ZHCSI26C August 2010 – April 2018 TPS54320
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Current Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.6 Safe Start-up into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.7 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 7.3.10 Slow Start (SS/TR)
- 7.3.11 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 7.3.12 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.13 Sequencing (SS/TR)
- 7.3.14 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Operating Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Slow-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 UVLO Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation Component Selection
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.4.2 Adjustable Switching Frequency (RT Mode)
To determine the RT resistance for a given switching frequency, use Equation 17 or the curve in Figure 32. To reduce the solution size, one would set the switching frequency as high as possible, but consider the tradeoffs of the supply efficiency and minimum controllable on-time.
Equation 17. 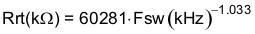
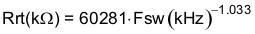
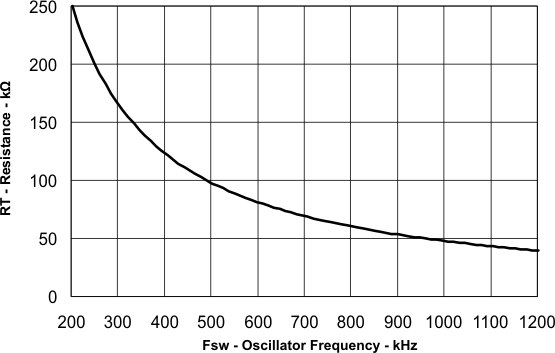 Figure 32. RT Set Resistor vs Switching Frequency
Figure 32. RT Set Resistor vs Switching Frequency