ZHCSHL4I October 2008 – December 2017 TPS23754 , TPS23754-1 , TPS23756
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
PoE Overview
- 7.4.1.1 Threshold Voltages
- 7.4.1.2 PoE Start-Up Sequence
- 7.4.1.3 Detection
- 7.4.1.4 Hardware Classification
- 7.4.1.5 Inrush and Start-Up
- 7.4.1.6 Maintain Power Signature
- 7.4.1.7 Start-Up and Converter Operation
- 7.4.1.8 PD Hotswap Operation
- 7.4.1.9 Converter Controller Features
- 7.4.1.10 Bootstrap Topology
- 7.4.1.11 Current Slope Compensation and Current Limit
- 7.4.1.12 Blanking – RBLNK
- 7.4.1.13 Dead Time
- 7.4.1.14 FRS and Synchronization
- 7.4.1.15 T2P, Start-Up, and Power Management
- 7.4.1.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.1.17 Adapter ORing
- 7.4.1.18 PPD ORing Features
- 7.4.1.19 Using DEN to Disable PoE
- 7.4.1.20 ORing Challenges
- 7.4.1
PoE Overview
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Bridges and Schottky Diodes
- 8.2.2.2 Protection, D1
- 8.2.2.3 Capacitor, C1
- 8.2.2.4 Detection Resistor, RDEN
- 8.2.2.5 Classification Resistor, RCLS
- 8.2.2.6 Dead Time Resistor, RDT
- 8.2.2.7 Switching Transformer Considerations and RVC
- 8.2.2.8 Special Switching MOSFET Considerations
- 8.2.2.9 Thermal Considerations and OTSD
- 8.2.2.10 APD Pin Divider Network, RAPD1, RAPD2
- 8.2.2.11 PPD Pin Divider Network, RPPD1, RPPD2
- 8.2.2.12 Setting Frequency (RFRS) and Synchronization
- 8.2.2.13 Current Slope Compensation
- 8.2.2.14 Blanking Period, RBLNK
- 8.2.2.15 Estimating Bias Supply Requirements and CVC
- 8.2.2.16 T2P Pin Interface
- 8.2.2.17 Advanced ORing Techniques
- 8.2.2.18 Soft Start
- 8.2.2.19 Frequency Dithering for Conducted Emissions Control
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.4.1.4 Hardware Classification
Hardware classification allows a PSE to determine a PD’s power requirements before powering, and helps with power management once power is applied. Type 2 hardware classification permits high power PSEs and PDs to determine whether the connected device can support high-power operation. A type 2 PD presents class 4 in hardware to indicate it is a high-power device. A type 1 PSE will treat a class 4 device like a class 0 device, allotting 13 W if it chooses to power the PD. A PD that receives a 2 event class understands that it is powered from a high-power PSE and it may draw up to 25.5 W immediately after the 80-ms start-up period completes. A type 2 PD that does not receive a 2-event hardware classification may choose to not start, or must start in a 13 W condition and request more power through the DLL after start-up. The standard requires a type 2 PD to indicate that it is underpowered if this occurs. Start-up of a high-power PD under 13 W implicitly requires some form of powering down sections of the application circuits.
The maximum power entries in Table 1 determine the class the PD must advertise. The PSE may disconnect a PD if it draws more than its stated class power, which may be the hardware class or a lower DLL-derived power level. The standard permits the PD to draw limited current peaks that increase the instantaneous power above the Table 1 limit; however, the average power requirement always applies.
The TPS23754 implements two-event classification. Selecting an RCLS of 63.4 Ω provides a valid type 2 signature. TPS23754 may be used as a compatible type 1 device simply by programming class 0–3 per Table 1. DLL communication is implemented by the ethernet communication system in the PD and is not implemented by the TPS23754.
The TPS23754 disables classification above VCU_OFF to avoid excessive power dissipation. CLS voltage is turned off during PD thermal limit or when APD or DEN are active. The CLS output is inherently current limited, but should not be shorted to VSS for long periods of time.
Figure 23 shows how classification works for the TPS23754. Transition from state-to-state occurs when comparator thresholds are crossed (see Figure 20 and Figure 21). These comparators have hysteresis, which adds inherent memory to the machine. Operation begins at idle (unpowered by PSE) and proceeds with increasing voltage from left to right. A 2-event classification follows the (heavy-lined) path towards the bottom, ending up with a latched type 2 decode along the lower branch that is highlighted. This state results in a low T2P during normal operation. Once the valid path to type 2 PSE detection is broken, the input voltage must transition below the mark reset threshold to start anew.
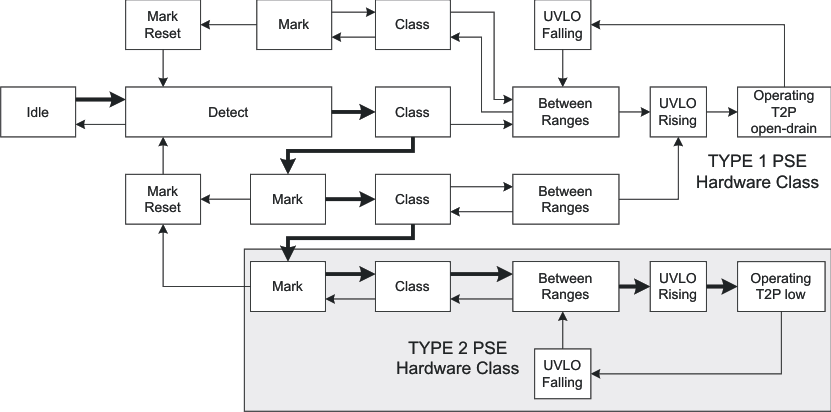 Figure 23. Two-Event Class Internal States
Figure 23. Two-Event Class Internal States