ZHCSJB4D April 2019 – January 2024 TAS2563
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.6 I2C Timing Requirements
- 5.7 SPI Timing Requirements
- 5.8 PDM Port Timing Requirements
- 5.9 TDM Port Timing Requirements
- 5.10 Timing Diagrams
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 PurePath Console 3 Software
- 7.3.2 Device Mode and Address Selection
- 7.3.3 General I2C Operation
- 7.3.4 General SPI Operation
- 7.3.5 Single-Byte and Multiple-Byte Transfers
- 7.3.6 Single-Byte Write
- 7.3.7 Multiple-Byte Write and Incremental Multiple-Byte Write
- 7.3.8 Single-Byte Read
- 7.3.9 Multiple-Byte Read
- 7.3.10 Register Organization
- 7.3.11 Operational Modes
- 7.3.12 Faults and Status
- 7.3.13 Digital Input Pull Downs
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Register Maps
- 7.5.1 Register Summary Table Page=0x00
- 7.5.2 PAGE (page=0x00 address=0x00) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.3 SW_RESET (page=0x00 address=0x01) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.4 PWR_CTL (page=0x00 address=0x02) [reset=Eh]
- 7.5.5 PB_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x03) [reset=20h]
- 7.5.6 MISC_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x04) [reset=C6h]
- 7.5.7 MISC_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x05) [reset=22h]
- 7.5.8 TDM_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x06) [reset=9h]
- 7.5.9 TDM_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x07) [reset=2h]
- 7.5.10 TDM_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x08) [reset=4Ah]
- 7.5.11 TDM_CFG3 (page=0x00 address=0x09) [reset=10h]
- 7.5.12 TDM_CFG4 (page=0x00 address=0x0A) [reset=13h]
- 7.5.13 TDM_CFG5 (page=0x00 address=0x0B) [reset=2h]
- 7.5.14 TDM_CFG6 (page=0x00 address=0x0C) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.15 TDM_CFG7 (page=0x00 address=0x0D) [reset=4h]
- 7.5.16 TDM_CFG8 (page=0x00 address=0x0E) [reset=5h]
- 7.5.17 TDM_CFG9 (page=0x00 address=0x0F) [reset=6h]
- 7.5.18 TDM_CFG10 (page=0x00 address=0x10) [reset=7h]
- 7.5.19 DSP Mode & TDM_DET (page=0x00 address=0x11) [reset=7Fh]
- 7.5.20 LIM_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x12) [reset=12h]
- 7.5.21 LIM_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x13) [reset=76h]
- 7.5.22 DSP FREQUENCY & BOP_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x14) [reset=1h]
- 7.5.23 BOP_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x15) [reset=2Eh]
- 7.5.24 BIL_and_ICLA_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x16) [reset=60h]
- 7.5.25 BIL_ICLA_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x17) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.26 GAIN_ICLA_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x18) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.27 ICLA_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x19) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.28 INT_MASK0 (page=0x00 address=0x1A) [reset=FCh]
- 7.5.29 INT_MASK1 (page=0x00 address=0x1B) [reset=A6h]
- 7.5.30 INT_MASK2 (page=0x00 address=0x1C) [reset=DFh]
- 7.5.31 INT_MASK3 (page=0x00 address=0x1D) [reset=FFh]
- 7.5.32 INT_LIVE0 (page=0x00 address=0x1F) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.33 INT_LIVE1 (page=0x00 address=0x20) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.34 INT_LIVE3 (page=0x00 address=0x21) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.35 INT_LIVE4 (page=0x00 address=0x22) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.36 INT_LTCH0 (page=0x00 address=0x24) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.37 INT_LTCH1 (page=0x00 address=0x25) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.38 INT_LTCH3 (page=0x00 address=0x26) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.39 INT_LTCH4 (page=0x00 address=0x27) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.40 VBAT_MSB (page=0x00 address=0x2A) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.41 VBAT_LSB (page=0x00 address=0x2B) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.42 TEMP (page=0x00 address=0x2C) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.43 INT & CLK CFG (page=0x00 address=0x30) [reset=19h]
- 7.5.44 DIN_PD (page=0x00 address=0x31) [reset=40h]
- 7.5.45 MISC (page=0x00 address=0x32) [reset=80h]
- 7.5.46 BOOST_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x33) [reset=34h]
- 7.5.47 BOOST_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x34) [reset=4Bh]
- 7.5.48 BOOST_CFG3 (page=0x00 address=0x35) [reset=74h]
- 7.5.49 MISC (page=0x00 address=0x3B) [reset=58h]
- 7.5.50 TG_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x3F) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.51 BST_ILIM_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x40) [reset=36h]
- 7.5.52 PDM_CONFIG0 (page=0x00 address=0x41) [reset=1h]
- 7.5.53 DIN_PD & PDM_CONFIG3 (page=0x00 address=0x42) [reset=F8h]
- 7.5.54 ASI2_CONFIG0 (page=0x00 address=0x43) [reset=8h]
- 7.5.55 ASI2_CONFIG1 (page=0x00 address=0x44) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.56 ASI2_CONFIG2 (page=0x00 address=0x45) [reset=1h]
- 7.5.57 ASI2_CONFIG3 (page=0x00 address=0x46) [reset=FCh]
- 7.5.58 PVDD_MSB_DSP (page=0x00 address=0x49) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.59 PVDD_LSB_DSP (page=0x00 address=0x4A) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.60 REV_ID (page=0x00 address=0x7D) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.61 I2C_CKSUM (page=0x00 address=0x7E) [reset=0h]
- 7.5.62 BOOK (page=0x00 address=0x7F) [reset=0h]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.5 Boost
The TAS2563 internal processing algorithm automatically enables the boost when needed. A look-ahead algorithm monitors the battery voltage and the digital audio stream. When the speaker output approaches the battery voltage the boost is enabled in-time to supply the required speaker output voltage. When the boost is no longer required it is disabled and bypassed to maximize efficiency. The boost can be configured in one of two modes. The first is low in-rush (Class-G) supporting only boost on-off and has the lowest in-rush current. The second is high-efficiency (Class-H) where the boost voltage level is adjusted to a value just above what is needed. This mode is more efficient but has a higher in-rush current to quickly transition the levels. This can be configured using Table 7-79.
