ZHCS901E May 2012 – September 2021 TPS55340
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Boost Converter
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency (R4)
- 8.2.1.2.3 Determining the Duty Cycle
- 8.2.1.2.4 Selecting the Inductor (L1)
- 8.2.1.2.5 Computing the Maximum Output Current
- 8.2.1.2.6 Selecting the Output Capacitors (C8, C9, C10)
- 8.2.1.2.7 Selecting the Input Capacitors (C2, C7)
- 8.2.1.2.8 Setting Output Voltage (R1, R2)
- 8.2.1.2.9 Setting the Soft-start Time (C7)
- 8.2.1.2.10 Selecting the Schottky Diode (D1)
- 8.2.1.2.11 Compensating the Control Loop (R3, C4, C5)
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2
SEPIC Converter
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency (R4)
- 8.2.2.2.2 Duty Cycle
- 8.2.2.2.3 Selecting the Inductor (L1)
- 8.2.2.2.4 Calculating the Maximum Output Current
- 8.2.2.2.5 Selecting the Output Capacitors (C8, C9, C10)
- 8.2.2.2.6 Selecting the Series Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.2.7 Selecting the Input Capacitor (C2, C7)
- 8.2.2.2.8 Selecting the Schottky Diode (D1)
- 8.2.2.2.9 Setting the Output Voltage (R1, R2)
- 8.2.2.2.10 Setting the Soft-start Time (C3)
- 8.2.2.2.11 MOSFET Rating Considerations
- 8.2.2.2.12 Compensating the Control Loop (R3, C4)
- 8.2.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Boost Converter
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Determining the Duty Cycle
The input-to-output voltage conversion ratio of the TPS55340 is limited by the worst case maximum duty cycle of 89% and the minimum duty cycle which is determined by the minimum on-time of 77 ns and the switching frequency. The minimum duty cycle can be estimated with Equation 7. With a 600-kHz switching frequency the minimum duty cycle is 4%.
The duty cycle at which the converter operates is dependent on the mode in which the converter is running. If the converter is running in DCM, where the inductor current ramps to zero at the end of each cycle, the duty cycle varies with changes of the load much more than it does when running in continuous conduction mode (CCM). In CCM, where the inductor maintains a minimum dc current, the duty cycle is related primarily to the input and output voltages as computed below. Assume a 0.5-V drop VD across the Schottky rectifier. At the minimum input of 5 V, the duty cycle will be 80%. At the maximum input of 12 V, the duty cycle is 51%.
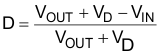
At light loads the converter will operate in DCM. In this case the duty cycle is a function of the load, input and output voltages, inductance, and switching frequency as computed below. This can be calculated only after an inductance is chosen in the following section. While operating in DCM with very light load conditions, the duty cycle demand will force the TPS55340 to operate with the minimum on-time. The converter will then begin pulse skipping which can increase the output ripple.
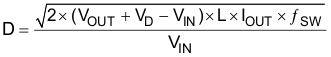
All converters using a diode as the freewheeling or catch component have a load current level at which they transit from DCM to CCM. At this point the inductor current just falls to zero during the off-time of the power switch. At higher load currents, the inductor current does not fall to zero and diode and switch current assume a trapezoidal wave shape as opposed to a triangular wave shape. The load current boundary between discontinuous conduction and continuous conduction can be found for a set of converter parameters as follows:
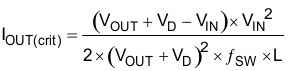
For loads higher than the result of Equation 10, the duty cycle is given by Equation 8. For loads less than the results of Equation 10, the duty cycle is given by Equation 9. For Equation 7 through Equation 10, the variable definitions are as follows:
- VOUT is the output voltage of the converter in V.
- VD is the forward conduction voltage drop across the rectifier or catch diode in V.
- VIN is the input voltage to the converter in V.
- IOUT is the output current of the converter in A.
- L is the inductor value in H.
- ƒSW is the switching frequency in Hz.
Unless otherwise stated, the design equations that follow assume that the converter is running in CCM which typically results in a higher efficiency for the power levels of this converter.