ZHCSEX7C November 2015 – February 2016 TPS22925
PRODUCTION DATA.
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
For best performance, all traces should be as short as possible. To be most effective, the input and load capacitors should be placed close to the device to minimize the effects that parasitic trace inductances may have on operation. Using wide traces for VIN, VOUT, and GND helps minimize the parasitic electrical effects.
11.2 Layout Example
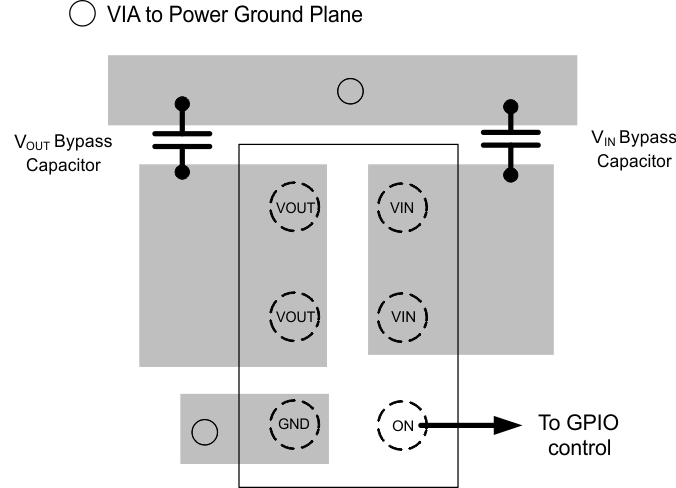 Figure 35. TPS22925xx Layout Example
Figure 35. TPS22925xx Layout Example