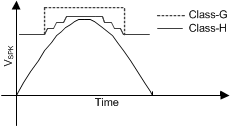 Figure 7-19 Boost Mode Signal Tracking Example
Figure 7-19 Boost Mode Signal Tracking Example| BST_MODE[1:0] | BOOST MODE |
|---|---|
| Class-H - High efficiency (default) |
| Class-G - Low in-rush |
| Always On |
| Always Off - Pass-throught |
The boost can be enabled and disabled using BST_EN register. When driving the Class-D amplifier using an external supply through the PVDD pin, the boost should be disabled and the VBST pin can be left floating. Do not drive an external voltage on the VBST pin. When suppling and external PVDD voltage the VBAT voltage must also be supplied to the device. While VBAT supply must be present it will not carry current to the speaker load.
| BST_EN | BOOST IS |
|---|---|
| Disabled |
| Enabled (default) |
| BST_PFML[1:0] | LOWER LIMIT (Hz) |
|---|---|
| No lower limit |
| 25 kHz |
| 50 kHz (default) |
| 100 kHz |
The boost has a soft-start to limit in-rush current during the initial charge. The current limit and soft-start timer are configurable to adjust to system component selection.
| BST_SSL[1:0] | CURRENT LIMIT (A) |
|---|---|
| Disabled - Boost Normal Limit |
| 1.0 A |
| 1.5 A (default) |
| 2 A |
| BST_GSST[1:0] | TIMEOUT (s) |
|---|---|
| 1 * BST_HSTT |
| 2 * BST_HSTT |
| 4 * BST_HSTT(default) |
| 8 * BST_HSTT |
| BST_HSST[3:0] | TIMEOUT (s) |
|---|---|
| 9 µS |
| 18 µS |
| 36 µS |
| 54 µS |
| 72 µS |
| 90 µS |
| 108 µS |
| 135 µS (default) |
| 162 µS |
| 198 µS |
| 252 µS |
| 342 µS |
| 477 µS |
| 612 µS |
| 792 µS |
| 990 µS |
The boost inductor and decoupling capacitor range needs to be specified using BST_IR and BST_CR registers. These setting optimize the boost to ensure current limit accuracy and avoid clipping in class-H operation.
| BST_IR[1:0] | INDUCTANCE (H) |
|---|---|
| < 0.6 µH |
| 0.6 µH-1.3 µH (default) |
| 1.3 µH - 2.5 µH |
| Reserved |
| BST_LR | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Reserved |
| 3 A/V; load regulation = 1V (default) |
| 2 A/V; load regulation = 1.5 V |
| Reserved |
The maximum boost voltage regulation is set by BST_VREG. When operating in class-G mode the boost when needed will be at this voltage. In class-H mode of operation the boost voltage is automatically selected based on the audio signal but, will not exceed this set value.
The peak current limits the boost current drawn from the VBAT supply. This setting allows flexibility in the inductor selection for various saturation currents. The current limit can be adjust in 45 mA steps with register BST_ILIM[5:0]. The peak current limit setting is the maximum and may be temporarily reduced if the ICLA current limit is active.
| BST_ILIM[5:0] | CURRENT (A) |
|---|---|
| 0.99 A |
| 1.045 A |
| 1.1 A |
| ... |
| 3.96 A (default) |
| 4 A |
| Reserved |
For multiple parts the TAS2563 can shift the boost phase to ensure each device will contribute to the load sharing. The boost syncing among multiple devices is enabled using BST_SYNC and then each part is configured to be on 0 or 180 phase using BST_PA. This avoids peak current align on and clock edges and spreads out battery ripple. The phase of additional devices can be set relative to the master using register BST_PA[1:0]. The phase align is performed over the Inter-chip Communication (ICC) bus and a slot for this feature needs to be configured if enabled.
| BST_SYNC | |
|---|---|
| Not Synced (default) |
| Synced to FSYNC |
| BST_PA[0] | PHASE (Deg) |
|---|---|
| ~0° (default) |
| ~180° |