ZHCSJZ2D August 2019 – April 2021 THS6222
PRODUCTION DATA
6.9 Typical Characteristics: VS = 32 V
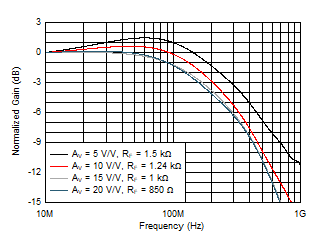
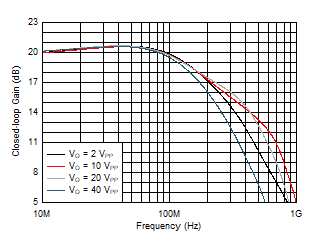
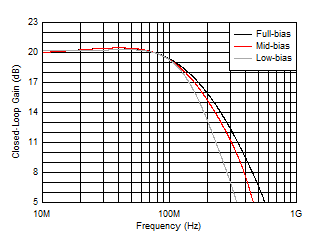
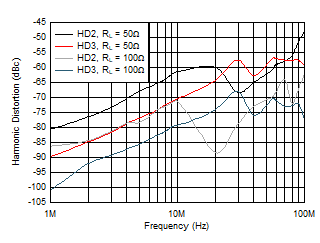
At TA ≈ 25°C, AV = 10 V/V, RF = 1.24 kΩ, RL = 100 Ω, RS = 2.5 Ω, RADJ = 0 Ω, full-bias mode, and VCM = open (unless otherwise noted).
| VO = 2 VPP |
| AV = 10 V/V |
| VO = 40 VPP |
| VO = 2 VPP |
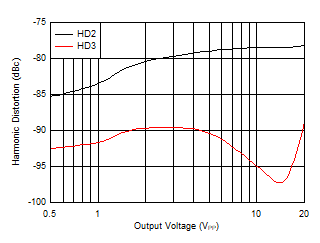
| f = 1 MHz, RL = 50 Ω |
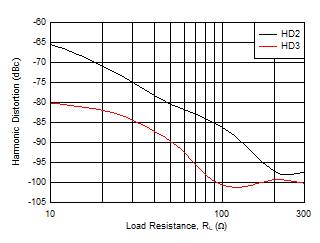
| f = 1 MHz, VO = 2 VPP |
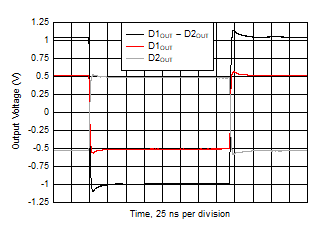
| VO step = 2 VPP |
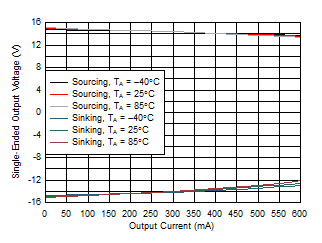
| Average of 30 devices | ||
| Output voltage is slammed and IO is pulsed to maintain TJ as close to TA as possible. |
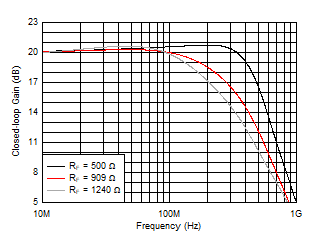
| VO = 2 VPP |
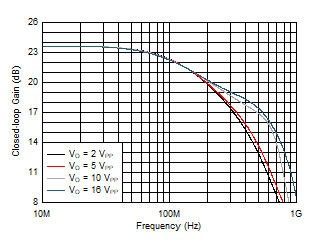
| AV = 15 V/V |
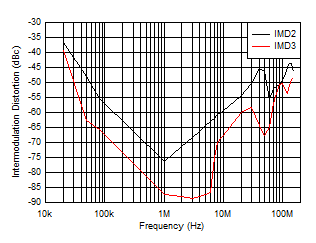
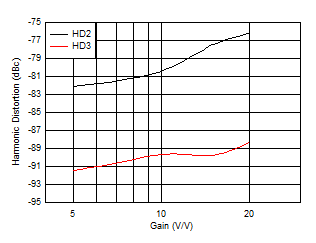
| f = 1 MHz, VO = 2 VPP RL = 50 Ω |
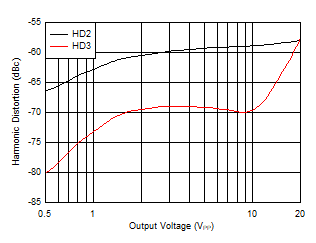
| f = 10 MHz, RL = 50 Ω |
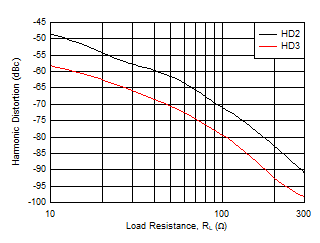
| f = 10 MHz, VO = 2 VPP |
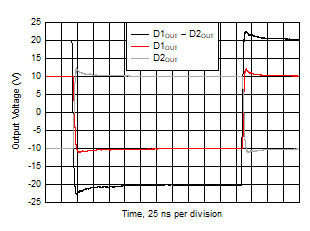
| VO step = 40 VPP |
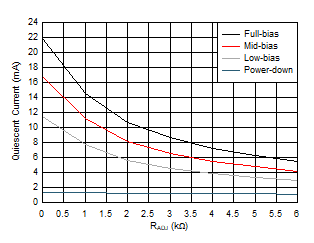
| Average of 30 devices | ||