ZHCSH32 November 2017 TLA2021 , TLA2022 , TLA2024
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1.6 I2C Communication Sequence Example
This section provides an example of an I2C communication sequence between a microcontroller (the master) and a TLA2024 (the slave) configured with a slave address of 1001 000 to start a single-shot conversion and subsequently read the conversion result.
- Write the configuration register as shown in Figure 21 to configure the device (for example, write MUX[2:0] = 000, PGA[2:0] = 010, MODE = 1, and DR[2:0] = 110) and start a single-shot conversion (OS = 1):
- Wait at least t = 1 / DR ± 10% for the conversion to complete.
- Then, as shown in Figure 23, read the conversion data register:
- Start a new single-shot conversion by writing a 1 to the OS bit in the configuration register.
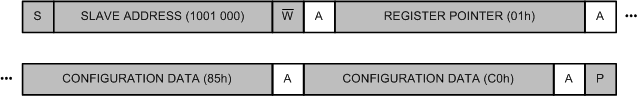 Figure 21. Write the Configuration Register
Figure 21. Write the Configuration Register
Alternatively, poll the OS bit for a 1 as shown in Figure 22 to determine when the conversion result is ready for retrieval. This option does not work in continuous-conversion mode because the OS bit always reads 0.
 Figure 22. Read the Configuration Register to Check for OS = 1
Figure 22. Read the Configuration Register to Check for OS = 1
 Figure 23. Read the Conversion Data Register
Figure 23. Read the Conversion Data Register
To save time, a new conversion can also be started (step 4) before reading the conversion result (step 3). Figure 24 lists a legend for Figure 21 to Figure 23.
 Figure 24. Legend for the I2C Sequence Diagrams
Figure 24. Legend for the I2C Sequence Diagrams