ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.5 Check MOSFET SOA
Once the power limit and fault timer are chosen, it’s critical to check that the FET stays within its SOA during all test conditions. During a Hot-Short, the circuit breaker trips and the LM5069 restarts into power limit until the timer runs out. In the worst case, the MOSFET’s VDS equals VIN,MAX, IDS equals PLIM / VIN,MAX and the stress event lasts for tflt. For this design example, the MOSFET has 30 V, 1.25 A across it for 7.06 ms.
Based on the SOA of the CSD19536KTT, it can handle 30 V, 9 A for 10 ms and it can handle 30 V, 20 A for
1 ms. The SOA for 7.06 ms can be extrapolated by approximating SOA versus time as a power function as shown Equation 15 through Equation 18.
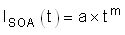
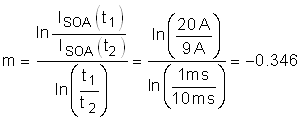
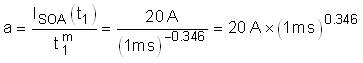
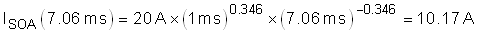
Note that the SOA of a MOSFET is specified at a case temperature of 25°C, while the case temperature can be much hotter during a hot-short. The SOA must be derated based on TC,MAX using Equation 19.
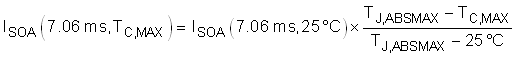
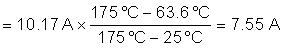
Based on this calculation the MOSFET can handle 7.55 A, 30 V for 7.06 ms at elevated case temperature, and is required to handle 1.25 A during a hot-short. This means the MOSFET is not at risk of getting damaged during a hot-short. In general, TI recommends for the MOSFET to be able to handle a minimum of 1.3× more power than what is required during a hot-short to provide margin to cover the variance of the power limit and fault time.