ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.3.6 Power Good Pin
During turnon, the Power Good pin (PGD) is high until the voltage at VIN increases above ≊ 5 V. PGD then switches low, remaining low as the VIN voltage increases. When the voltage at OUT increases to within 1.25 V of the SENSE pin (VDS <1.25 V), PGD switches high. PGD switches low if the VDS of Q1 increases above 2.5 V. A pullup resistor is required at PGD as shown in Figure 20. The pullup voltage (VPGD) can be as high as 80 V, with transient capability to 100 V, and can be higher or lower than the voltages at VIN and OUT.
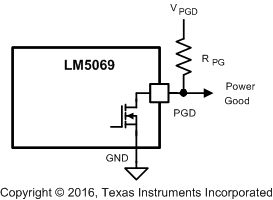 Figure 20. Power Good Output
Figure 20. Power Good Output If a delay is required at PGD, suggested circuits are shown in Figure 21. In Figure 21a, capacitor CPG adds delay to the rising edge, but not to the falling edge. In Figure 21b, the rising edge is delayed by RPG1 + RPG2 and CPG, while the falling edge is delayed a lesser amount by RPG2 and CPG. Adding a diode across RPG2 (Figure 21c) allows for equal delays at the two edges, or a short delay at the rising edge and a long delay at the falling edge.
 Figure 21. Adding Delay to the Power Good Output Pin
Figure 21. Adding Delay to the Power Good Output Pin