SLLS632C December 2005 – February 2015 SN65HVD1050
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Device Switching Characteristics
- 7.8 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 7.10 Supply Current
- 7.11 S-Pin Characteristics
- 7.12 VREF-Pin Characteristics
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9 Detailed Description
9.1 Overview
The SN65HVD1050 CAN tranceivers is compatible with the ISO1189-2 High Speed CAN (Controller Area Network) physical layer standard. It is designed to interface between the differential bus lines in controller area network and the CAN protocol controller at data rates up to 1 Mbps.
9.2 Functional Block Diagram
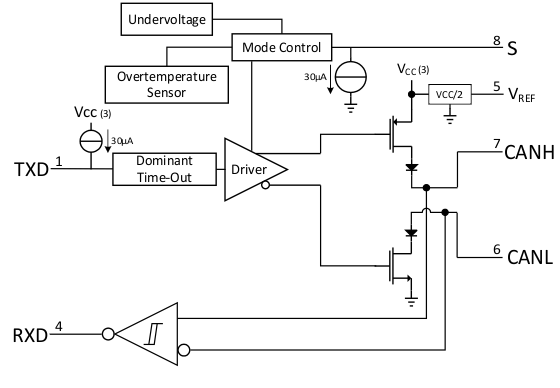
9.3 Feature Description
9.3.1 Mode Control
9.3.1.1 Normal Mode
Select the normal mode of the device operation by setting the S pin low. The CAN bus driver and receiver are fully operational and the CAN communication is bidirectional. The driver is translating a digital input on TXD to a differential output on CANH and CANL. The receiver is translating the differential signal from CANH and CANL to a digital output on RXD.
9.3.1.2 Silent Mode
Activate silent mode (receive only) by setting the S pin high. The CAN driver is turned off while the receiver remains active and RXD outputs the received bus data.
NOTE
Silent mode may be used to implement babling idiot protection, to ensure that the driver does not disrupt the network during a local fault. Silent mode may also be used in redundant systems to select or deselect the redundant transceiver (driver) when needed.
9.3.2 TXD Dominant Timeout (DTO)
During normal mode, the mode where the CAN driver is active, the TXD DTO circuit prevents the transceiver from blocking network communication in the event of a hardware or software failure where TXD is held dominant longer than the timeout period tTXD_DTO. The DTO circuit is triggered on a falling edge on the driver input, TXD. The DTO circuit disables the CAN bus driver if no rising edge is seen on TXD before the timeout period expires. This frees the CAN bus for communication between other nodes on the network. The CAN driver is re-enabled when a rising edge is seen on the drvier input, TXD, thus clearing the TXD DTO condition. The receiver and RXD pin still reflect the CAN bus, and the bus pins are biased to recessive level during a TXD DTO.
NOTE
The minimum dominant TXD time allowed by the TXD DTO circuit limits the minimum possible transmitted data rate on the device. The CAN protocol allows a maximum of eleven successive dominant bits (on TXD) for the worst case, where five successive dominant bits are followed immediately by an error frame. This, along with the tTXD_DTO minimum, limits the minimum data rate. Calculate the minimum transmitted data rate using: Minimum Data Rate = 11 / tTXD_DTO
9.3.3 Thermal Shutdown
The SN65HVD1050 has a thermal shutdown feature that turns off the driver outputs when the junction temperature nears 190°C. This shutdown prevents catastrophic failure from bus shorts, but does not protect the circuit from possible damage. The user should strive to maintain recommended operating conditions and not exceed absolute-maximum ratings at all times. If an SN65HVD1050 is subjected to many, or long-duration faults that can put the device into thermal shutdown, it should be replaced.
9.3.4 VREF
A reference voltage of VCC/2 is available through the VREF output pin. The VREF voltage should be tied to the common mode point in a split termination network to help stabilize the output common mode voltage. See Figure 27 for more application specific information on properly terminating the CAN bus.
If the VREF output pin is not used it can be left floating.
9.3.5 Operating Temperature Range
The SN65HVD1050 is characterized for operation from –40°C to 125°C.
