ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.6.2 Option B
If all four thresholds must be accurately defined, the configuration in Figure 31 can be used.
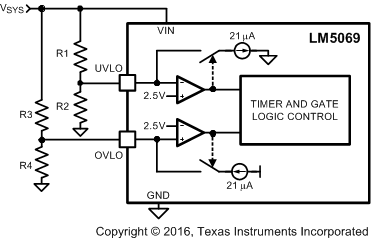 Figure 31. Programming the Four Thresholds
Figure 31. Programming the Four Thresholds The four resistor values are calculated as follows:
- Choose the upper UVLO threshold (VUVH) and lower UVLO threshold (VUVL) with Equation 34 and Equation 35.
- Choose the upper OVLO threshold (VOVH) and lower OVLO threshold (VOVL) with Equation 36 and Equation 37.
Equation 34. 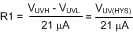
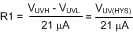
Equation 35. 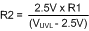
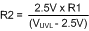
Equation 36. 

Equation 37. 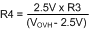
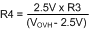
As an example, assume the application requires the following thresholds: VUVH = 22 V, VUVL = 17 V, VOVH = 60 V, and VOVL = 58 V. Therefore VUV(HYS) = 5 V, and VOV(HYS) = 2 V. The resistor values are:
- R1 = 238 kΩ, R2 = 41 kΩ
- R3 = 95.2 kΩ, R4 = 4.14 kΩ
Where the R1-R4 resistor values are known, the threshold voltages and hysteresis are calculated from Equation 38 to Equation 43.
Equation 38. 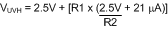
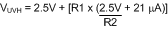
Equation 39. 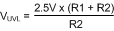
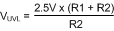
Equation 40. VUV(HYS) = R1 x 21 µA
Equation 41. 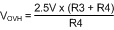
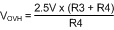
Equation 42. 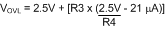
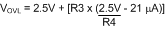
Equation 43. VOV(HYS) = R3 x 21 µA