OPAx317-Q1 零漂移、低偏移、轨到轨 I/O 运算放大器
1 特性
- 适用于汽车电子 应用
- 具有符合 AEC-Q100 标准的下列结果:
- 器件温度 1 级:-40℃ 至 +125℃ 的环境运行温度范围
- 器件人体放电模型 (HBM) 静电放电 (ESD) 分类等级 3A
- 器件带电器件模型 (CDM) ESD 分类等级 C6
- 电源电压:1.8V 至 5.5V
- 微型封装:
- 单通道:SOT23-5
- 双通道:VSSOP-8
- 四通道:TSSOP-14
- 低偏移电压:20μV(典型值)
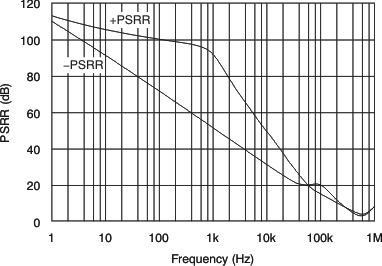
- 共模抑制比 (CMRR):108dB(典型值)电源抑制比 (PSRR)
- 静态电流:35μA(最大值)
- 增益带宽:300kHz
- 轨到轨输入和输出
- 内部电磁干扰 (EMI) 和内部射频干扰 (RFI) 滤波功能
2 应用
- 混合动力汽车-电动汽车 (HEV-EV) 动力传动
- 高级驾驶员辅助系统 (ADAS)
- 自动恒温控制
- 低噪声、低功耗电路
- 航空电子设备、起落装置
- 医疗器械
- 电流感测
3 说明
OPA317-Q1 系列 CMOS 运算放大器不但具备精密的性能,而且价格极具竞争力。这些器件属于采用专有自动校准技术的零漂移系列放大器,在整个时间和温度范围内的偏移电压非常低(最大 90μV)且几乎零漂移,并且静态电流只有 35μA(最大值)。
OPA317-Q1 系列放大器 具有 轨到轨输入和输出以及几乎不变的 1/f 噪声特性,因此是许多应用 应用的理想选择,更容易设计到系统中。此类器件经过优化,适合在 1.8V (±0.9V) 至 5.5V (±2.75V) 的低电压状态下工作。
OPA317-Q1(单通道版本)提供 SOT23-5 三种封装。OPA2317-Q1(双通道版本)提供 VSSOP-8 两种封装。OPA4317-Q1 提供 TSSOP-14 两种封装。所有器件版本的额定工作温度范围均为 -40°C 至 +125°C。
器件信息(1)
| 米6体育平台手机版_好二三四型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| OPA317-Q1 | SOT-23 (5) | 1.60mm x 2.90mm |
| OPA2317-Q1 | VSSOP (8) | 3.00mm × 3.00mm |
| OPA4317-Q1 | TSSOP (14) | 4.40mm × 5.00mm |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购米6体育平台手机版_好二三四附录。
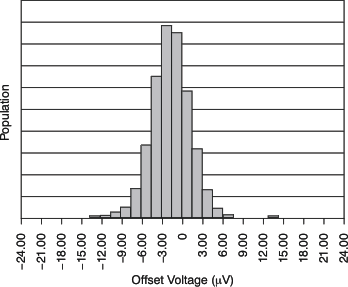
偏移电压分布
4 修订历史记录
| 日期 | 修订版本 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 年 2016 | * | 最初发布。 |
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
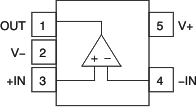
Pin Functions: OPA317-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| SOT-23 | |||
| +IN | 3 | I | Noninverting input |
| –IN | 4 | I | Inverting input |
| OUT | 1 | O | Output |
| V+ | 5 | — | Positive (highest) power supply |
| V– | 2 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
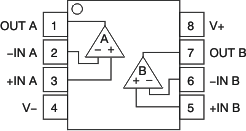
Pin Functions: OPA2317-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| VSSOP | |||
| +IN A | 3 | I | Noninverting input, channel A |
| –IN A | 2 | I | Inverting input, channel A |
| +IN B | 5 | I | Noninverting input, channel B |
| –IN B | 6 | I | Inverting input, channel B |
| OUT A | 1 | O | Output, channel A |
| OUT B | 7 | O | Output, channel B |
| V+ | 8 | — | Positive (highest) power supply |
| V– | 4 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
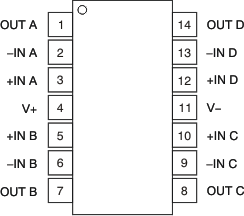
Pin Functions: OPA4317-Q1
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| TSSOP | |||
| +IN A | 3 | I | Noninverting input, channel A |
| –IN A | 2 | I | Inverting input, channel A |
