ZHCSJZ2D August 2019 – April 2021 THS6222
PRODUCTION DATA
7.3.4 Breakdown Supply Voltage
To estimate the margin beyond the maximum supply voltage specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table and exercise the robustness of the device, several typical units were tested beyond the specifications in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table. Figure 7-5 shows the configuration used for the test. The supply voltage, VS, was swept manually and quiescent current was recorded at each 0.5-V supply voltage increment. Figure 7-6 shows the results of the single-supply voltage where the typical units started breaking. Under a similar configuration as the one shown in Figure 7-5, a unit was subjected to VS = 42 V for 168 hours and tested for quiescent current at the beginning and at the end of the test. There was no notable difference in the quiescent current before and after the 168 hours of testing and the device did not show any signs of damage or abnormality.
The primary objective of these tests was to estimate the margins of robustness for typical devices and does not imply performance or maximum limits beyond those specified in the Abolute Maximum Ratings and Recommended Operating Conditions tables.
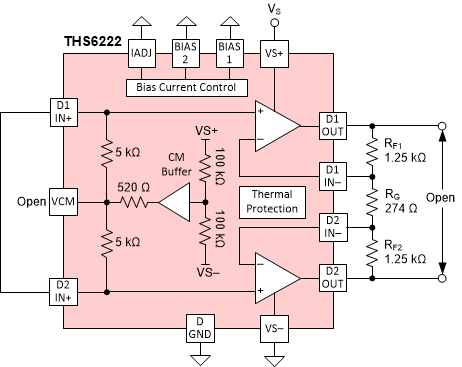 Figure 7-5 Breakdown Supply Voltage Test
Configuration
Figure 7-5 Breakdown Supply Voltage Test
Configuration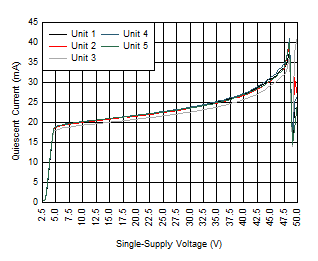 Figure 7-6 Typical Device Breakdown
Supply Voltage (TA = 27°C)
Figure 7-6 Typical Device Breakdown
Supply Voltage (TA = 27°C)