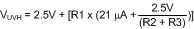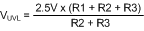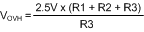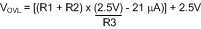ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.6.1 Option A
The configuration shown in Figure 30 requires three resistors (R1-R3) to set the thresholds.
 Figure 30. UVLO and OVLO Thresholds Set By R1-R3
Figure 30. UVLO and OVLO Thresholds Set By R1-R3 The procedure to calculate the resistor values is as follows:
- Choose the upper UVLO threshold (VUVH), and the lower UVLO threshold (VUVL).
- Choose the upper OVLO threshold (VOVH).
- The lower OVLO threshold (VOVL) cannot be chosen in advance in this case, but is determined after the values for R1-R3 are determined. If VOVL must be accurately defined in addition to the other three thresholds, see Option B below.
The resistors are calculated with Equation 21, Equation 22, and Equation 23.
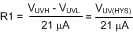
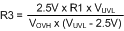
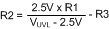
The lower OVLO threshold is calculated from Equation 24.
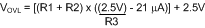
As an example, assume the application requires the following thresholds: VUVH = 36 V, VUVL = 32 V, VOVH = 60 V.
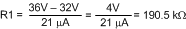
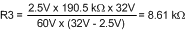

The lower OVLO threshold calculates to 55.8 V, and the OVLO hysteresis is 4.2 V. Note that the OVLO hysteresis is always slightly greater than the UVLO hysteresis in this configuration. When the R1-R3 resistor values are known, the threshold voltages and hysteresis are calculated from Equation 28 through Equation 33.