ZHCSMZ3A December 2020 – June 2021 PCM1820 , PCM1821
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Hardware Control
- 8.3.2 Audio Serial Interfaces
- 8.3.3 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 8.3.4 Input Channel Configurations
- 8.3.5 Reference Voltage
- 8.3.6
Signal-Chain Processing
- 8.3.6.1 Digital High-Pass Filter
- 8.3.6.2
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 8.3.6.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 8.3.6.2.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 8.3.6.2.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 8.3.6.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 8.3.7 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.6 Signal-Chain Processing
The PCM182x signal chain is comprised of very-low-noise, high-performance, and low-power analog blocks and highly flexible and programmable digital processing blocks. The high performance and flexibility combined with a compact package makes the PCM182x optimized for a variety of end-equipments and applications that require multichannel audio capture. Figure 8-5 shows a conceptual block diagram for the PCM1820 that highlights the various building blocks used in the signal chain, and how the blocks interact in the signal chain. The PCM1821 does not support DRE.
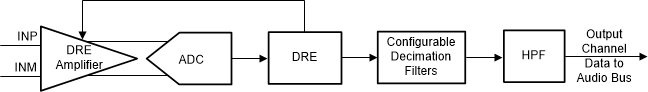 Figure 8-5 Signal-Chain Processing Flowchart
Figure 8-5 Signal-Chain Processing FlowchartThe front-end dynamic range enhancer (DRE) gain amplifier in the PCM1820 is very low noise, with a 123-dB dynamic range performance. Along with a low-noise and low-distortion, multibit, delta-sigma ADC, the front-end DRE gain amplifier enables the PCM1820 to record a far-field audio signal with very high fidelity, both in quiet and loud environments. Moreover, the ADC architecture has inherent antialias filtering with a high rejection of out-of-band frequency noise around multiple modulator frequency components. Therefore, the device prevents noise from aliasing into the audio band during ADC sampling. Further on in the signal chain, an integrated, high-performance multistage digital decimation filter sharply cuts off any out-of-band frequency noise with high stop-band attenuation.
The device supports an input signal bandwidth up to 80 kHz, which allows the high-frequency non-audio signal to be recorded by using a 176.4-kHz (or higher) sample rate.