SLVSH22 May 2024 DRV8000-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 External Components
- 7.4
Feature Description
- 7.4.1 Heater MOSFET Driver
- 7.4.2 High-side Drivers
- 7.4.3 Electro-chromic Glass Driver
- 7.4.4 Half-bridge Drivers
- 7.4.5
Gate Drivers
- 7.4.5.1 Input PWM Modes
- 7.4.5.2
Smart Gate Driver - Functional Block
Diagram
- 7.4.5.2.1 Smart Gate Driver
- 7.4.5.2.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.4.5.2.3 Slew Rate Control (IDRIVE)
- 7.4.5.2.4 Gate Driver State Machine (TDRIVE)
- 7.4.5.2.5 Propagation Delay Reduction (PDR)
- 7.4.5.2.6 PDR Pre-Charge/Pre-Discharge Control Loop Operation Details
- 7.4.5.2.7 PDR Post-Charge/Post-Discharge Control Loop Operation Details
- 7.4.5.2.8 Detecting Drive and Freewheel MOSFET
- 7.4.5.2.9 Automatic Duty Cycle Compensation (DCC)
- 7.4.5.2.10 Closed Loop Slew Time Control (STC)
- 7.4.5.3 Tripler (Double-Stage) Charge Pump
- 7.4.5.4 Wide Common Mode Differential Current Shunt Amplifier
- 7.4.5.5 Gate Driver Protection Circuits
- 7.4.6 Sense Output (IPROPI)
- 7.4.7
Protection Circuits
- 7.4.7.1 Fault Reset (CLR_FLT)
- 7.4.7.2 DVDD Logic Supply Power on Reset (DVDD_POR)
- 7.4.7.3 PVDD Supply Undervoltage Monitor (PVDD_UV)
- 7.4.7.4 PVDD Supply Overvoltage Monitor (PVDD_OV)
- 7.4.7.5 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (VCP_UV)
- 7.4.7.6 Thermal Clusters
- 7.4.7.7 Watchdog Timer
- 7.4.7.8 Fault Detection and Response Summary Table
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 DRV8000-Q1 Register Map
- 9 DRV8000-Q1_STATUS Registers
- 10DRV8000-Q1_CNFG Registers
- 11DRV8000-Q1_CTRL Registers
- 12Application and Implementation
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Revision History
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.5.1.2 H-Bridge Control
In H-bridge control, both half-bridge gate drivers can be controlled as an H-bridge gate driver through a configurable combination of IN1 and IN2 input pins or the S_IN1 and S_IN2 bits in registerGD_HB_CTRL.
To set the control mode for the half-bridge gate drivers, the SPI BRG_MODE bit can be configured to either PH/EN or PWM control modes. The PH/EN mode allows for the H-bridge to be controlled with a speed/direction type of interface commanded by one PWM signal and one GPIO signal. The PWM mode allows for the H-bridge to be controlled with a more advanced scheme typically requiring two PWM signals. This allows the H-bridge driver to enter four different output states for additional control flexibility if required.
In PH/EN mode, each half-bridge input control modes are configured with bits INx_MODE in register GD_CNFG. By default, INx_MODE = 0b and both half-bridge are controlled from pins. If INx_MODE = 1b, the half-bridge is controlled with SPI bit S_INx. If IN1_MODE is set to 1b and IN2_MODE is set to 0b, the half-bridge 1 is controlled through SPI bit S_IN1, and half-bridge 2 is controlled with pin IN2. If both INx_MODE = 1b, then S_IN1 becomes EN and S_IN2 becomes PH, following pins IN1 and IN2.
The H-bridge freewheeling state is configurable through the BRG_FW register setting. In both the PH/EN and PWM modes the default active freewheeling mode is active low-side. This setting can be utilized to modify the bridge between low-side or high-side active freewheeling.
The H-bridge can be set to the Hi-Z state through the PWM or PH/EN control mode, using DRVOFF pin or S_HIZx bits. The S_HIZx bits are an OR when the gate driver is in PH/EN control mode, and puts both outputs SHx into high impedance.
| DRVOFF | IN1 (EN) | IN2 (PH) | BRG_FW | GH1 | GL1 | GH2 | GL2 | SH1 | SH2 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | X | X | X | L | L | L | L | Z | Z | High Impedance |
| 0 | 0 | X | 0b | L | H | L | H | L | L | Low-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 0 | X | 1b | H | L | H | L | H | H | High-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | X | L | H | H | L | L | H | Drive SH2 → SH1 (Reverse) |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | X | H | L | L | H | H | L | Drive SH1 → SH2 (Forward) |
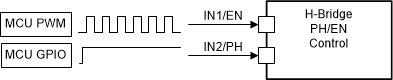 Figure 7-20 H-Bridge PH/EN Control
Figure 7-20 H-Bridge PH/EN Control| DRVOFF | IN1 (EN) | S_IN2 (PH) | BRG_FW | GH1 | GL1 | GH2 | GL2 | SH1 | SH2 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | X | X | X | L | L | L | L | Z | Z | High Impedance |
| 0 | 0 | X | 0b | L | H | L | H | L | L | Low-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 0 | X | 1b | H | L | H | L | H | H | High-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 1 | 0b | X | L | H | H | L | L | H | Drive SH2 → SH1 (Reverse) |
| 0 | 1 | 1b | X | H | L | L | H | H | L | Drive SH1 → SH2 (Forward) |
 Figure 7-21 H-Bridge PH/EN Mixed Control
Figure 7-21 H-Bridge PH/EN Mixed Control| DRVOFF | S_IN1 (EN) | IN2 (PH) | BRG_FW | GH1 | GL1 | GH2 | GL2 | SH1 | SH2 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | X | X | X | L | L | L | L | Z | Z | High Impedance |
| 0 | 0 | X | 0b | L | H | L | H | L | L | Low-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 0 | X | 1b | H | L | H | L | H | H | High-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 1b | 0 | X | L | H | H | L | L | H | Drive SH2 → SH1 (Reverse) |
| 0 | 1b | 1 | X | H | L | L | H | H | L | Drive SH1 → SH2 (Forward) |
 Figure 7-22 H-Bridge PH/EN Control
(BRG_MODE = 01b, IN1_MODE = 1b)
Figure 7-22 H-Bridge PH/EN Control
(BRG_MODE = 01b, IN1_MODE = 1b)| DRVOFF | IN1 | IN2 | BRG_FW | GH1 | GL1 | GH2 | GL2 | SH1 | SH2 | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | X | X | X | L | L | L | L | Z | Z | High Impedance |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | X | L | L | L | L | Z | Z | Diode Freewheel (Coast) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | X | L | H | H | L | L | H | Drive SH2 → SH1 (Reverse) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | X | H | L | L | H | H | L | Drive SH1 → SH2 (Forward) |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0b | L | H | L | H | L | L | Low-Side Active Freewheel |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1b | H | L | H | L | H | H | High-Side Active Freewheel |
 Figure 7-23 H-Bridge
PWM Control
Figure 7-23 H-Bridge
PWM Control