| +IN B | 5 | I | Noninverting input, channel B |
| –IN B | 6 | I | Inverting input, channel B |
| +IN C | 10 | I | Noninverting input, channel C |
| –IN C | 9 | I | Inverting input, channel C |
| +IN D | 12 | I | Noninverting input, channel D |
| –IN D | 13 | I | Inverting input, channel D |
| OUT A | 1 | O | Output, channel A |
| OUT B | 7 | O | Output, channel B |
| OUT C | 8 | O | Output, channel C |
| OUT D | 14 | O | Output, channel D |
| V+ | 4 | — | Positive (highest) power supply |
| V– | 11 | — | Negative (lowest) power supply |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range, unless otherwise noted.(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS = (V+) – (V–) | Supply voltage | 7 | V | |
| Signal input terminals (2) | (V–) – 0.3 | (V+) + 0.3 | V | |
| Signal input terminals(2) | –10 | 10 | mA | |
| Output short circuit(3) | Continuous | |||
| TA | Operating temperature | –40 | 150 | °C |
| TJ | Junction temperature | 150 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±4000 | V | |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±1000 | |||
| Corner pins | ±1000 | ||||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted).| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (V+ – V–) | Supply voltage | 1.8 (±0.9) | 5.5 (±2.25) | V |
| TA | Specified temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information: OPA317-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | OPA317-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) | |||
| 5 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 220.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 97.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 61.7 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 7.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 61.1 | °C/W |
6.5 Thermal Information: OPA2317-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | OPA2317-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DGK (VSSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 180.3 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 48.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 100.9 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 2.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 99.3 | °C/W |
6.6 Thermal Information: OPA4317-Q1
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | OPA4317-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PW (TSSOP) | |||
