ZHCSN76B January 2021 – April 2022 DRV8316
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 Control Modes
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 Step-Down Mixed-Mode Buck Regulator
- 8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.6 Charge Pump
- 8.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.8 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.9 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.10 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.11 Current Sense Amplifiers
- 8.3.12 Active Demagnetization
- 8.3.13 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 8.3.14
Protections
- 8.3.14.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (NPOR)
- 8.3.14.2 AVDD Undervoltage Lockout (AVDD_UV)
- 8.3.14.3 BUCK Undervoltage Lockout (BUCK_UV)
- 8.3.14.4 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.14.5 Overvoltage Protections (OV)
- 8.3.14.6 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.14.7 Buck Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.14.8 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.14.9 Thermal Shutdown (OTS)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.13 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
The current-limit circuit activates if the current flowing through the low-side MOSFET exceeds the ILIMIT current. This feature restricts motor current to less than the ILIMIT.
The current-limit circuitry utilizes the current sense amplifier output of the three phases compared with the voltage at ILIM pin. Figure 8-35 shows the implementation of current limit circuitry. As shown in this figure, the output of current sense amplifiers is combined with star connected resistive network. This measured voltage VMEAS is compared with the external reference voltage e VILIM pin to realize the current limit implementation. The relation between current sensed on OUTX pin and VMEAS threshold is given as:
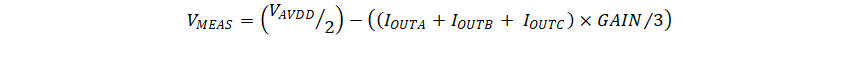
where
- AVDD is 3.3-V LDO output
- OUTX is current flowing into the low-side MOSFET
- GAIN is the CSA_GAIN setting
The ILIMIT threshold can be adjusted by configuring ILIM pin between AVDD/2 to (AVDD/2 - 0.4) V. AVDD/2 is minimum value and when it is applied on ILIM pin cycle by cycle current limit is disabled, whereas maximum threshold of 8A can be configured by applying (AVDD/2 - 0.4) V on ILIM pin.
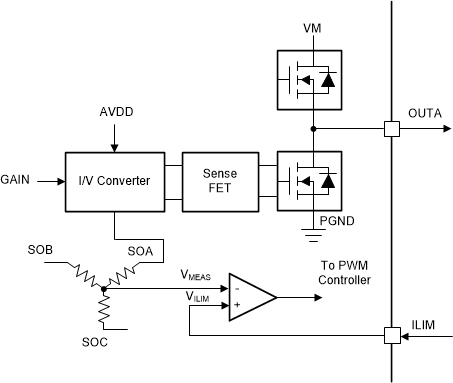 Figure 8-35 Current Limit Implementation
Figure 8-35 Current Limit ImplementationWhen then the current limit activates, the high-side FET is disabled until the beginning of the next PWM cycle as shown in Figure 8-36. The low-side FETs can operate in brake mode or high-Z mode by configuring the ILIM_RECIR bit in the SPI device variant.
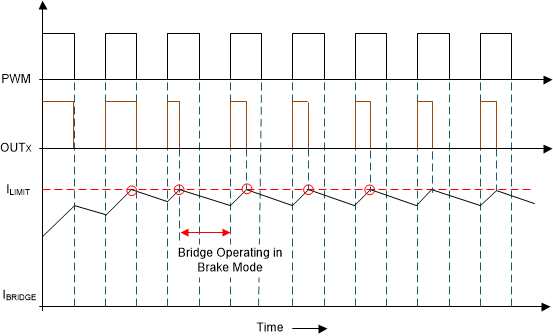 Figure 8-36 Cycle-by-Cycle Current-Limit
Operation
Figure 8-36 Cycle-by-Cycle Current-Limit
Operation