer Register 5 (SEQ5) (Address = 0x1D) [reset = X]
- 8.6.31 Sequencer Register 6 (SEQ6) (Address = 0x1E) [reset = 0x00]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.5.1 I2C Bus Operation
The TPS65217x device hosts a slave I2C interface that is compliant with I2C standard 3.0 and supports data rates up to 400 kbit/s and auto-increments addressing.
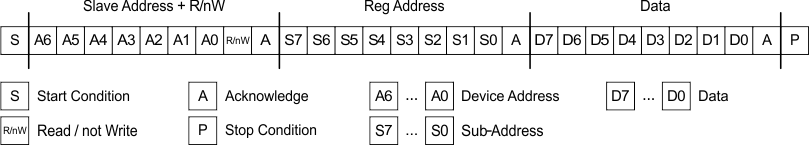 Figure 25. Subaddress in I2C Transmission
Figure 25. Subaddress in I2C Transmission
The I2C bus is a communications link between a controller and a series of slave terminals. The link is established using a two-wire bus consisting of a serial clock signal (SCL) and a serial data signal (SDA). The serial clock is sourced from the controller in all cases, where the serial data line is bidirectional for data communication between the controller and the slave terminals. Each device has an open-drain output to transmit data on the serial data line. An external pullup resistor must be placed on the serial data line to pull the drain output high during data transmission.
Data transmission is initiated with a start bit from the controller as shown in Figure 28. The start condition is recognized when the SDA line goes from high to low during the high portion of the SCL signal. On reception of a start bit, the device receives serial data on the SDA input and checks for valid address and control information. If the appropriate group and address bits are set for the device, then the device issues an acknowledge (ACK) pulse and prepares for the reception of subaddress data. Subaddress data is decoded and responded to according to the Register Maps. Data transmission is completed by either the reception of a stop condition or the reception of the data word sent to the device. A stop condition is recognized as a low-to-high transition of the SDA input during the high portion of the SCL signal. All other transitions of the SDA line must occur during the low portion of the SCL signal. An acknowledge is issued after the reception of a valid address, subaddress, and data words. The I2C interface auto-sequences through the register addresses, so that multiple data words can be sent for a given I2C transmission. For details, see Figure 26, Figure 27, and Figure 28.
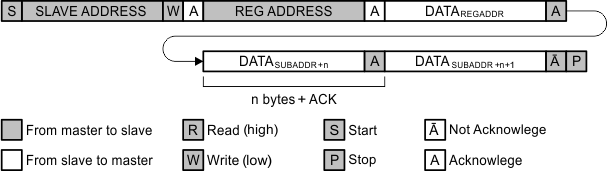 Figure 26. I2C Data Protocol—Master Writes Data To Slave
Figure 26. I2C Data Protocol—Master Writes Data To Slave
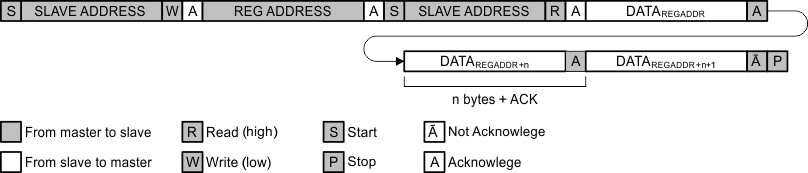 Figure 27. I2C Data Protocol—Master Reads Data from Slave
Figure 27. I2C Data Protocol—Master Reads Data from Slave
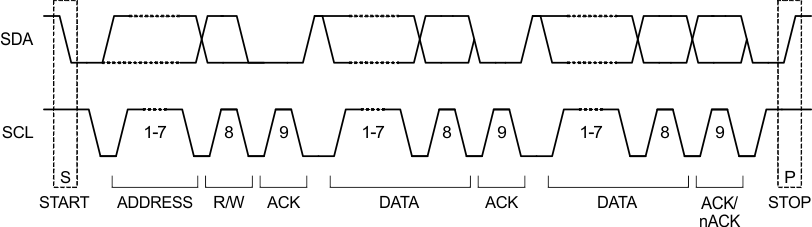 Figure 28. I2C Start-Stop-Acknowledge Protocol
Figure 28. I2C Start-Stop-Acknowledge Protocol