ZHCSCW5B August 2014 – September 2017 LM43600
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 简化电路原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Controlled Step-Down Regulator
- 8.3.2 Light Load Operation
- 8.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Enable (ENABLE)
- 8.3.5 VCC, UVLO and BIAS
- 8.3.6 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking (SS/TRK)
- 8.3.7 Switching Frequency (RT) and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 8.3.8 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 8.3.9 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 8.3.10 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 8.3.11 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 8.3.12 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Applications and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 9.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.4 Input Capacitors
- 9.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.7 Feedforward Capacitor
- 9.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 9.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor
- 9.2.2.10 BIAS Capacitors
- 9.2.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitors
- 9.2.2.12 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 9.2.2.13 PGOOD
- 9.2.3 Application Performance Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.9 Internal Compensation and CFF
The LM43600 is internally compensated with RC = 400 kΩ and CC = 50 pF as shown in Functional Block Diagram. The internal compensation is designed such that the loop response is stable over the entire operating frequency and output voltage range. Depending on the output voltage, the compensation loop phase margin can be low with all ceramic capacitors. An external feed-forward cap CFF is recommended to be placed in parallel with the top resistor divider RFBT for optimum transient performance.
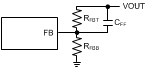 Figure 43. Feed-Forward Capacitor for Loop Compensation
Figure 43. Feed-Forward Capacitor for Loop Compensation
The feed-forward capacitor CFF in parallel with RFBT places an additional zero before the cross over frequency of the control loop to boost phase margin. The zero frequency can be found by
An additional pole is also introduced with CFF at the frequency of
The CFF should be selected such that the bandwidth of the control loop without the CFF is centered between fZ-CFF and fP-CFF. The zero fZ-CFF adds phase boost at the crossover frequency and improves transient response. The pole fP-CFF helps maintaining proper gain margin at frequency beyond the crossover.
Designs with different combinations of output capacitors need different CFF. Different types of capacitors have different Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR). Ceramic capacitors have the smallest ESR and need the most CFF. Electrolytic capacitors have much larger ESR and the ESR zero frequency
would be low enough to boost the phase up around the crossover frequency. Designs using mostly electrolytic capacitors at the output may not need any CFF.
The CFF creates a time constant with RFBT that couples in the attenuated output voltage ripple to the FB node. If the CFF value is too large, it can couple too much ripple to the FB and affect VOUT regulation. It could also couple too much transient voltage deviation and falsely trip PGOOD thresholds. Therefore, CFF should be calculated based on output capacitors used in the system. At cold temperatures, the value of CFF might change based on the tolerance of the chosen component. This may reduce its impedance and ease noise coupling on the FB node. To avoid this, more capacitance can be added to the output or the value of CFF can be reduced. See Detailed Design Procedure for the calculation of CFF.