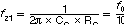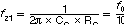ZHCSHF4J May 2004 – January 2018 TPS51116
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VDDQ SMPS, Light Load Condition
- 7.3.2 Low-Side Driver
- 7.3.3 High-Side Driver
- 7.3.4 Current Sensing Scheme
- 7.3.5 PWM Frequency and Adaptive On-Time Control
- 7.3.6 VDDQ Output Voltage Selection
- 7.3.7 VTT Linear Regulator and VTTREF
- 7.3.8 Controling Outputs Using the S3 and S5 Pins
- 7.3.9 Soft-Start Function and Powergood Status
- 7.3.10 VDDQ and VTT Discharge Control
- 7.3.11 Current Protection for VDDQ
- 7.3.12 Current Protection for VTT
- 7.3.13 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection for VDDQ
- 7.3.14 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Protection, V5IN (PWP), V5FILT (RGE)
- 7.3.15 Input Capacitor, V5IN (PWP), V5FILT (RGE)
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.2.7 Calculate CC.
The purpose of CC is to cut DC component to obtain high DC feedback gain. However, as it causes phase delay, another zero to cancel this effect at f0 frequency is need. This zero, ωz1, is determined by CC and RC. Recommended ωz1 is 10 times lower to the f0 frequency.
Equation 24.