ZHCSIQ9 September 2018 OPA859
PRODUCTION DATA.
9.3.3 Wide Gain-Bandwidth Product
Figure 10 shows the open-loop magnitude and phase response of the OPA859. Calculate the gain bandwidth product of any op amp by determining the frequency at which the AOL is 40 dB and multiplying that frequency by a factor of 100. The open-loop response shows the OPA859 to have approximately 63° of phase-margin when configured as a unity-gain buffer.
Figure 51 shows the open-loop magnitude (AOL) of the OPA859 as a function of temperature. The results show approximately 5° of phase-margin variation over the entire temperature range. Semiconductor process variation is the naturally occurring variation in the attributes of a transistor (Early-voltage, β, channel-length and width) and other passive elements (resistors and capacitors) when fabricated into an integrated circuit. The process variation can occur across devices on a single wafer, or, across devices over multiple wafer lots over time. Typically the variation across a single wafer is tightly controlled. Figure 52 shows the AOL magnitude of the OPA859 as a function of process variation over time. The results show the AOL curve for the nominal process corner and the variation one standard deviation from the nominal. The simulated results show less than 2° of phase-margin difference within a standard deviation of process variation when the amplifier is configured as a unity-gain bufffer.
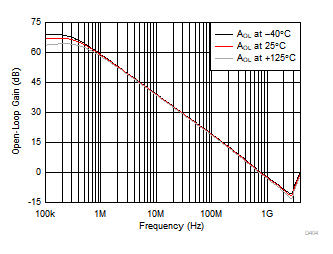 Figure 51. Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature
Figure 51. Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature  Figure 52. Open-Loop Gain vs Process Variation
Figure 52. Open-Loop Gain vs Process Variation