SLUSA29D April 2010 – August 2015 UCC28250
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VDD (5/12)
- 7.3.2 VREF (Reference Generator) (20/7)
- 7.3.3 EN (Enable Pin) (18/5)
- 7.3.4 RT (Oscillator Frequency Set and Synchronization) (15/2)
- 7.3.5 SP (Synchronous Rectifier Turnoff to Primary Output Turnon Dead Time Programming) (13/19)
- 7.3.6 PS (Primary Output Turnoff to Synchronous Rectifier Turnon Dead Time Programming) (11/18)
- 7.3.7 RAMP/CS (PWM Ramp Input or Current Sense Input) (16/3)
- 7.3.8 REF/EA+ (1/8)
- 7.3.9 FB/EA- (2/9)
- 7.3.10 COMP (3/10)
- 7.3.11 VSENSE (14/1)
- 7.3.12 SS (Soft Start Programming Pin) (13/20)
- 7.3.13 ILIM (Current Limit for Cycle-By-Cycle Overcurrent Protection) (17/4)
- 7.3.14 HICC (10/17)
- 7.3.15 OVP/OTP (19/6)
- 7.3.16 OUTA (9/16) and OUTB (8/15)
- 7.3.17 SRA (7/14) and SRB (6/13)
- 7.3.18 GND (4/11)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Design Example
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Step 1, Power Stage Design
- 8.2.1.2.2 Step 2, Feedback Loop Design
- 8.2.1.2.3 Step 3, Programming the Device
- 8.2.1.2.4 Step 3-3, Determine Soft-Start Capacitance
- 8.2.1.2.5 Step 3-4, Determine Dead-Time Resistance
- 8.2.1.2.6 Step 3-5, Determine OCP Hiccup Off-Time Capacitance
- 8.2.1.2.7 Step 3-6, Determine Primary-Side OVP Resistance
- 8.2.1.2.8 Step 3-7, Select Capacitance for VDD and VREF
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Secondary-Side Half-Bridge Controller with Synchronous Rectification
- 8.2.1
Design Example
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
1 Features
- Prebiased Start-up
- Synchronous Rectifier Control Outputs With Programmable Delays (Including Zero Delay Support)
- Voltage Mode Control With Input Voltage Feed-Forward or Current Mode Control
- Primary or Secondary-Side Control
- 3.3-V, 1.5% Accurate Reference Output
- 1-MHz Capable Switching Frequency
- 1% Accurate Cycle-by-Cycle Overcurrent Protection with Matched Duty Cycle Outputs
- Programmable Soft-Start and Hiccup Restart Timer
- Thermally Enhanced 4-mm × 4-mm QFN-20 Package and 20-pin TSSOP Package
2 Applications
- Half-Bridge, Full-Bridge, Interleaved Forward, and Push-Pull Isolated Converters
- Telecom and Data-com Power
- Wireless Base Station Power
- Server Power
- Industrial Power Systems
3 Description
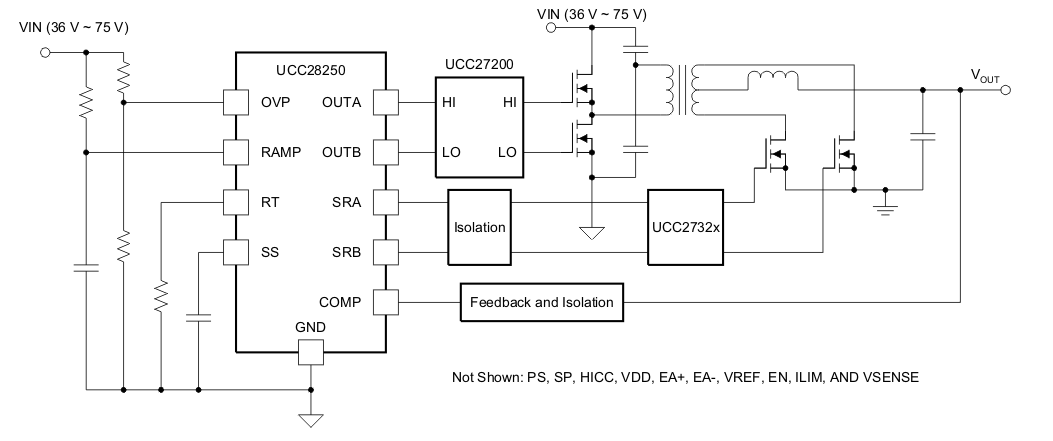
The UCC28250 PWM controller is designed for high power density applications that may have stringent prebiased start-up requirements. The integrated synchronous rectifier control outputs target high-efficiency and high-performance topologies such as half-bridge, full-bridge, interleaved forward, and push-pull. The UCC27200 half-bridge drivers and UCC2732X MOSFET drivers used in conjunction with the UCC28250 provide a complete power converter solution.
Externally programmable soft-start, used in conjunction with an internal prebiased start-up circuit, allows the controller to gradually reach a steady-state operating point under all output conditions. The UCC28250 can be configured for primary or secondary-side control and either voltage or current mode control can be implemented.
The oscillator operates at frequencies up to 2 MHz, and can be synchronized to an external clock. Input voltage feedforward, cycle-by-cycle current limit, and a programmable hiccup timer allow the system to stay within a safe operation range. Input voltage, output voltage and temperature protection can be implemented. Dead time between primary-side switch and secondary-side synchronous rectifiers can be independently programmed.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| UCC28250 | TSSOP (20) | 6.50 mm × 4.40 mm |
| VQFN (20) | 4.00 mm × 3.50 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Simplified Application Diagram