ZHCSG63C December 2013 – July 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Details of a Qi Wireless Power System and bq51003 Power Transfer Flow Diagrams
- 8.3.2 Dynamic Rectifier Control
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
- 8.3.4 RILIM Calculations
- 8.3.5 Input Overvoltage
- 8.3.6 Adapter Enable Functionality and EN1/EN2 Control
- 8.3.7 End Power Transfer Packet (WPC Header 0x02)
- 8.3.8 Status Outputs
- 8.3.9 WPC Communication Scheme
- 8.3.10 Communication Modulator
- 8.3.11 Adaptive Communication Limit
- 8.3.12 Synchronous Rectification
- 8.3.13 Temperature Sense Resistor Network (TS)
- 8.3.14 3-State Driver Recommendations for the TS-CTRL Pin
- 8.3.15 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.16 WPC v1.2 Compliance – Foreign Object Detection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.3 Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
The Dynamic Efficiency Scaling feature allows for the loss characteristics of the bq51003 to be scaled based on the maximum expected output power in the end application. This effectively optimizes the efficiency for each application. This feature is achieved by scaling the loss of the internal LDO based on a percentage of the maximum output current. Note that the maximum output current is set by the KIMAX term and the RILIM resistance (where RILIM = KIMAX / IMAX). The flow diagram show in Figure 19 illustrates how the rectifier is dynamically controlled (Dynamic Rectifier Control) based on a fixed percentage of the IMAX setting. Table 2 summarizes how the rectifier behavior is dynamically adjusted based on two different RILIM settings.
Table 2. Dynamic Efficiency Scaling
| OUTPUT CURRENT PERCENTAGE | RILIM = 1116 Ω
IMAX = 250 mA |
RILIM = 488 Ω
IMAX = 500 mA |
VRECT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 to 10% | 0 A to 0.025 A | 0 A to 0.05 A | 7.08 V |
| 10 to 20% | 0.025 A to 0.050 A | 0.050 A to 0.100 A | 6.28 V |
| 20 to 40% | 0.050 A to 0.100 A | 0.100 A to 0.200 A | 5.53 V |
| >40% | > 0.100 A | > 0.200 A | 5.11 V |
Figure 5 illustrates the shift in the Dynamic Rectifier Control behavior based on the two different RILIM settings. With the rectifier voltage (VRECT) being the input to the internal LDO, this adjustment in the Dynamic Rectifier Control thresholds will dynamically adjust the power dissipation across the LDO where:
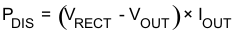
Figure 3 illustrates how the system efficiency is improved due to the Dynamic Efficiency Scaling feature. Note that this feature balances efficiency with optimal system transient response.