ZHCSMU0D July 2009 – December 2020 TPS23753A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Product Information
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Threshold Voltages
- 8.4.2 PoE Start-Up Sequence
- 8.4.3 Detection
- 8.4.4 Hardware Classification
- 8.4.5 Maintain Power Signature (MPS)
- 8.4.6 TPS23753A Operation
- 8.4.7 Special Switching MOSFET Considerations
- 8.4.8 Thermal Considerations
- 8.4.9 FRS and Synchronization
- 8.4.10 Blanking – RBLNK
- 8.4.11 Current Slope Compensation
- 8.4.12 Adapter ORing
- 8.4.13 Protection
- 8.4.14 Frequency Dithering for Conducted Emissions Control
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.10 Blanking – RBLNK
The TPS23753A BLNK feature permits programming of the blanking period with specified tolerance. Selection of the blanking period is often empirical because it is affected by parasitics and thermal effects of every device between the gate-driver and output capacitors.
There is a critical range of blanking period that is bounded on the short side by erratic operation, and on the long side by potentially harmful switching-MOSFET and output rectifier currents during a short circuit. The minimum blanking period prevents the current limit and PWM comparators from being falsely triggered by the inherent current spike that occurs when the switching MOSFET turns on. The maximum blanking period is bounded by the ability of the output rectifier to withstand the currents experienced during a converter output short.
The TPS23753A provides a choice between internal fixed and programmable blanking periods. The blanking period is specified as an increase in the minimum GATE on time over the inherent gate driver and comparator delays. The default period (see Electrical Characteristics: Controller Section Only and Electrical Characterisics: PoE and Control) is selected by connecting BLNK to RTN, and the programmable period is set with a resistor from BLNK to RTN using Equation 6.
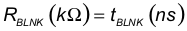
For example, a 100-ns period is programmed by a 100-kΩ resistor. For a brand-new design, TI recommends designing an initial blanking period of 125 ns. This period must be turned when the converter is operational.