| 14 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 120.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 34.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 62.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 56.5 | °C/W |
6.7 Electrical Characteristics: VS = 1.8 V to 5.5 V
At TA = 25°C, RL = 10 kΩ connected to midsupply, VCM = VOUT = midsupply, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFFSET VOLTAGE | ||||||
| VOS | Input offset voltage | VS = 5 V | 20 | ±90 | μV | |
| TA = –40°C to +125°C, VS = 5 V | ±100 | |||||
| dVOS/dT | Input offset voltage vs temperature |
TA = –40°C to +125°C | 0.05 | μV/°C | ||
| PSRR | Input offset voltage vs power supply |
TA = –40°C to +125°C, VS = 1.8 V to 5.5 V | 1 | 10 | μV/V | |
| Long-term stability(1) | See (1) | |||||
| Channel separation, DC | 5 | μV/V | ||||
| INPUT BIAS CURRENT | ||||||
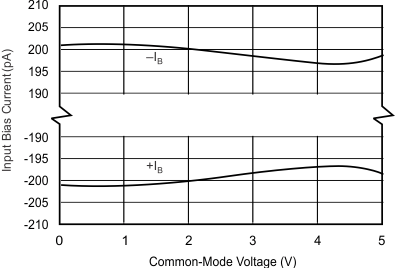
| IB | Input bias current | ±275 | pA | |||
| OPA4317-Q1 | ±155 | |||||
| TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±300 | |||||
| IOS | Input offset current | ±400 | pA | |||
| OPA4317-Q1 | ±140 | |||||
| NOISE | ||||||
| en | Input voltage noise density | f = 1 kHz | 55 | nV/√Hz | ||
| Input voltage noise | f = 0.01 Hz to 1 Hz | 0.3 | μVPP | |||
| f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 1.1 | |||||
| in | Input current noise | f = 10 Hz | 100 | fA/√Hz | ||
| INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE | ||||||
| VCM | Common-mode voltage | (V–) – 0.1 | (V+) + 0.1 | V | ||
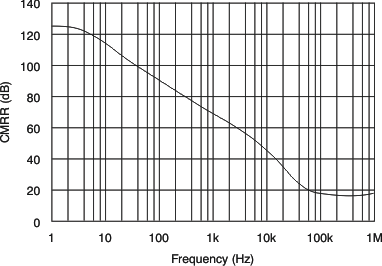
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | TA = –40°C to +125°C (V–) – 0.1 V < VCM < (V+) + 0.1 V |
95 | 108 | dB | |
| OPA4317 TA = –40°C to +125°C (V–) – 0.1 V < VCM < (V+) + 0.1 V, VS = 5.5 V |
95 | 108 | ||||
| INPUT CAPACITANCE | ||||||
| Differential | 2 | pF | ||||
| Common-mode | 4 | pF | ||||
| OPEN-LOOP GAIN | ||||||
| AOL | Open-loop voltage gain | TA = –40°C to +125°C, RL = 10 kΩ (V–) + 100 mV < VO < (V+) – 100 mV |
100 | 110 | dB | |
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | ||||||
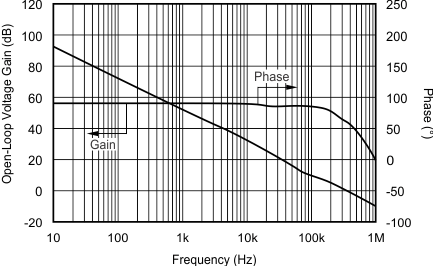
| GBW | Gain-bandwidth product | CL = 100 pF | 300 | kHz | ||
| SR | Slew rate | G = 1 | 0.15 | V/μs | ||
| OUTPUT | ||||||
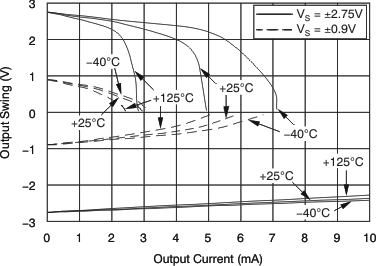
| Voltage output swing from rail | TA = –40°C to +125°C | 30 | 100 | mV | ||
| ISC | Short-circuit current | ±5 | mA | |||
