ZHCSH87B September 2017 – February 2020 TMP461-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Map
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 7.6.1.1 Pointer Register
- 7.6.1.2 Local and Remote Temperature Registers
- 7.6.1.3 Status Register
- 7.6.1.4 Configuration Register
- 7.6.1.5 Conversion Rate Register
- 7.6.1.6 One-Shot Start Register
- 7.6.1.7 Channel Enable Register
- 7.6.1.8 Consecutive ALERT Register
- 7.6.1.9 η-Factor Correction Register
- 7.6.1.10 Remote Temperature Offset Register
- 7.6.1.11 Manufacturer Identification Register
- 7.6.1
Register Information
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Remote temperature sensing on the TMP461-SP device measures very small voltages using very low currents; therefore, noise at the device inputs must be minimized. Most applications using the TMP461-SP have high digital content, with several clocks and logic-level transitions that create a noisy environment. Layout must adhere to the following guidelines:
- Place the TMP461-SP device as close to the remote junction sensor as possible.
- Route the D+ and D– traces next to each other and shield them from adjacent signals through the use of ground guard traces, as shown in Figure 20. If a multilayer PCB is used, bury these traces between the ground or V+ planes to shield them from extrinsic noise sources. 5-mil (0.127 mm) PCB traces are recommended.
- Minimize additional thermocouple junctions caused by copper-to-solder connections. If these junctions are used, make the same number and approximate locations of copper-to-solder connections in both the D+ and D– connections to cancel any thermocouple effects.
- Use a 0.1-μF local bypass capacitor directly between the V+ and GND of the TMP461-SP device. For optimum measurement performance, minimize filter capacitance between D+ and D– to 1000 pF or less. This capacitance includes any cable capacitance between the remote temperature sensor and the TMP461-SP device.
- If the connection between the remote temperature sensor and the TMP461-SP device is less than 8-in (20.32 cm) long, use a twisted-wire pair connection. For lengths greater than 8 in, use a twisted, shielded pair with the shield grounded as close to the TMP461-SP device as possible. Leave the remote sensor connection end of the shield wire open to avoid ground loops and 60-Hz pickup.
- Thoroughly clean and remove all flux residue in and around the pins of the TMP461-SP device to avoid temperature offset readings as a result of leakage paths between D+ and GND, or between D+ and V+.
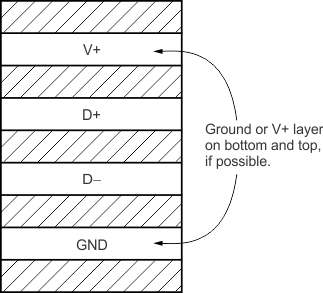
NOTE: Use a minimum of 5-mil (0.127 mm) traces with 5-mil spacing.
Figure 20. Suggested PCB Layer Cross-Section