ZHCSPP4A june 2022 – july 2023 ADC12QJ1600-SP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 说明(续)
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications
- 7.8 Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 Timing Requirements
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Analog Input
- 8.3.2 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 8.3.3 Timestamp
- 8.3.4 Clocking
- 8.3.5
JESD204C Interface
- 8.3.5.1 Transport Layer
- 8.3.5.2 Scrambler
- 8.3.5.3 Link Layer
- 8.3.5.4 8B or 10B Link Layer
- 8.3.5.5 64B or 66B Link Layer
- 8.3.5.6 Physical Layer
- 8.3.5.7 JESD204C Enable
- 8.3.5.8 Multi-Device Synchronization and Deterministic Latency
- 8.3.5.9 Operation in Subclass 0 Systems
- 8.3.5.10 Alarm Monitoring
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Low Power Mode and High Performance Mode
- 8.4.2 JESD204C Modes
- 8.4.3 Power-Down Modes
- 8.4.4 Test Modes
- 8.4.5 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 8.4.6 Offset Calibration
- 8.4.7 Trimming
- 8.5 Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.5.6 Streaming Mode
The serial interface supports streaming reads and writes. In this mode, the initial 24 bits of the transaction specifics the access type, register address, and data value as normal. Additional clock cycles of write or read data are immediately transferred, as long as the SCS input is maintained in the asserted (logic low) state. The register address auto increments (default) or decrements for each subsequent 8-bit transfer of the streaming transaction. ASCEND controls whether the address value ascends (increments) or descends (decrements). Streaming mode can be disabled by setting the ADDR_HOLD bit. Figure 8-17 shows the streaming mode transaction details.
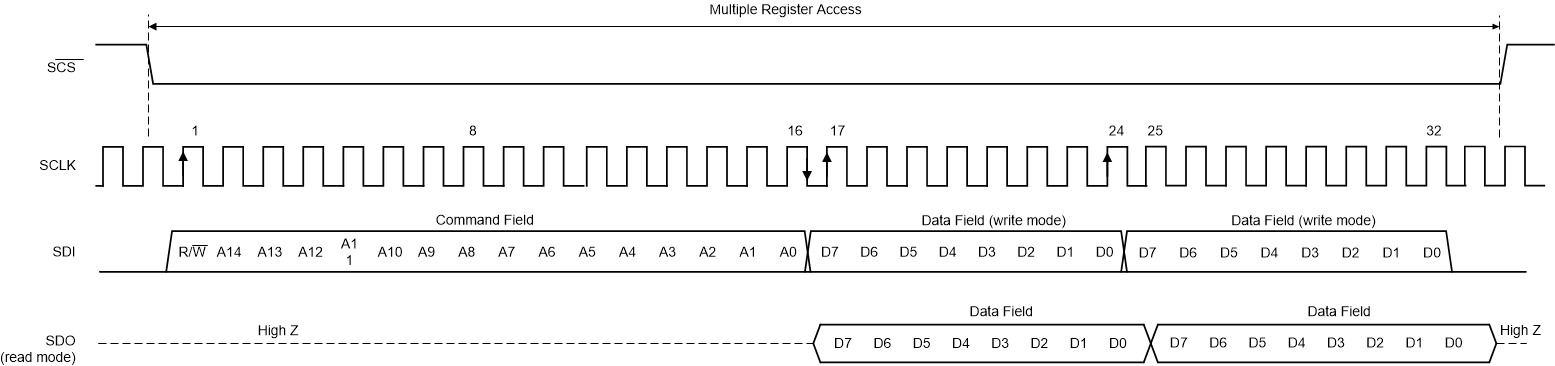 Figure 8-17 Serial
Interface Protocol: Streaming Read/Write
Figure 8-17 Serial
Interface Protocol: Streaming Read/WriteSee the SPI_Register_Map Registers section for detailed information regarding the registers
The serial interface must not be accessed during ADC calibration. Accessing the serial interface during this time impairs the performance of the device until the device is calibrated correctly. Writing or reading the serial registers also reduces dynamic ADC performance for the duration of the register access times.