| CL | Capacitive load drive | See the Typical Characteristics section | ||||
| Open-loop output impedance | f = 350 kHz, IO = 0 | 2 | kΩ | |||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| VS | Specified voltage | 1.8 | 5.5 | V | ||
| IQ | Quiescent current per amplifier | TA = –40°C to +125°C, IO = 0 | 21 | 35 | μA | |
| Turnon time | VS = 5 V | 100 | µs | |||
6.8 Typical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, CL = 0 pF, RL = 10 kΩ connected to midsupply, VCM = VOUT = midsupply, unless otherwise noted. Figure 1. Offset Voltage Production Distribution
Figure 1. Offset Voltage Production Distribution
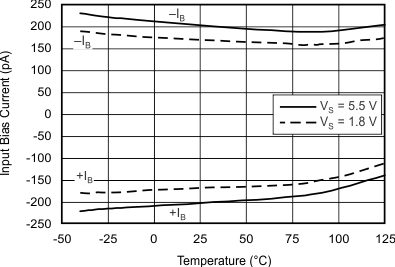
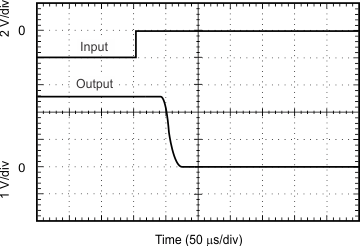
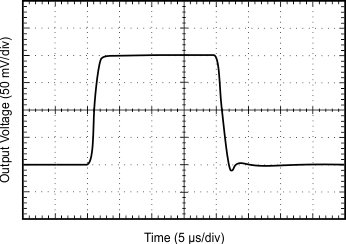
| G = 1 | RL = 10 kΩ |
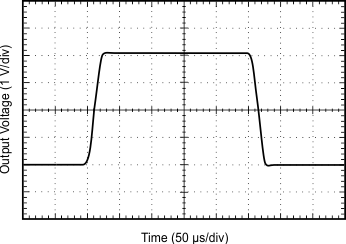
| 4-V Step |
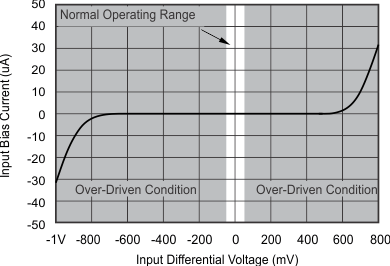
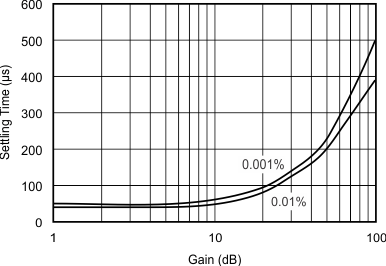
| See the Input Differential Voltage section |
Input Differential Voltage
| G = 1 | RL = 10 kΩ |
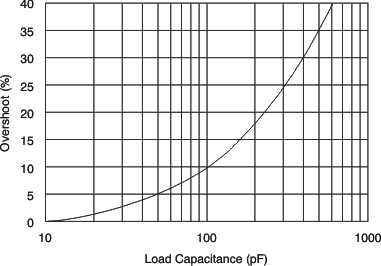
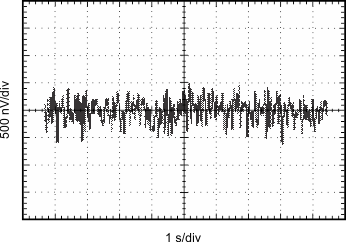
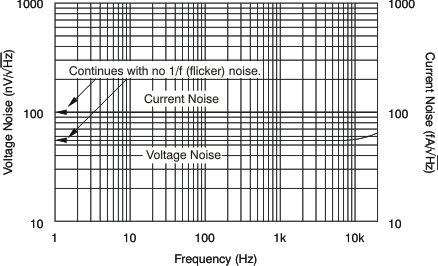 Figure 16. Current and Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency
Figure 16. Current and Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency
7 Parameter Measurement Information
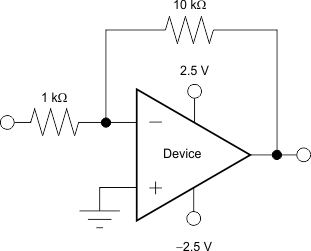 Figure 18. Overvoltage Recovery Circuit
Figure 18. Overvoltage Recovery Circuit
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The OPA317-Q1 is a family of low-power, rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifiers. These devices operate from 1.8 V to 5.5 V, are unity-gain stable, and are suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications. The class AB output stage is capable of driving ≤ 10-kΩ loads connected to any point between V+ and ground. The input common-mode voltage range includes both rails and allows the OPA317 series to be used in virtually any single-supply application. Rail-to-rail input and output swing significantly increases dynamic range, especially in low-supply applications, and makes them ideal for driving sampling analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
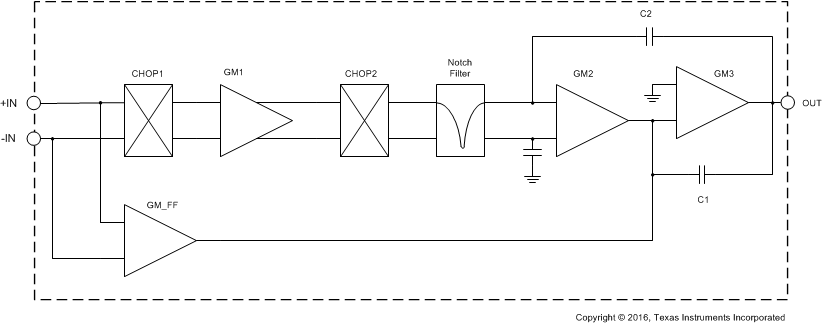
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Operating Voltage
The OPA317-Q1 series of operational amplifiers can be used with single or dual supplies from an operating range of VS = 1.8 V (±0.9 V) up to 5.5 V (±2.75 V).
CAUTION
Supply voltages greater than 7 V can permanently damage the device.
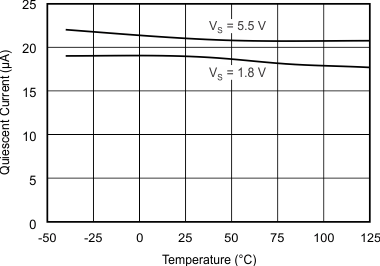
See the Absolute Maximum Ratings table. Key parameters that vary over the supply voltage or temperature range are shown in the Typical Characteristics section.
8.3.2 Input Voltage
The OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 input common-mode voltage range extends 0.1 V beyond the supply rails. The OPA317-Q1 device is designed to cover the full range without the troublesome transition region found in some other rail-to-rail amplifiers.
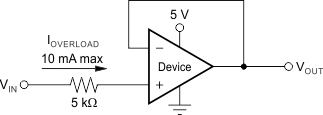
Typically, input bias current is about 200 pA; however, input voltages exceeding the power supplies can cause excessive current to flow into or out of the input pins. Momentary voltages greater than the power supply can be tolerated if the input current is limited to 10 mA. This limitation is easily accomplished with an input resistor, as shown in Figure 19.
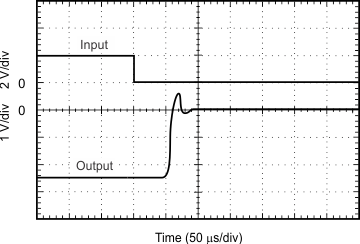
8.3.3 Input Differential Voltage
The typical input bias current of the OPA317-Q1 during normal operation is approximately 200 pA. In overdriven conditions, the bias current can increase significantly (see Figure 17).The most common cause of an overdriven condition occurs when the operational amplifier is outside of the linear range of operation. When the output of the operational amplifier is driven to one of the supply rails, the feedback loop requirements cannot be satisfied, and a differential input voltage develops across the input pins. This differential input voltage results in activation of parasitic diodes inside the front-end input chopping switches that combine with 10-kΩ electromagnetic interference (EMI) filter resistors to create the equivalent circuit shown in Figure 20.
NOTE
The input bias current remains within specification within the linear region.
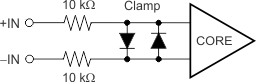 Figure 20. Equivalent Input Circuit
Figure 20. Equivalent Input Circuit
8.3.4 Internal Offset Correction
The OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 operational amplifiers use an auto-calibration technique with a time-continuous, 125-kHz operational amplifier in the signal path. This amplifier is zero-corrected every 8 μs using a proprietary technique. Upon power up, the amplifier requires approximately 100 μs to achieve specified VOS accuracy. This design has no aliasing or flicker noise.
