ZHCSE15F July 2015 – May 2018 SN65DP159 , SN75DP159
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Supply Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Differential Input Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 HDMI and DVI TMDS Output Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 AUX, DDC, and I2C Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 HPD Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 HDMI and DVI Main Link Switching Characteristics
- 7.11 AUX Switching Characteristics (Only for RGZ Package)
- 7.12 HPD Switching Characteristics
- 7.13 DDC and I2C Switching Characteristics
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Reset Implementation
- 9.3.2 Operation Timing
- 9.3.3 I2C-over-AUX to DDC Bridge (SNx5DP159 48-Pin Package Version Only)
- 9.3.4 Input Lane Swap and Polarity Working
- 9.3.5 Main Link Inputs
- 9.3.6 Main Link Inputs Debug Tools
- 9.3.7 Receiver Equalizer
- 9.3.8 Termination Impedance Control
- 9.3.9 TMDS Outputs
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1.2 DDC Pullup Resistors
NOTE
This section is for information only and subject to change depending upon system implementation.
The pullup resistor value is determined by two requirements:
- The maximum sink current of the I2C buffer:
The maximum sink current is 3-mA or slightly higher for an I2C driver supporting standard-mode I2C[4] operation. - The maximum transition time on the bus:
The maximum transition time, T, of an I2C bus is set by an RC time constant, where R is the pullup resistor value, and C is the total load capacitance. The parameter, k, can be calculated from Equation 3 by solving for t, the times at which certain voltage thresholds are reached. Different input threshold combinations introduce different values of t. Table 11 summarizes the possible values of k under different threshold combinations.

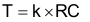
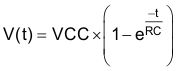
Table 11. Value k Upon Different Input Threshold Voltages
| Vth–\Vth+ | 0.7 VCC | 0.65 VCC | 0.6 VCC | 0.55 VCC | 0.5 VCC | 0.45 VCC | 0.4 VCC | 0.35 VCC | 0.3 VCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 VCC | 1.0986 | 0.9445 | 0.8109 | 0.6931 | 0.5878 | 0.4925 | 0.4055 | 0.3254 | 0.2513 |
| 0.15 VCC | 1.0415 | 0.8873 | 0.7538 | 0.6360 | 0.5306 | 0.4353 | 0.3483 | 0.2683 | 0.1942 |
| 0.2 VCC | 0.9808 | 0.8267 | 0.6931 | 0.5754 | 0.4700 | 0.3747 | 0.2877 | 0.2076 | 0.1335 |
| 0.25 VCC | 0.9163 | 0.7621 | 0.6286 | 0.5108 | 0.4055 | 0.3102 | 0.2231 | 0.1431 | 0.0690 |
| 0.3 VCC | 0.8473 | 0.6931 | 0.5596 | 0.4418 | 0.3365 | 0.2412 | 0.1542 | 0.0741 |
From Equation 1, Rup(min) = 5.5-V / 3-mA = 1.83-kΩ to operate the bus under a 5-V pullup voltage and provide less than 3-mA when the I2C device is driving the bus to a low state. If a higher sink current, for example 4 mA, is allowed, Rup(min) can be as low as 1.375-kΩ.
If DDC is working at a standard mode of 100-Kbps, the maximum transition time, T, is fixed, 1 μs, and using the k values from Table 11, the recommended maximum total resistance of the pullup resistors on an I2C bus can be calculated for different system setups. If DDC is working in a fast mode of 400-kbps, the transition time should be set at 300 ns, according to I2C[4] specification.
To support the maximum load capacitance specified in the HDMI specification, Ccable(max) = 700-pF, Csource = 50-pF, Ci = 50-pF, and R(max) can be calculated as shown in Table 12.
Table 12. Pullup Resistor Upon Different Threshold Voltages and 800-pF Loads
| Vth–\Vth+ | 0.7 VCC | 0.65 VCC | 0.6 VCC | 0.55 VCC | 0.5 VCC | 0.45 VCC | 0.4 VCC | 0.35 VCC | 0.3 VCC | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 VCC | 1.14 | 1.32 | 1.54 | 1.8 | 2.13 | 2.54 | 3.08 | 3.84 | 4.97 | kΩ |
| 0.15 VCC | 1.2 | 1.41 | 1.66 | 1.97 | 2.36 | 2.87 | 3.59 | 4.66 | 6.44 | kΩ |
| 0.2 VCC | 1.27 | 1.51 | 1.8 | 2.17 | 2.66 | 3.34 | 4.35 | 6.02 | 9.36 | kΩ |
| 0.25 VCC | 1.36 | 1.64 | 1.99 | 2.45 | 3.08 | 4.03 | 5.6 | 8.74 | 18.12 | kΩ |
| 0.3 VCC | 1.48 | 1.8 | 2.23 | 2.83 | 3.72 | 5.18 | 8.11 | 16.87 | — | kΩ |
To accommodate the 3-mA drive current specification, a narrower threshold voltage range is required to support a maximum 800-pF load capacitance for a standard-mode I2C bus.