ZHCSIP8B August 2018 – April 2020 AMC1035
PRODUCTION DATA.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
minimum and maximum specifications apply from TA = –40°C to +125°C, VDD = 3.0 V to 5.5 V, AINP = –1 V to 1 V, AINN = GND, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted); typical specifications are at TA = 25°C, CLKIN = 20 MHz, and VDD = 3.3 V| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VCMuv(1) | Negative common-mode undervoltage detection level(2) | (VAINP + VAINN) / 2, VAINP = VAINN | –1.45 | V | ||
| (VAINP + VAINN) / 2, |VAINP – VAINN| = 1.25 V | –0.85 | |||||
| VCMov(1) | Positive common-mode overvoltage detection level(2) | 3.0 V ≤ VDD < 4 V, VAINP = VAINN | VDD – 1.35 | V | ||
| 3.0 V ≤ VDD < 4.5 V, |VAINP – VAINN| = 1.25 V | VDD – 2.35 | |||||
| 4 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V, VAINP = VAINN | 2.75 | |||||
| 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V, |VAINP – VAINN| = 1.25 V | 2.15 | |||||
| RIN | Single-ended input resistance | AINN = GND | 0.1 | 0.4 | GΩ | |
| RIND | Differential input resistance | 0.16 | 1.6 | GΩ | ||
| CIN | Single-ended input capacitance | AINN = GND | 2 | pF | ||
| CIND | Differential input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||
| IIB | Input bias current | AINP = AINN = GND, (IAINP + IAINN) / 2 | –10 | ±3 | 10 | nA |
| TCIIB | Input bias current thermal drift | AINP = AINN = GND, (IAINP + IAINN) / 2 | ±5 | pA/°C | ||
| IIO | Input offset current | IIO = IAINP – IAINN | –5 | ±1 | 5 | nA |
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | AINP = AINN, fIN = 0 Hz, VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max | –104 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN, fIN from 0.1 Hz to 50 kHz,
–0.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 0.5 V |
–88 | |||||
| DC ACCURACY | ||||||
| Resolution(3) | 16 | Bits | ||||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity(4) | Resolution: 16 bits | –12 | ±2 | 12 | LSB |
| EO | Offset error | Initial, at TA = 25°C, AINP = AINN = GND | –0.5 | ±0.03 | 0.5 | mV |
| TCEO | Offset error thermal drift(5) | –6 | ±0.1 | 6 | µV/°C | |
| EG | Gain error | Initial, at TA = 25°C | –0.25% | ±0.02% | 0.25% | |
| Initial, at TA = 25°C, ratiometric mode | –0.3% | ±0.02% | 0.3% | |||
| TCEG | Gain error thermal drift(6) | –45 | ±20 | 45 | ppm/°C | |
| Ratiometric mode | –15 | ±4 | 15 | |||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | AINP = AINN = GND, at dc | –90 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN = GND, 10 kHz, 100-mV ripple | –84 | |||||
| AC ACCURACY | ||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | fIN = 1 kHz | 81 | 87 | dB | |
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise + distortion | fIN = 1 kHz | 77 | 83 | dB | |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | fIN = 1 kHz | –87 | –78 | dB | |
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | fIN = 1 kHz | 78 | 87 | dB | |
| REFERENCE OUTPUT | ||||||
| VREFOUT | Reference output voltage | Initial, at TA = 25°C, no load | 2.495 | 2.5 | 2.505 | V |
| TCVREFOUT | Reference output voltage drift | –50 | ±20 | 50 | ppm/°C | |
| IREFOUT | Reference output current | CLOAD < 1 nF(7) | –5 | 5 | mA | |
| Load regulation | Load to GND or VDD | 0.15 | 0.35 | mV/mA | ||
| ISC | Short-circuit current | REFOUT to GND | 23 | mA | ||
| REFOUT to VDD | –21 | |||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | –200 | ±30 | 200 | µV/V | |
| DIGITAL INPUTS (CMOS Logic With Schmitt-Trigger) | ||||||
| IIN | Input current | GND ≤ VIN ≤ VDD | 35 | μA | ||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 3 | pF | |||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × VDD | VDD + 0.3 | V | ||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | –0.3 | 0.3 × VDD | V | ||
| DIGITAL OUTPUT: CMOS | ||||||
| CLOAD | Output load capacitance | fCLKIN = 21 MHz | 15 | 30 | pF | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –20 µA | VDD – 0.1 | V | ||
| IOH = –4 mA | VDD – 0.4 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 20 µA | 0.1 | V | ||
| IOL = 4 mA | 0.4 | |||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| IVDD | High-side supply current | 3.0 V ≤ VDD ≤ 3.6 V, IREFOUT = 0 mA, MCE = 0, CLOAD = 15 pF | 5.2 | 6.8 | mA | |
| 3.0 V ≤ VDD ≤ 3.6 V, IREFOUT = 0 mA, MCE = 1, CLOAD = 15 pF(8) | 4.6 | 6.1 | ||||
| 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V, IREFOUT = 0 mA, MCE = 0, CLOAD = 15 pF | 6.4 | 8.3 | ||||
| 4.5 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V, IREFOUT = 0 mA, MCE = 1, CLOAD = 15 pF(8) | 5.4 | 7.2 | ||||
(1) See the Analog Input section for more details.
(2) The common-mode overvoltage detection level has a typical hysteresis of 35 mV.
(3) The filter output is truncated to 16 bits. 16 bits of no missing codes is specified by design.
(4) Integral nonlinearity is defined as the maximum deviation from a straight line passing through the end-points of the ideal ADC transfer function expressed as number of LSBs or as a percent of the specified linear full-scale range FSR.
(5) Offset error drift is calculated using the box method, as described by the following equation: 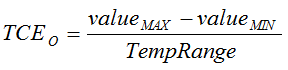 .
.
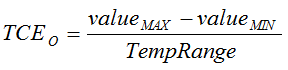 .
. (6) Gain error drift is calculated using the box method, as described by the following equation: 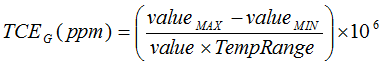 .
.
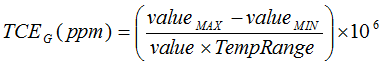 .
.(7) Capacitive load with a value ≥ 1nF requires series resistor to be connected to the REFOUT pin. See the Reference Output section for more details.
(8) Typical value is specified at fCLKIN = 10 MHz, maximum value is specified at fCLKIN = 11 MHz.