8.3.5 EMI Susceptibility and Input Filtering
Operational amplifiers vary in susceptibility to EMI. If conducted EMI enters the operational amplifier, the DC offset observed at the amplifier output may shift from its nominal value while the EMI is present. This shift is a result of signal rectification associated with the internal semiconductor junctions. While all operational amplifier pin functions can be affected by EMI, the input pins are likely to be the most susceptible. The OPA317-Q1 operational amplifier family incorporates an internal input low-pass filter that reduces the amplifier response to EMI. Both common-mode and differential mode filtering are provided by the input filter. The filter is designed for a cutoff frequency of approximately 8 MHz (–3 dB), with a roll-off of 20 dB per decade.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
The OPAx317-Q1 family of devices are powered on when the supply is connected. The device can be operated as a single-supply operational amplifier or a dual-supply amplifier, depending on the application.
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 are unity-gain stable, precision operational amplifiers free from unexpected output and phase reversal. Proprietary Zerø-Drift circuitry gives the benefit of low input offset voltage over time and temperature, as well as lowering the 1/f noise component. As a result of the high PSRR, these devices work well in applications that run directly from battery power without regulation. The OPA317-Q1 family is optimized for low-voltage, single-supply operation. These miniature, high-precision, low quiescent current amplifiers offer high impedance inputs that have a common-mode range 100 mV beyond the supplies, and a rail-to-rail output that swings within 100 mV of the supplies under normal test conditions. The OPA317-Q1 series are precision amplifiers for cost-sensitive applications.
9.1.1 Achieving Output Swing to the Op Amp Negative Rail
Some applications require output voltage swings from 0 V to a positive full-scale voltage (such as 2.5 V) with excellent accuracy. With most single-supply operational amplifiers, problems arise when the output signal approaches 0 V, near the lower output swing limit of a single-supply operational amplifier. A good single-supply operational amplifier may swing close to single-supply ground, but does not reach ground. The output of the OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 can be made to swing to ground, or slightly below, on a single-supply power source. To do so requires the use of another resistor and an additional, more negative power supply than the operational amplifier negative supply. A pulldown resistor can be connected between the output and the additional negative supply to pull the output down below the value that the output would otherwise achieve, as shown in Figure 21.
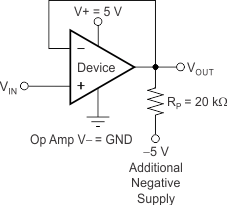 Figure 21. For VOUT Range to Ground
Figure 21. For VOUT Range to Ground
The OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 have an output stage that allows the output voltage to be pulled to its negative supply rail, or slightly below, using the technique previously described. This technique only works with some types of output stages. The OPA317-Q1, OPA2317-Q1, and OPA4317-Q1 have been characterized to perform with this technique; the recommended resistor value is approximately 20 kΩ. This configuration increases the current consumption by several hundreds of microamps. Accuracy is excellent down to 0 V and as low as –2 mV. Limiting and nonlinearity occur below –2 mV, but excellent accuracy returns as the output drives back up above –2 mV. Lowering the resistance of the pulldown resistor allows the operational amplifier to swing even further below the negative rail. Use resistances as low as 10 kΩ to achieve excellent accuracy down to –10 mV.
9.2 Typical Applications
The circuit shown in Figure 22 is a high-side voltage-to-current (V-I) converter. It translates an input voltage of 0 V to 2 V to an output current of 0 mA to 100 mA. Figure 23 shows the measured transfer function for this circuit. The low offset voltage and offset drift of the OPA317 facilitate excellent DC accuracy for the circuit.
