ZHCSUL6 February 2024 ADC12DL1500 , ADC12DL2500 , ADC12DL500
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Dual-Channel Mode)
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Single-Channel Mode)
- 5.9 Timing Requirements
- 5.10 Switching Characteristics
- 5.11 Timing Diagrams
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics - ADC12DL500
- 5.13 Typical Characteristics - ADC12DL1500 (1GSPS)
- 5.14 Typical Characteristics - ADC12DL1500 (1.5GSPS)
- 5.15 Typical Characteristics - ADC12DL2500 (2GSPS)
- 5.16 Typical Characteristics - ADC12DL2500 (2.5GSPS)
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Analog Inputs
- 6.3.2 ADC Core
- 6.3.3 Timestamp
- 6.3.4 Clocking
- 6.3.5 LVDS Digital Interface
- 6.3.6 Alarm Monitoring
- 6.3.7 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 6.3.8 Analog Reference Voltage
- 6.4
Device Functional Modes
- 6.4.1 Dual-Channel Mode (Non-DES Mode)
- 6.4.2 Internal Dither Modes
- 6.4.3 Single-Channel Mode (DES Mode)
- 6.4.4 LVDS Output Driver Modes
- 6.4.5 LVDS Output Modes
- 6.4.6 Power-Down Modes
- 6.4.7 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 6.4.8 Offset Calibration
- 6.4.9 Trimming
- 6.5 Programming
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Register Maps
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.2.1 ADC Theory of Operation
The differential voltages at the analog inputs are captured by the rising edge of CLK± in dual-channel mode or by the rising and falling edges of CLK± in single-channel mode. After capturing the input signal, the ADC converts the analog voltage to a digital value by comparing the voltage to the internal reference voltage. If the voltage on INA– or INB– is higher than the voltage on INA+ or INB+, respectively, then the digital output is a negative 2's complement value. If the voltage on INA+ or INB+ is higher than the voltage on INA– or INB–, respectively, then the digital output is a positive 2's complement value. Equation 1 can calculate the differential voltage at the input pins from the digital output.
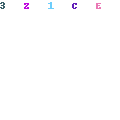
where
- Code is the signed decimation output code (for example, –2048 to +2047)
- N is the ADC resolution
- VFS is the full-scale input voltage of the ADC as specified in the Recommended Operating Conditions table, including any adjustment performed by programming FS_RANGE_A or FS_RANGE_B