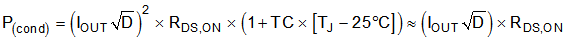ZHCSI13J October 2004 – November 2018 TPS75003
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Operation (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.2 Enable (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.3 UVLO (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.4 Current Limit (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.5 Short-Circuit Protection (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.6 Soft-Start (Buck Controllers)
- 7.3.7 LDO Operation
- 7.3.8 Internal Current Limit (LDO)
- 7.3.9 Enable Pin (LDO)
- 7.3.10 Dropout Voltage (LDO)
- 7.3.11 Transient Response (LDO)
- 7.3.12 Thermal Protection (LDO)
- 7.3.13 Power Dissipation (LDO)
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Capacitor CIN1, CIN2 Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.2 Inductor Value Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.3 External PMOS Transistor Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.4 Diode Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.6 Output Voltage Ripple Effect on VOUT (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.7 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.8 Output Voltage Setting Selection (Buck Controllers)
- 8.2.2.9 Input Capacitor Selection (LDO)
- 8.2.2.10 Output Capacitor Selection (LDO)
- 8.2.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection (LDO)
- 8.2.2.12 Setting Output Voltage (LDO)
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.2.3 External PMOS Transistor Selection (Buck Controllers)
The external PMOS transistor is selected based on threshold voltage (VT), on-resistance (RDS,ON), gate capacitance (CG) and voltage rating. The PMOS VT magnitude must be much lower than the lowest voltage at IN1 or IN2 that will be used. A VT magnitude that is 0.5V less than the lowest input voltage is normally sufficient. The PMOS gate will see voltages from 0V to the maximum input voltage, so gate-to-source breakdown should be a few volts higher than the maximum input supply. The drain-to-source of the device will also see this full voltage swing, and should therefore be a few volts higher than the maximum input supply. The RMS current in the PMOS can be estimated by using Equation 9:
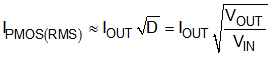
The power dissipated in the PMOS is comprised of both conduction and switching losses. Switching losses are typically insignificant. The conduction losses are a function of the RMS current and the RDS,ON of the PMOS, and are calculated by Equation 10: