ZHCSH09 October 2017 MSP432E401Y
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Characteristics
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Recommended DC Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Recommended GPIO Operating Characteristics
- 5.6 Recommended Fast GPIO Pad Operating Conditions
- 5.7 Recommended Slow GPIO Pad Operating Conditions
- 5.8 GPIO Current Restrictions
- 5.9 I/O Reliability
- 5.10 Current Consumption
- 5.11 Peripheral Current Consumption
- 5.12 LDO Regulator Characteristics
- 5.13 Power Dissipation
- 5.14 Thermal Resistance Characteristics, 128-Pin PDT (TQFP) Package
- 5.15
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.15.1 Load Conditions
- 5.15.2 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.15.3 Reset Timing
- 5.15.4
Clock Specifications
- 5.15.4.1 PLL Specifications
- 5.15.4.2 PIOSC Specifications
- 5.15.4.3 Low-Frequency Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.4 Hibernation Low-Frequency Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.5 Main Oscillator Specifications
- 5.15.4.6 Main Oscillator Specification WIth ADC
- 5.15.4.7 System Clock Characteristics With USB Operation
- 5.15.5 Sleep Modes
- 5.15.6 Hibernation Module
- 5.15.7 Flash Memory
- 5.15.8 EEPROM
- 5.15.9 Input/Output Pin Characteristics
- 5.15.10 External Peripheral Interface (EPI)
- 5.15.11 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 5.15.12 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
- 5.15.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 5.15.14 Ethernet Controller
- 5.15.15 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 5.15.16 Analog Comparator
- 5.15.17 Pulse-Width Modulator (PWM)
- 5.15.18 Emulation and Debug
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Arm Cortex-M4F Processor Core
- 6.4 On-Chip Memory
- 6.5
Peripherals
- 6.5.1 External Peripheral Interface (EPI)
- 6.5.2 Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 6.5.3 Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Accelerator
- 6.5.4 Data Encryption Standard (DES) Accelerator
- 6.5.5 Secure Hash Algorithm/Message Digest Algorithm (SHA/MD5) Accelerator
- 6.5.6 Serial Communications Peripherals
- 6.5.7 System Integration
- 6.5.8 Advanced Motion Control
- 6.5.9 Analog
- 6.5.10 JTAG and Arm Serial Wire Debug
- 6.5.11 Peripheral Memory Map
- 6.6 Identification
- 6.7 Boot Modes
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
5.15.2.1.1 VDDA Levels
The VDDA supply has three monitors:
- Power-on reset (POR)
- Power-OK (POK)
- Brownout reset (BOR)
The POR monitor is used to keep the analog circuitry in reset until the VDDA supply reaches the correct range for the analog circuitry to begin operating. The POK monitor is used to keep the digital circuitry in reset until the VDDA power supply is at an acceptable operational level. The digital reset is only released when the Power-On Reset has deasserted and the Power-OK monitor for each supply indicates that power levels are in operational ranges. The BOR monitor is used to generate a reset to the device or assert an interrupt if the VDDA supply drops below its operational range.
NOTE
VDDA BOR and VDD BOR events are a combined BOR to the system logic, such that if either BOR event occurs, the following bits are affected:
- The BORRIS bit in the Raw Interrupt Status (RIS) register, System Control offset 0x050
- The BORMIS bit in the Masked Interrupt Status and Clear (MISC) register, System Control offset 0x058. This bit is set only if the BORIM bit in the Interrupt Mask Control (IMC) register has been set.
- The BOR bit in the Reset Cause (RESC) register, System Control offset 0x05C. This bit is set only if either of the BOR events have been configured to initiate a reset.
In addition, the following bits control both BOR events:
- The BORIM bit in the Interrupt Mask Control (IMC) register, System Control offset 0x054
- The VDDA_UBOR0 and VDD_UBOR0 bits in the Power-Temperature Cause (PWRTC) register
See the System Control chapter of the MSP432E4 SimpleLink™ Microcontrollers Technical Reference Manual for more information on how to configure these registers.
Figure 5-2 shows the relationship between VDDA, POK, POR, and a BOR event.
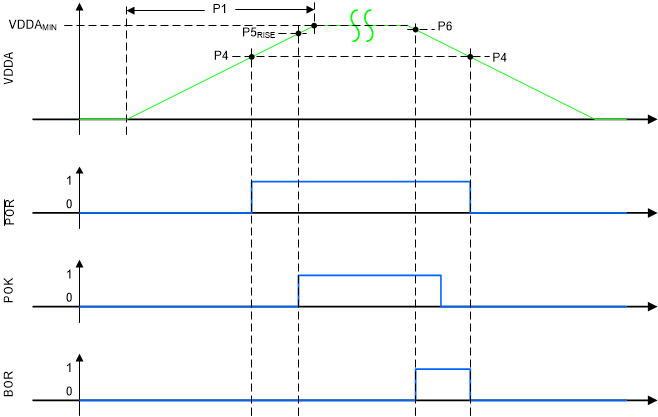 Figure 5-2 Power and Brownout Assertions vs VDDA Levels
Figure 5-2 Power and Brownout Assertions vs VDDA Levels