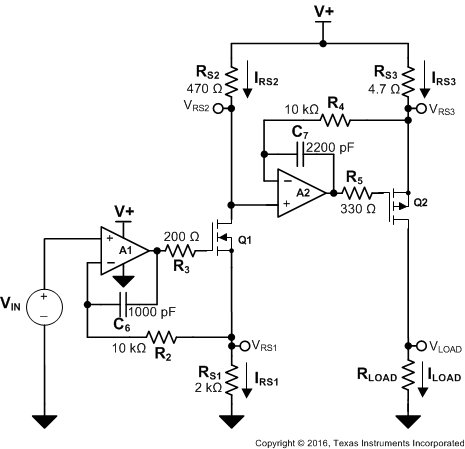 Figure 22. High-Side Voltage-to-Current (V-I) Converter
Figure 22. High-Side Voltage-to-Current (V-I) Converter
9.2.1 Design Requirements
The design requirements are as follows:
- Supply Voltage: 5-V DC
- Input: 0-V to 2-V DC
- Output: 0-mA to 100-mA DC
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The V-I transfer function of the circuit is based on the relationship between the input voltage, VIN, and the three current-sensing resistors: RS1, RS2, and RS3. The relationship between VIN and RS1 determines the current that flows through the first stage of the design. The current gain from the first stage to the second stage is based on the relationship between RS2 and RS3.
For a successful design, pay close attention to the DC characteristics of the operational amplifier chosen for the application. To meet the performance goals, this application benefits from an operational amplifier with low offset voltage, low temperature drift, and rail-to-rail output. The OPA2317 CMOS operational amplifier is a high-precision, 5-µV offset, 0.05-μV/°C drift amplifier optimized for low-voltage, single-supply operation with an output swing to within 50 mV of the positive rail. The OPA2317 family uses chopping techniques to provide low initial offset voltage and near-zero drift over time and temperature. Low offset voltage and low drift reduce the offset error in the system, making these devices appropriate for precise DC control. The rail-to-rail output stage of the OPA2317 ensures that the output swing of the operational amplifier is able to fully control the gate of the MOSFET devices within the supply rails.
9.2.3 Application Curve
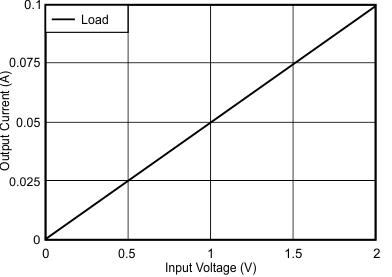 Figure 23. Measured Transfer Function for High-Side V-I Converter
Figure 23. Measured Transfer Function for High-Side V-I Converter
9.3 System Example
RN are operational resistors used to isolate the ADS1100 from the noise of the digital I2C bus. The ADS1100 device is a 16-bit converter; therefore, a precise reference is essential for maximum accuracy. If absolute accuracy is not required and the 5-V power supply is sufficiently stable, the REF3130 device may be omitted.
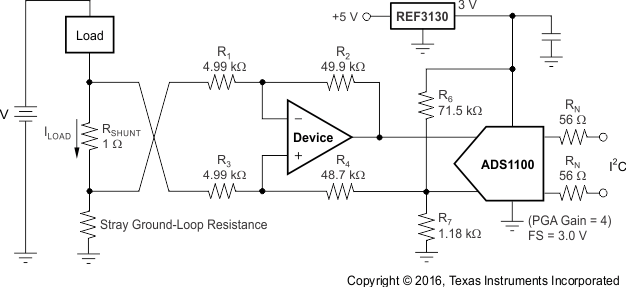
NOINDENT:
NOTE: 1% resistors provide adequate common-mode rejection at small ground-loop errors.10 Power Supply Recommendations
The OPAx317-Q1 device is specified for operation from 1.8 V to 5.5 V (±0.9 V to ±2.75 V); many specifications apply from –40°C to +125°C. The Electrical Characteristics: VS = 1.8 V to 5.5 V table presents parameters that can exhibit significant variance with regard to operating voltage or temperature.
CAUTION
Supply voltages larger than 7 V can permanently damage the device (see the Absolute Maximum Ratings) table.
Place 0.1-μF bypass capacitors close to the power-supply pins to reduce errors coupling in from noisy or high-impedance power supplies. For more detailed information on bypass capacitor placement, see the Layout Guidelines section.