9.4 Device Functional Modes
Table 2. Driver
| INPUTS | OUTPUTS | BUS STATE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TXD(1) | S(1) | CANH(1) | CANL(1) | |
| L | L or Open | H | L | DOMINANT |
| H | X | Z | Z | RECESSIVE |
| Open | X | Z | Z | RECESSIVE |
| X | H | Z | Z | RECESSIVE |
Table 3. Receiver
| DIFFERENTIAL INPUTS VID = V(CANH) – V(CANL) |
OUTPUT RXD(1) | BUS STATE |
|---|---|---|
| VID ≥ 0.9V | L | DOMINANT |
| 0.5V < VID < 0.9V | ? | ? |
| VID ≤ 0.5V | H | RECESSIVE |
| Open | H | RECESSIVE |
Table 4. Parametric Cross Reference With the TJA1050
| TJA1050(1) | PARAMETER | HVD1050 |
|---|---|---|
| TRANSMITTER SECTION | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | Recommended VIH |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | Recommended VIL |
| IIH | High-level input current | Driver IIH |
| IIL | Low-level input current | Driver IIL |
| BUS SECTION | ||
| ILI | Power-off bus input current | Receiver II(off) |
| IO(SC) | Short-circuit output current | Driver IOS(SS) |
| VO(dom) | Dominant output voltage | Driver VO(D) |
| Vi(dif)(th) | Differential input voltage | Receiver VIT and recommended VID |
| Vi(dif)(hys) | Diffrential input hysteresis | Receiver Vhys |
| VO(reces) | Recessive output voltage | Driver VO(R) |
| VO(dif)(bus) | Differential bus voltage | Driver VOD(D) and VOD(R) |
| Ri(cm) | CANH, CANL input resistance | Receiver RIN |
| Ri(dif) | Differential input resistance | Receiver RID |
| Ri(cm)(m) | Input resistance matching | Receiver RI (m) |
| Ci | Input capacitance to ground | Receiver CI |
| Ci(dif) | Differential input capacitance | Receiver CID |
| RECEIVER SECTION | ||
| IOH | High-level output current | Recommended IOH |
| IOL | Low-level output current | Recommended IOL |
| Vref PIN SECTION | ||
| Vref | Reference output voltage | VO |
| TIMING SECTION | ||
| td(TXD-BUSon) | Delay TXD to bus active | Driver tPLH |
| td(TXD-BUSoff) | Delay TXD to bus inactive | Driver tPHL |
| td(BUSon-RXD) | Delay bus active to RXD | Receiver tPHL |
| td(BUSoff-RXD) | Delay bus inactive to RXD | Receiver tPLH |
| td(TXD-BUSon) + td(BUSon-RXD) | Device tLOOP1 | |
| td(TXD-BUSoff) + td(BUSoff-RXD) | Device tLOOP2 | |
| tdom(TXD) | Dominant time out | Driver t(dom) |
| S PIN SECTION | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | Recommended VIH |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | Recommended VIL |
| IIH | High-level input current | IIH |
| IIL | Low-level input current | IIL |
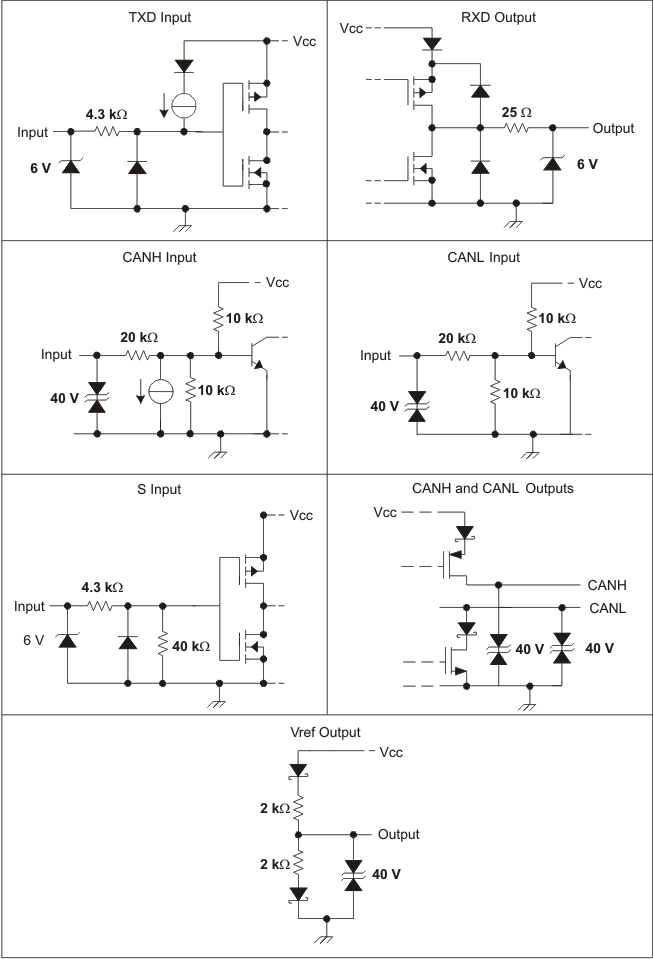 Figure 22. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams
Figure 22. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams