ZHCSJ41 December 2018 SN55HVD233-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 7.8 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 Device Switching Characteristics
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
8 Parameter Measurement Information
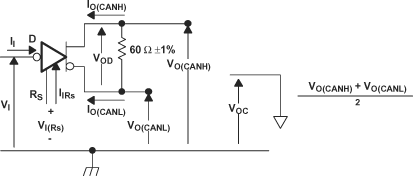 Figure 12. Driver Voltage, Current, and Test Definition
Figure 12. Driver Voltage, Current, and Test Definition 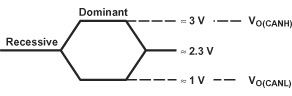 Figure 13. Bus Logic State Voltage Definitions
Figure 13. Bus Logic State Voltage Definitions 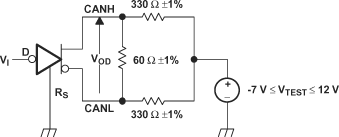 Figure 14. Driver VOD
Figure 14. Driver VOD 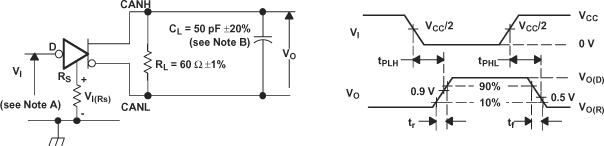
A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics:
- Pulse repetition rate (PRR) ≤ 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle
- tr ≤ 6 ns
- tf ≤ 6 ns
- ZO = 50 Ω
B. CL includes fixture and instrumentation capacitance.
Figure 15. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms 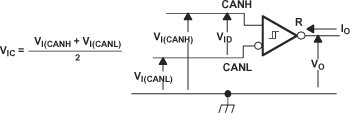 Figure 16. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 16. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions 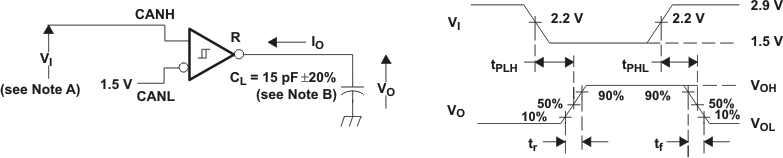
A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics:
- PRR ≤ 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle
- tr ≤ 6 ns
- tf ≤ 6 ns
- ZO = 50 Ω
B. CL includes fixture and instrumentation capacitance.
Figure 17. Receiver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms Table 1. Differential Input Voltage Threshold Test
| INPUT | OUTPUT | MEASURED | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCANH | VCANL | R | |VID| | |
| –6.1 V | –7 V | L | VOL | 900 mV |
| 12 V | 11.1 V | L | 900 mV | |
| –1 V | –7 V | L | 6 V | |
| 12 V | 6 V | L | 6 V | |
| –6.5 V | –7 V | H | VOH | 500 mV |
| 12 V | 11.5 V | H | 500 mV | |
| –7 V | –1 V | H | 6 V | |
| 6 V | 12 V | H | 6 V | |
| Open | Open | H | X | |
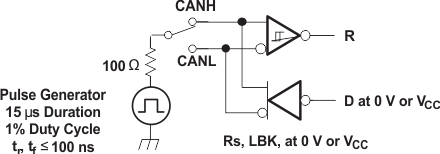
NOTE:
This test is conducted to test survivability only. Data stability at the R output is not specified.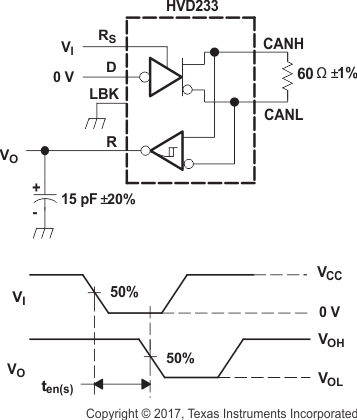
NOTE:
All VI input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics:- tr or tf ≤ 6 ns
- PRR = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle
NOTE:
All VI input pulses are supplied by a generator having the following characteristics:- tr or tf ≤ 6 ns
- PRR = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle
 Figure 21. T(loop) Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
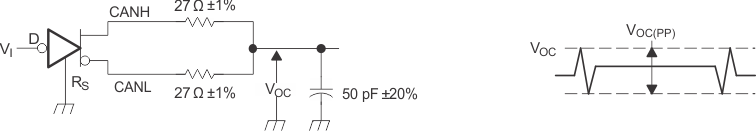
Figure 21. T(loop) Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms 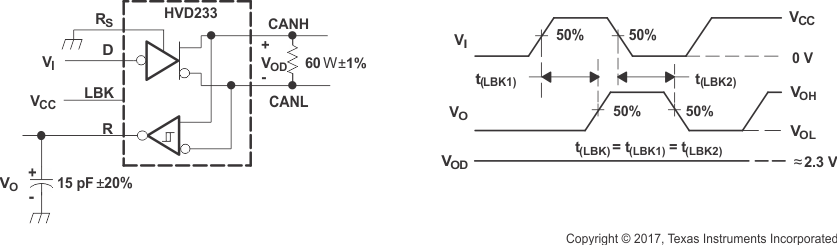 Figure 22. T(LBK) Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 22. T(LBK) Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms 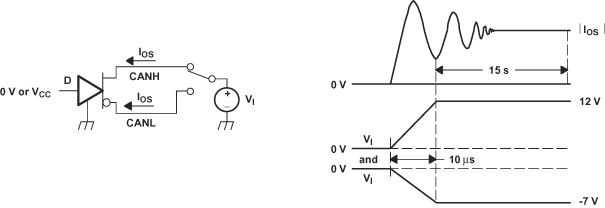 Figure 23. IOS Test Circuit and Waveforms
Figure 23. IOS Test Circuit and Waveforms 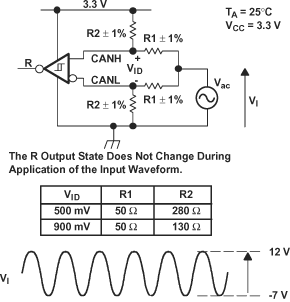
NOTE:
All input pulses are supplied by a generator with ƒ ≤ 1.5 MHz.