ZHCSGJ8B April 2017 – October 2017 LM36010
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.2.1 Thermal Performance
Output power is limited by three things: the peak current limit, the ambient temperature, and the maximum power dissipation in the package. If the die temperature of the device is below the absolute maximum rating of 125°C, the maximum output power can be over 6 W. However, any appreciable output current causes the internal power dissipation to increase and therefore increase the die temperature. Any circuit configuration must ensure that the die temperature remains below 125°C taking into account the ambient temperature derating. The thermal scale-back protection (TSB) helps ensure that temperature requirement is held valid. If the TSB feature is disabled, thermal shutdown (TSD) is the next level of protection for the device, which is set to 150°C. This mechanism cannot be disabled, and operation of the device above 125°C is not ensured by the electrical specification.
In boost mode, where VIN < VLED + VHR, the power dissipation can be approximated by Equation 1:
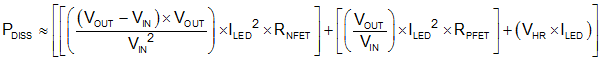
When the device is in pass mode, where VIN > VLED + VHR, the power dissipation equals:
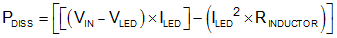
Use Equation 3 to calculate the junction temperature (TJ) of the device:
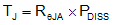
Note that these equations only provide approximation of the junction temperature and do not take into account thermal time constants, which play a large role in determining maximum deliverable output power and flash durations.